Configuration Guide
Instructions for setting up and maintaining Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform, including running applications and services.
Abstract
Providing feedback on JBoss EAP documentation
To report an error or to improve our documentation, log in to your Red Hat Jira account and submit an issue. If you do not have a Red Hat Jira account, then you will be prompted to create an account.
Procedure
- Click the following link to create a ticket.
- Enter a brief description of the issue in the Summary.
- Provide a detailed description of the issue or enhancement in the Description. Include a URL to where the issue occurs in the documentation.
- Clicking Submit creates and routes the issue to the appropriate documentation team.
Making open source more inclusive
Red Hat is committed to replacing problematic language in our code, documentation, and web properties. We are beginning with these four terms: master, slave, blacklist, and whitelist. Because of the enormity of this endeavor, these changes will be implemented gradually over several upcoming releases. For more details, see our CTO Chris Wright’s message.
Chapter 1. Introduction
Before using this guide to configure JBoss EAP, it is assumed that the latest version of JBoss EAP has been downloaded and installed. For installation instructions, see Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform Installation Methods.
Since the installation location of JBoss EAP will vary between host machines, this guide refers to the installation location as EAP_HOME. The actual location of the JBoss EAP installation should be used instead of EAP_HOME when performing administrative tasks.
Chapter 2. Starting and Stopping JBoss EAP
2.1. Starting and stopping JBoss EAP
The method for starting JBoss EAP depends on whether you are running JBoss EAP as a standalone server or on servers in a managed domain.
The method for stopping JBoss EAP depends on whether you are running an interactive or background instance of JBoss EAP.
2.1.1. Starting JBoss EAP as a standalone server
You can run JBoss EAP as a standalone server to manage a single instance of JBoss EAP.
The server starts in a suspended state and does not accept requests until all required services start. After required services start, the server transitions into a normal running state and can start accepting requests.
This startup script uses the EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.conf file, or standalone.conf.bat for Windows Server, to set default preferences, such as JVM options. You can customize the settings in this file.
To see a list of startup script arguments in your terminal, use the --help argument.
JBoss EAP uses the standalone.xml configuration file by default, but you can start it using a different one.
Prerequisites
- Install JBoss EAP.
Procedure
- Open a terminal.
Start JBoss EAP as a standalone server by using the following script:
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
For Windows Server, use the
EAP_HOME\bin\standalone.batscript.
-
For Windows Server, use the
2.1.2. Starting JBoss EAP for servers in a managed domain
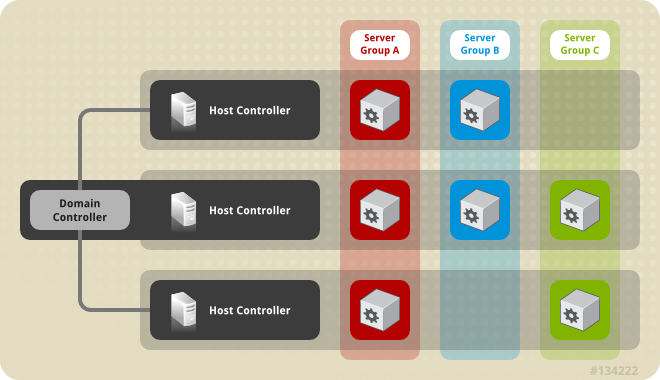
You can run JBoss EAP in a managed domain operating mode to manage several JBoss EAP instances using a single domain controller.
Servers start in a suspended state and do not accept requests until all required services start. After required services start, the servers transition into a normal running state and start accepting requests.
You must start the domain controller before the servers in any of the server groups in the domain.
Prerequisites
- Install JBoss EAP.
Procedure
- Open a terminal.
Start the domain controller first and then start each associated host controller by using the following script:
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
For Windows Server, use the
EAP_HOME\bin\domain.batscript.
-
For Windows Server, use the
This startup script uses the EAP_HOME/bin/domain.conf file, or domain.conf.bat for Windows Server, to set default preferences, such as JVM options. You can customize the settings in this file.
JBoss EAP uses the host.xml host configuration file by default, but you can start it using a different configuration file.
When setting up a managed domain, you must pass additional arguments into the startup script.
For a complete listing of all available startup script arguments and their purposes, use the --help argument.
2.1.3. Stopping an interactive instance of JBoss EAP
You can stop an interactive instance of a standalone server or a domain controller from the terminal where you started it.
Prerequisites
- Have a running instance of JBoss EAP.
Procedure
-
Press
Ctrl+Cin the terminal where you started JBoss EAP.
2.1.4. Stopping a background instance of JBoss EAP
You can connect to the management CLI to shut down a running instance of a standalone server or servers in a managed domain.
Prerequisites
- Have a running instance of JBoss EAP running in a terminal.
Procedure
Start the management CLI by using the following script:
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connectCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Issue the
shutdowncommand:shutdown
shutdownCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
When running an instance of JBoss EAP on servers in a managed domain, you must specify the host name to shut down by using the --host argument with the shutdown command.
2.2. Running JBoss EAP in admin-only mode
JBoss EAP can start in admin-only mode. This mode enables JBoss EAP to run and accept management requests without starting other runtime services or handling end user requests. Admin-only mode is available in both standalone servers as well as managed domains.
2.2.1. Running a standalone server in admin-only mode
You can run a JBoss EAP instance in admin-only mode using a standalone server.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is installed.
Procedure
- Open your terminal.
To start a JBoss EAP instance in admin-only mode, use the
--start-mode=admin-onlyruntime argument when starting the JBoss EAP instance.EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --start-mode=admin-only
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --start-mode=admin-onlyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the following command to check the running mode of the server. The result will be
ADMIN_ONLYif the server is running in admin-only mode.:read-attribute(name=running-mode) { "outcome" => "success", "result" => "ADMIN_ONLY" }:read-attribute(name=running-mode) { "outcome" => "success", "result" => "ADMIN_ONLY" }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteAdditionally, you can check the initial running mode in which JBoss EAP was launched by using the following command.
/core-service=server-environment:read-attribute(name=initial-running-mode)
/core-service=server-environment:read-attribute(name=initial-running-mode)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In addition to stopping and starting a JBoss EAP instance with a different runtime switch, the management CLI may also be used to reload it in a different mode.
To reload the server in admin-only mode:
reload --start-mode=admin-only
reload --start-mode=admin-onlyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To reload the server in normal mode:
reload --start-mode=normal
reload --start-mode=normalCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf the server was started in admin-only mode and no
--start-modeargument is specified in thereloadcommand, the server will be started in normal mode.
2.2.2. Running a managed domain in admin-only mode
In a managed domain, if a domain controller is started in admin-only mode, it will not accept incoming connections from secondary host controllers. A host controller started in admin-only mode will not start servers.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is installed.
Procedure
- Open your terminal.
Pass in the
--admin-onlyruntime argument to start a host controller in admin-only mode.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --admin-only
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --admin-onlyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the following command to check the running mode of a host controller. The result will be
ADMIN_ONLYif the host controller is running in admin-only mode./host=HOST_NAME:read-attribute(name=running-mode) { "outcome" => "success", "result" => "ADMIN_ONLY" }/host=HOST_NAME:read-attribute(name=running-mode) { "outcome" => "success", "result" => "ADMIN_ONLY" }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In addition to stopping and starting a host controller with a different runtime switch, the management CLI may also be used to reload it in a different mode.
To reload the host controller in admin-only mode:
reload --host=HOST_NAME --admin-only=true
reload --host=HOST_NAME --admin-only=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To reload a host controller in normal mode:
reload --host=HOST_NAME --admin-only=false
reload --host=HOST_NAME --admin-only=falseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf the host controller was started in admin-only mode and no
--admin-onlyargument is specified to thereloadcommand, the host controller will be started in normal mode.
2.3. Suspend and shut down JBoss EAP gracefully
JBoss EAP can be suspended or shut down gracefully. This allows active requests to complete normally, without accepting any new requests. A timeout value specifies how long the suspend or shut down operation will wait for active requests to complete. While the server is suspended, management requests are still processed.
Suspend and graceful shutdown is coordinated server-wide, focusing on the entry points where requests enter the server. The following subsystems support suspend and graceful shutdown:
- Undertow
-
The
undertowsubsystem will wait for all requests to finish. - mod_cluster
-
The
modclustersubsystem will notify the load balancer that the server is suspending in thePRE_SUSPENDphase. - Jakarta Enterprise Beans
-
The
ejb3subsystem will wait for all remote session bean requests and MDB message deliveries to finish. Delivery to MDBs is stopped during thePRE_SUSPENDphase. Jakarta Enterprise Bean timers are suspended, and missed timers will be activated when the server is resumed. - Transactions
Once suspended, the server will not accept new requests, but in-flight transactions and requests can continue until they complete or the timeout period expires. For example, the server will accept incoming remote calls that are related to an active transaction at the suspending server.
This also applies to web service requests associated with an XTS transaction.
If you initiate a transaction before graceful shutdown and it fails (for example, a necessary database is unavailable), the transaction will not be recovered automatically as the Recovery Manager may not be functional due to the graceful shutdown proceedings. You will need to resume your JBoss EAP instance to utilize the Recovery Manager and complete the failed transaction.
By default, transaction graceful shutdown is disabled for the
ejb3subsystem. You must enable transaction graceful shutdown if you want the server to wait for Jakarta Enterprise Beans-related transactions to complete before suspending. For example:/subsystem=ejb3:write-attribute(name=enable-graceful-txn-shutdown,value=true)
/subsystem=ejb3:write-attribute(name=enable-graceful-txn-shutdown,value=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This behavior is disabled by default because it can cause Jakarta Enterprise Beans clients to invoke cluster nodes during graceful shutdown. In cluster environments, the server notifies remote clients after transactions are completed that the node is no longer available for remote calls. If the client sends a new request during this window of time (before transactions are complete) to a node that is shutting down, the node will refuse the request.
- Jakarta Concurrency
The server will wait for all active jobs to finish. All queued jobs will be skipped. Since Jakarta Concurrency does not have persistence, any queued jobs that are skipped will be lost.
While the server is in a suspended state, scheduled tasks will continue to execute at their scheduled times but will throw a
java.lang.IllegalStateException. Once the server resumes, scheduled tasks will continue to execute normally, and in most cases, tasks will not need to be rescheduled.- Batch
- The server will stop all running jobs within the timeout period and defer all scheduled jobs.
Graceful shutdown will not currently reject new inbound Jakarta Messaging messages. Jakarta Batch jobs and Jakarta Concurrency tasks scheduled by in-flight activity are currently allowed to proceed; however, Jakarta Concurrency tasks submitted that pass the timeout window currently error when executed.
Requests are tracked by the request-controller subsystem. Without this subsystem, suspend and resume capabilities are limited, and the server will not wait for requests to complete before suspending or shutting down. If you do not need this capability, you can remove the request-controller subsystem for a slight performance improvement.
2.3.1. Suspend servers
JBoss EAP 8.0 provides a suspend mode that gracefully suspends server operations. This allows all active requests to complete normally, but will not accept any new requests. Once the server has been suspended, it can be shut down, returned back to a running state, or left in a suspended state to perform maintenance.
The management interfaces are not affected by suspending the server.
The server can be suspended and resumed using the management console or the management CLI.
Check the server suspend state
The server suspend state can be viewed using the following management CLI commands. The resulting value will be one of RUNNING, PRE_SUSPEND, SUSPENDING, or SUSPENDED.
Check the suspend state for a standalone server.
:read-attribute(name=suspend-state)
:read-attribute(name=suspend-state)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Check the suspend state for a server in a managed domain.
/host=primary/server=server-one:read-attribute(name=suspend-state)
/host=primary/server=server-one:read-attribute(name=suspend-state)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Suspend
Use the following management CLI commands to suspend the server, specifying the timeout value, in seconds, for the server to wait for active requests to complete. The default is 0, which will suspend immediately. A value of -1 will cause the server to wait indefinitely for all active requests to complete.
Each example waits up to 60 seconds for requests to complete before suspending.
Suspend a standalone server.
:suspend(suspend-timeout=60)
:suspend(suspend-timeout=60)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Suspend all servers in a managed domain.
:suspend-servers(suspend-timeout=60)
:suspend-servers(suspend-timeout=60)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Suspend a single server in a managed domain.
/host=primary/server-config=server-one:suspend(suspend-timeout=60)
/host=primary/server-config=server-one:suspend(suspend-timeout=60)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Suspend all servers in a server group.
/server-group=main-server-group:suspend-servers(suspend-timeout=60)
/server-group=main-server-group:suspend-servers(suspend-timeout=60)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Suspend all servers managed by a particular Host Controller.
/host=primary:suspend-servers(suspend-timeout=60)
/host=primary:suspend-servers(suspend-timeout=60)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Resume
The resume command returns the server to a normal running state to accept new requests. You can initiate the command at the host, server, server group, or domain level. For example:
:resume
:resumeStart a Server in a Suspended State
You can start a server in a suspended state so that no requests are accepted by the server until it is resumed.
To start a standalone server in a suspended state, use the
--start-mode=suspendruntime argument when starting the JBoss EAP instance.EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --start-mode=suspend
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --start-mode=suspendCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To start a managed domain server in a suspended state, pass the
start-mode=suspendargument to thestartoperation in the management CLI command./host=HOST_NAME/server-config=SERVER_NAME:start(start-mode=suspend)
/host=HOST_NAME/server-config=SERVER_NAME:start(start-mode=suspend)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can also pass the
start-modeargument to thereloadandrestartoperations for a server.To start all servers in a managed domain server group in a suspended state, pass the
start-mode=suspendargument to thestart-serversoperation in the management CLI command./server-group=SERVER_GROUP_NAME:start-servers(start-mode=suspend)
/server-group=SERVER_GROUP_NAME:start-servers(start-mode=suspend)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can also pass the
start-modeargument to thereload-serversandrestart-serversoperations for a server group.
2.3.2. Shut down servers gracefully using the management CLI
A server will be shut down gracefully if an appropriate timeout value is specified when stopping the server. Once the command is issued, the server will be suspended and will wait up to the specified timeout for all requests to finish before shutting down.
Use the following management CLI commands to shut down the server gracefully. Specify the timeout value, in seconds, for the server to wait for active requests to complete. The default is 0, which shuts down the server immediately. A value of -1 will cause the server to wait indefinitely for all active requests to complete before shutting down.
Each example waits up to 60 seconds for requests to complete before shutting down.
Shut down a standalone server gracefully.
shutdown --suspend-timeout=60
shutdown --suspend-timeout=60Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop all servers in a managed domain gracefully.
:stop-servers(suspend-timeout=60)
:stop-servers(suspend-timeout=60)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop a single server in a managed domain gracefully.
/host=primary/server-config=server-one:stop(suspend-timeout=60)
/host=primary/server-config=server-one:stop(suspend-timeout=60)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Stop all servers in a server group gracefully.
/server-group=main-server-group:stop-servers(suspend-timeout=60)
/server-group=main-server-group:stop-servers(suspend-timeout=60)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Shut down the host controller and all the servers it manages.
/host=primary:shutdown(suspend-timeout=60)
/host=primary:shutdown(suspend-timeout=60)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The suspend-timeout attribute is only applied to the servers managed by the host controller, not the host controller itself.
Shut down servers gracefully using an OS signal
A server can be shut down gracefully by setting org.wildfly.sigterm.suspend.timeout system property and then sending an OS TERM signal, such as kill -15 PID. By default, this behavior is identical to the management CLI’s shutdown --suspend-timeout=0 command, resulting in immediate termination of any currently processing requests. The timeout can be configured by the org.wildfly.sigterm.suspend.timeout system property, indicating the maximum number of seconds to wait for requests to complete before the server shuts down. A value of -1 indicates that the server will wait indefinitely.
In a managed domain, OS signals should not be used to shut down servers. Instead, servers should be shut down using the management CLIor the management console, through the managing Host Controller.
Graceful shutdown using an OS signal will not work if the JVM is configured to disable signal handling, such as when the -Xrs java argument is passed to the JVM options, or if the signal sent is not one the process can respond to, such as if a KILL signal is sent.
2.4. Starting and stopping JBoss EAP (RPM installation)
Starting and stopping JBoss EAP is different for an RPM installation compared to a ZIP or installer installation.
2.4.1. Starting an RPM installation of JBoss EAP
You can use a command to start an RPM installation of JBoss EAP in either standalone server or managed domain operating modes. Note that the following commands are only compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8 and later versions.
Start JBoss EAP as a standalone server (RPM installation)
sudo systemctl start eap8-standalone.service
$ sudo systemctl start eap8-standalone.service
This will start JBoss EAP using the standalone.xml configuration file by default. You can start JBoss EAP with a different standalone server configuration file by setting a property in the RPM service configuration file. For more information, see the Configure RPM Service Properties section below.
Start JBoss EAP in a managed domain (RPM installation)
sudo systemctl start eap8-domain.service
$ sudo systemctl start eap8-domain.service
This will start JBoss EAP using the host.xml configuration file by default. You can start JBoss EAP with a different managed domain configuration file by setting a property in the RPM service configuration file. For more information, see the Configure RPM Service Properties section below.
2.4.2. Configure RPM service properties
This section shows you how to configure the RPM service properties and other startup options for your JBoss EAP installation. Note that it is recommended to back up your configuration files before making modifications.
For a listing of all available startup options for an RPM installation, see the RPM Service Configuration Properties section.
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 and later, RPM service configuration files are loaded using systemd, so variable expressions are not expanded.
Specify the server configuration file.
When starting a standalone server, the
standalone.xmlfile is used by default. When running in a managed domain, thehost.xmlfile is used by default. You can start JBoss EAP with a different configuration file by setting theWILDFLY_SERVER_CONFIGproperty in the appropriate RPM configuration file, for example,eap8-standalone.conf.WILDFLY_SERVER_CONFIG=standalone-full.xml
WILDFLY_SERVER_CONFIG=standalone-full.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Bind to a specific IP address.
By default, a JBoss EAP RPM installation binds to
0.0.0.0. You can bind JBoss EAP to a specific IP address by setting theWILDFLY_BINDproperty in the appropriate RPM configuration file, for example,eap8-standalone.conf.WILDFLY_BIND=192.168.0.1
WILDFLY_BIND=192.168.0.1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf you want to bind the management interfaces to a specific IP address, this can be configured in the JBoss EAP startup configuration file as shown in the next example.
Set JVM options or Java properties.
You can specify JVM options or Java properties to pass into the JBoss EAP startup script by editing the startup configuration file. This file is
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.conffor a standalone server orEAP_HOME/bin/domain.conffor a managed domain. The below example configures the heap size and binds the JBoss EAP management interfaces to an IP address.JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Xms2048m -Xmx2048m" JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djboss.bind.address.management=192.168.0.1"
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Xms2048m -Xmx2048m" JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djboss.bind.address.management=192.168.0.1"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf required, the JBoss EAP bind address must be configured using the
WILDFLY_BINDproperty and not using thejboss.bind.addressstandard property here.
If a property has the same name in both the RPM service configuration file, such as /usr/lib/systemd/system/eap8-standalone.service:, and in the JBoss EAP startup configuration file, such as EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.conf, the value that takes precedence is the one in the JBoss EAP startup configuration file. One such property is JAVA_HOME.
2.4.3. Stopping an RPM installation of JBoss EAP
You can use a command to stop an RPM installation of JBoss EAP in either standalone server or managed domain operating modes. Note that the following commands are only compatible with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8 and later versions.
Stop JBoss EAP as a standalone server (RPM installation)
sudo systemctl stop eap8-standalone.service
$ sudo systemctl stop eap8-standalone.serviceStop JBoss EAP in a managed domain (RPM installation)
sudo systemctl stop eap8-domain.service
$ sudo systemctl stop eap8-domain.serviceFor a list of all available startup options for an RPM installation, see the RPM Service Configuration Files section.
2.5. PowerShell scripts for Windows Server
The collection of PowerShell scripts is provided as Technology Preview only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend using them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
JBoss EAP includes PowerShell script equivalents for most of the JBoss EAP management scripts. This includes a PowerShell script to start JBoss EAP on Microsoft Windows Server.
The JBoss EAP PowerShell scripts are designed to work with PowerShell version 2 and newer running on tested versions of Windows Server.
The JBoss EAP PowerShell scripts are located in EAP_HOME\bin, and are used in mostly the same way as the JBoss EAP batch scripts.
For example, to start a standalone JBoss EAP server with the standalone-full.xml configuration file, use the following PowerShell command:
.\standalone.ps1 "-c=standalone-full.xml"
.\standalone.ps1 "-c=standalone-full.xml"Arguments of the JBoss EAP PowerShell scripts must be in quotes.
Chapter 3. JBoss EAP management
You can configure JBoss EAP using the command-line management CLI, web-based management console, Java API, or HTTP API. Changes made using these management interfaces persist automatically, and the XML configuration files are overwritten by the Management API. The management CLI and management console are the preferred methods, and it is not recommended to edit the XML configuration files manually. These are example configuration files that you can modify using the management CLI when you start JBoss EAP.
JBoss EAP uses a simplified configuration, with one configuration file per standalone server or managed domain. If you do not specify a different configuration file, JBoss EAP will use one of the following example configuration files:
-
Default configuration for a standalone server is stored in the
EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/standalone.xmlfile. -
Default configuration for a managed domain is stored in the
EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/domain.xmlfile. -
Default configuration for a host controller is stored in the
EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/host.xmlfile.
JBoss EAP provides support for configuring a standalone server using YAML configuration files. For more information, see Configure a standalone server using YAML configuration files.
YAML configuration is not supported for servers in a managed domain.
3.1. About subsystems, extensions, and profiles
Different subsystems in JBoss EAP configure various aspects of JBoss EAP functionality. For example, the logging subsystem configures application and server logging.
An extension is a module that extends the core functionality of the server. Extensions are loaded as they are needed by deployments, and are unloaded when they are no longer needed.
A subsystem provides configuration options for a particular extension. For more information on the available subsystems, see Overview of JBoss EAP Subsystems.
A collection of subsystem configurations makes up a profile, which is configured to satisfy the needs for the server. A standalone server has a single, unnamed profile. A managed domain can define many profiles for use by server groups in the domain.
Using the management console or the management CLI
Both the management console and the management CLI are valid, supported ways of updating the configuration of a JBoss EAP instance. Deciding between the two is a matter of preference. Those who prefer to use a graphical, web-based interface should use the management console. Those who prefer a command-line interface should use the management CLI.
3.2. Management users
The default JBoss EAP configuration provides local authentication so that a user can access the management CLI on the local host without requiring authentication.
However, you must add a management user if you want to access the management CLI remotely or use the management console, which is considered remote access even if the traffic originates on the local host. If you attempt to access the management console before adding a management user, you will receive an error message.
If JBoss EAP is installed using the graphical installer, then a management user is created during the installation process.
This guide covers simple user management for JBoss EAP using the add-user script, which is a utility for adding new users to the properties files for out-of-the-box authentication.
For more advanced authentication and authorization options, such as LDAP or Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), see the Core Management Authentication section of the JBoss EAP Security Architecture.
3.2.1. Adding a management user
You can use the add-user utility script to add a management user.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Run the
add-userutility script and follow the prompts.EAP_HOME/bin/add-user.sh
$ EAP_HOME/bin/add-user.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteFor Windows Server, use the
EAP_HOME\bin\add-user.batscript.Press
ENTERto select the default optionato add a management user.This user will be added to the ManagementRealm and will be authorized to perform management operations using the management console or management CLI. The other choice,
b, adds a user to the ApplicationRealm, which is used for applications and provides no particular permissions.Enter the desired username and password. You will be prompted to confirm the password.
NoteUser names can only contain the following characters, in any number and in any order:
- Alphanumeric characters (a-z, A-Z, 0-9)
- Dashes (-), periods (.), commas (,), at sign (@)
- Backslash (\)
- Equals (=)
By default, JBoss EAP allows weak passwords but will issue a warning.
See Setting add-user utility password restrictions for details on changing this default behavior.
-
Enter a comma-separated list of groups to which the user belongs. If you do not want the user to belong to any groups, press
ENTERto leave it blank. -
Review the information and enter
yesto confirm.
Users can also be created non-interactively by passing parameters to the add-user script. This approach is not recommended on shared systems, because the passwords will be visible in log and history files. For more information, see Running the add-user utility non-interactively.
3.2.2. Running the add-user utility non-interactively
You can run the add-user script non-interactively by passing in arguments on the command line. At a minimum, the username and password must be provided.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
This approach is not recommended on shared systems, because the passwords will be visible in log and history files.
Create a user belonging to multiple groups
The following command adds a management user, mgmtuser1, with the guest and mgmtgroup groups.
EAP_HOME/bin/add-user.sh -u 'mgmtuser1' -p 'password1!' -g 'guest,mgmtgroup'
$ EAP_HOME/bin/add-user.sh -u 'mgmtuser1' -p 'password1!' -g 'guest,mgmtgroup'Specify an alternative properties file
By default, user and group information created using the add-user script are stored in properties files located in the server configuration directory.
User information is stored in the following properties files:
-
EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/mgmt-users.properties -
EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/mgmt-users.properties
Group information is stored in the following properties files:
-
EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/mgmt-groups.properties -
EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/mgmt-groups.properties
These default directories and properties file names can be overridden. The following command adds a new user, specifying a different name and location for the user properties files.
EAP_HOME/bin/add-user.sh -u 'mgmtuser2' -p 'password1!' -sc '/path/to/standaloneconfig/' -dc '/path/to/domainconfig/' -up 'newname.properties'
$ EAP_HOME/bin/add-user.sh -u 'mgmtuser2' -p 'password1!' -sc '/path/to/standaloneconfig/' -dc '/path/to/domainconfig/' -up 'newname.properties'
The new user was added to the user properties files located at /path/to/standaloneconfig/newname.properties and /path/to/domainconfig/newname.properties. Note that these files must already exist or you will see an error.
For a complete listing of all available add-user arguments and their purposes, use the --help argument or see the Add-user utility arguments section.
3.2.3. Add-user utility password restrictions
The password restrictions for the add-user utility script can be configured using the EAP_HOME/bin/add-user.properties file.
The add-user.properties file is an unprotected plain-text file and must be secured to avoid unwarranted access to its contents.
To avoid setting an unintentional password, check that your keyboard’s system keymap is correct. The default system keymap is en-qwerty. If you change this default setting and create a new password, you must check that the password meets the criteria located in the class SimplePasswordStrengthChecker.
By default, JBoss EAP allows weak passwords but issues a warning. To reject passwords that do not meet the minimum requirements specified, set the password.restriction property to REJECT.
The following table describes the additional password requirement settings that can be configured in the EAP_HOME/bin/add-user.properties file:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The minimum number of characters for a password. For example, |
|
| Sets the threshold that a password must meet to be valid. Valid threshold entries include:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
The default value is
NOTE: If you do not specify a threshold value, |
|
|
The minimum number of alphabetic characters set for a password. For example, |
|
|
The minimum number of numeric characters set for a password. For example, |
|
|
The minimum number of symbols set for a password. For example, |
|
|
Restricts a user from setting an easily determined password, such as root. For example, |
|
|
Restricts the user from setting their user name as the password. For example, |
Additional resources
See the Configuring Basic System Settings guide on the Red Hat Customer Portal.
3.2.4. Updating a management user
You can update the settings for an existing management user using the add-user utility script by entering the username when prompted.
When you enter a username that already exists, you are presented with several options:
-
Type
ato update the password for the existing user. -
Type
bto disable the existing user. -
Type
cto enter a new username.
When updating a user using the add-user script non-interactively, the user is updated automatically with no confirmation prompt.
3.3. Management interfaces
3.3.1. Management CLI
The management command-line interface (CLI) is a command-line administration tool for JBoss EAP.
Use the management CLI to start and stop servers, deploy and undeploy applications, configure system settings, and perform other administrative tasks. Operations can be performed in batch mode, allowing multiple tasks to be run as a group.
Many common terminal commands are available, such as ls, cd, and pwd. The management CLI also supports tab completion.
For detailed information on using the management CLI, including commands and operations, syntax, and running in batch mode, see the JBoss EAP Management CLI Guide.
Launch the management CLI
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh
For Windows Server, use the EAP_HOME\bin\jboss-cli.bat script.
Connect to a running server
connect
connect
Or you can launch the management CLI and connect in one step by using the EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect command.
Display help
Use the following command for general help.
help
help
Use the --help flag on a command to receive instructions on using that specific command. For instance, to receive information on using deploy, the following command is executed.
deploy --help
deploy --helpQuit the management CLI
quit
quitView system settings
The following command uses the read-attribute operation to display whether the example datasource is enabled.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:read-attribute(name=enabled)
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => true
}
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:read-attribute(name=enabled)
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => true
}
When running in a managed domain, you must specify which profile to update by preceding the command with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
/profile=default/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:read-attribute(name=enabled)
/profile=default/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:read-attribute(name=enabled)Update system settings
The following command uses the write-attribute operation to disable the example datasource.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=enabled,value=false)
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=enabled,value=false)Start servers
The management CLI can also be used to start and stop servers when running in a managed domain.
/host=HOST_NAME/server=server-one:start
/host=HOST_NAME/server=server-one:start3.3.2. Overview of the management console
The management console is a web-based administration tool for JBoss EAP.
Use the management console to start and stop servers, deploy and remove applications, tune system settings, and make persistent modifications to the server configuration. The management console can also perform administrative tasks, with live notifications when a user makes any changes that require you to restart or reload the server.
In a managed domain, server instances and server groups in the same domain are centrally managed from the management console of the domain controller.
For a JBoss EAP instance running on the local host using the default management port, you can access the management console through a web browser at http://localhost:9990/console/index.html. Log in as a user with the required role to access the management console.
The management console provides the following tabs for navigating and managing your JBoss EAP standalone server or managed domain.
- Homepage
- Learn how to accomplish several common configuration and management tasks. Take a tour to become familiar with the JBoss EAP management console.
- Deployments
- Add, remove, and enable deployments. In a managed domain, assign deployments to server groups.
- Configuration
- Configure available subsystems, which provide capabilities such as web services, messaging, or high availability. In a managed domain, manage the profiles that contain different subsystem configurations.
- Runtime
- View runtime information, such as server status, JVM usage, and server logs. In a managed domain, manage your hosts, server groups, and servers.
- Update Manager
- Update the existing installation and manage channels.
- Access control
- Assign roles to users and groups when using Role-Based Access Control.
3.3.2.1. Updating resource attributes in the management console
If you have the required permissions, you can edit resource attributes in the management console.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have the proper permissions to modify the selected resource.
- You have created a user.
Procedure
- Log in to the management console. For a local server running at the default port, you can access the management console at http://localhost:9990/console/index.html.
- Go to the appropriate section of the management console for the resource that you want to modify.
- Click Edit.
Make the required changes.
Required fields are marked with an asterisk (*). You can view the attribute descriptions by clicking Help.
NoteDepending on the attribute type, the input field can be a text field, an ON/OFF field, or a dropdown. In some text fields, as you type, values from elsewhere in the configuration might appear as suggestions.
- Click Save.
If necessary, reload the server for the changes to take effect.
A pop-up window opens when you make changes that require a reload in order to take effect. To reload a standalone server, click Reload in the pop-up window. To reload a server in a managed domain, click Topology, select the appropriate server, and select Reload from the drop-down list.
To view the history of recent configuration actions you have performed, click the notification icon.
3.3.2.2. Enable or disable the management console
You can enable or disable the management console by setting the console-enabled boolean attribute of the /core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface resource. For the primary host in domain mode, use /host=primary/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface.
After you enable or disable the management console, you must restart or reload your JBoss EAP instance.
Enable management console example
/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=console-enabled,value=true)
/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=console-enabled,value=true)Disable management console example
/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=console-enabled,value=false)
/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=console-enabled,value=false)3.3.2.3. Changing the language of the management console
By default, the language settings of the management console is English. You can choose to use one of the following languages instead:
- German (de)
- Simplified Chinese (zh-Hans)
- Brazilian Portuguese (pt-BR)
- French (fr)
- Spanish (es)
- Japanese (ja)
Prerequisite
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have created a user.
Procedure
- Log in to the management console. For a local server running at the default port, you can access the management console at http://localhost:9990/console/index.html.
- Click Settings.
- Select the required language from the Locale list.
- Click Save. A confirmation box informs you that you need to reload the application.
- Click Yes. The system refreshes your web browser automatically to use the selected locale.
3.3.2.4. Customizing the management console title
You can customize the management console title so that each of your JBoss EAP instances can be quickly and easily identified. If you customize the management console title, the changes do not persist after you close your instance of the management console. When you open a new instance of the console and login, the management console title is reset.
Prerequisite
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have created a user.
Procedure
- Log in to the management console. For a local server running at the default port, you can access the management console at http://localhost:9990/console/index.html.
- Click Settings and modify the title in the Title field.
Click Save.
A confirmation box informs you that you must reload the management console.
Click Yes.
The system refreshes your web browser automatically and the new title is displayed on the tab header.
3.4. Management APIs
Management API endpoints act as entry points for management clients to integrate with the JBoss EAP management layer.
3.4.1. HTTP API
The HTTP API endpoint is the entry point for management clients that rely on the HTTP protocol to integrate with the JBoss EAP management layer.
The HTTP API is used by the JBoss EAP management console but offers integration capabilities for other clients as well. By default, the HTTP API is accessible at http://HOST_NAME:9990/management. This URL will display the raw attributes and values exposed to the API.
Read resources
While you can read, write, or perform other operations using the HTTP POST method, you can perform some read operations using a GET request. The HTTP GET method uses the following URL format.
http://HOST_NAME:9990/management/PATH_TO_RESOURCE?operation=OPERATION&PARAMETER=VALUE
http://HOST_NAME:9990/management/PATH_TO_RESOURCE?operation=OPERATION&PARAMETER=VALUE
Be sure to replace all of the replaceable values with those that are appropriate for your request. The following values are the available options for the OPERATION replaceable value:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| attribute |
Performs the |
| operation-description |
Performs the |
| operation-names |
Performs the |
| resource |
Performs the |
| resource-description |
Performs the |
| snapshots |
Performs the |
The following example URLs show how to perform read operations using the HTTP API.
Example: Read all attributes and values for a resource
http://HOST_NAME:9990/management/subsystem/undertow/server/default-server/http-listener/default
http://HOST_NAME:9990/management/subsystem/undertow/server/default-server/http-listener/default
This displays all attributes and their values for the default HTTP listener.
The default operation is read-resource.
Example: Read the value of an attribute for a resource
http://HOST_NAME:9990/management/subsystem/datasources/data-source/ExampleDS?operation=attribute&name=enabled
http://HOST_NAME:9990/management/subsystem/datasources/data-source/ExampleDS?operation=attribute&name=enabled
This reads the value of the enabled attribute for the ExampleDS datasource.
Update resources
You can use the HTTP POST method to update configuration values or perform other operations using the HTTP API. You must provide authentication for these operations.
The following examples show how to update resources using the HTTP API.
Example: Update the value of an attribute for a resource
curl --digest http://HOST_NAME:9990/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u USERNAME:PASSWORD -d '{"operation":"write-attribute", "address":["subsystem","datasources","data-source","ExampleDS"], "name":"enabled", "value":"false", "json.pretty":"1"}'
$ curl --digest http://HOST_NAME:9990/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u USERNAME:PASSWORD -d '{"operation":"write-attribute", "address":["subsystem","datasources","data-source","ExampleDS"], "name":"enabled", "value":"false", "json.pretty":"1"}'
This updates the value of the enabled attribute for the ExampleDS datasource to false.
Example: Issue an operation to the server
curl --digest http://localhost:9990/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u USERNAME:PASSWORD -d '{"operation":"reload"}'
$ curl --digest http://localhost:9990/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u USERNAME:PASSWORD -d '{"operation":"reload"}'This reloads the server.
See Deploying Applications Using the HTTP API for information on how to deploy applications to JBoss EAP using the HTTP API.
3.4.1.1. Custom-constant HTTP headers
The HTTP management endpoint of JBoss EAP returns a predefined set of HTTP headers in all the responses that are sent to clients. You can define custom-constant HTTP headers to be returned in addition to this predefined set of HTTP headers.
JBoss EAP applies custom-constant HTTP headers to requests as follows:
JBoss EAP applies the custom-constant HTTP headers by matching a configured prefix against the request path.
For example, you can map custom-constant HTTP headers to requests on the request path such as
/or/management.If a request matches multiple prefixes, JBoss EAP applies the custom-constant HTTP headers from all of the mappings.
For example, a request to the path
/managementmatches mappings for both/and/management. JBoss EAP applies headers from both of the mappings.At the end of processing a request, before a response returns to a client, by overriding headers set by the corresponding endpoint.
For example, the management endpoint sets an
X-Frame-Optionsheader in each response. If you define a custom-constant HTTP header with the nameX-Frame-Options, the custom-constant HTTP header overrides the default header.
You can define multiple custom-constant HTTP headers to be returned in the response on a single mapping.
The following are the rules for defining custom-constant HTTP headers:
- The custom-constant HTTP headers can only contain the characters that are supported in RFC-7231 - Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content.
You cannot override the following predefined HTTP headers:
-
Connection -
Content-Length -
Content-Type -
Date Transfer-EncodingAttempting to override any of these predefined headers results in an error.
For example, if you attempt to set a custom-constant HTTP header with the name
Date, the following error is returned:{ "outcome" => "failed", "failure-description" => "WFLYCTL0458:Disallowed HTTP Header name 'Date'", "rolled-back" => true }{ "outcome" => "failed", "failure-description" => "WFLYCTL0458:Disallowed HTTP Header name 'Date'", "rolled-back" => true }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Important considerations when creating custom-constant HTTP headers:
- JBoss EAP does not verify whether the specified path is reachable.
- Subsystems can dynamically add contexts that the HTTP management interface supports.
- Custom-constant HTTP headers do not alter how an endpoint handles a response to a request.
3.4.1.2. Defining custom-constant HTTP headers
Define a custom-constant HTTP header to be returned in every response on the required path prefix.
Before creating custom-constant HTTP headers, you must understand the following considerations:
- JBoss EAP does not verify whether the specified path is reachable.
- Subsystems can dynamically add contexts that the HTTP management interface supports.
- Custom-constant HTTP headers do not alter how an endpoint handles a response to a request.
Procedure
Define a custom constant HTTP header:
/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path="PATH_PREFIX",headers=[{name="HEADER_NAME",value="HEADER_VALUE"}]}])/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path="PATH_PREFIX",headers=[{name="HEADER_NAME",value="HEADER_VALUE"}]}])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
write-attributeoperation causes areload-requiredprompt to open.Reload the server for the changes to take effect:
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Requests to the HTTP management interface now return HTTP header HEADER_NAME with the value HEADER_VALUE in addition to the predefined set of HTTP headers.
Example custom-constant HTTP header X-help
/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path="/",headers=[{name="X-Help",value="http://mywebsite.com/help"}]}])/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path="/",headers=[{name="X-Help",value="http://mywebsite.com/help"}]}])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification steps
Send a request to the HTTP managment interface:
curl -s -D - -o /dev/null --digest http://localhost:9990/management/ -u USERNAME:PASSWORD
curl -s -D - -o /dev/null --digest http://localhost:9990/management/ -u USERNAME:PASSWORDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Sample response for the example custom-constant HTTP header
X-HelpCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The response contains the
X-Helpcustom-constant HTTP header.
Additional resources
3.4.1.3. CLI commands for defining custom-constant HTTP headers
The following CLI commands define custom-constant HTTP headers in standalone and managed domain modes.
Standalone mode
To define a single custom-constant HTTP header, use the following command:
/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path=/PREFIX,headers=[{name=X-HEADER,value=HEADERVALUE}]}])/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path=/PREFIX,headers=[{name=X-HEADER,value=HEADERVALUE}]}])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command results in the following XML configuration:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To define multiple custom-constant HTTP headers, use the following command:
/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path=/PREFIX1,headers=[{name=X-HEADER,value=HEADERVALUE-FOR-X}]},{path=/PREFIX2,headers=[{name=Y-HEADER,value=HEADERVALUE-FOR-Y}]}])/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path=/PREFIX1,headers=[{name=X-HEADER,value=HEADERVALUE-FOR-X}]},{path=/PREFIX2,headers=[{name=Y-HEADER,value=HEADERVALUE-FOR-Y}]}])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Domain mode
To define a single custom-constant HTTP header, use the following command:
/host=primary/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path=/PREFIX,headers=[{name=X-HEADER,value=HEADER-VALUE}]}])/host=primary/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[{path=/PREFIX,headers=[{name=X-HEADER,value=HEADER-VALUE}]}])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The command results in the following XML configuration:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To define multiple custom-constant HTTP headers, use the following command:
/host=primary/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[ {path=/PREFIX-1,headers=[{name=X-HEADER,value=HEADER-VALUE-FOR-X}]},{path=/PREFIX-2,headers=[{name=Y-HEADER,value=HEADER-VALUE-FOR-Y}]}])/host=primary/core-service=management/management-interface=http-interface:write-attribute(name=constant-headers,value=[ {path=/PREFIX-1,headers=[{name=X-HEADER,value=HEADER-VALUE-FOR-X}]},{path=/PREFIX-2,headers=[{name=Y-HEADER,value=HEADER-VALUE-FOR-Y}]}])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Additional resources
3.4.2. Native API
The native API endpoint is the entry point for management clients that rely on the native protocol to integrate with the JBoss EAP management layer. The native API is used by the JBoss EAP management CLI but offers integration capabilities for other clients as well.
The following Java code shows an example of how to execute management operations from Java code using the native API.
You must add the required JBoss EAP libraries, found in the EAP_HOME/bin/client/jboss-cli-client.jar file, to your class path.
Example: Using the native API to read resources
3.5. Configuration data
3.5.1. Standalone server configuration files
The standalone configuration files are located in the EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/ directory. A separate file exists for each of the five predefined profiles (default, ha, full, full-ha, load-balancer). These are example configuration files that you can modify using the management CLI when you start JBoss EAP.
| Configuration file | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
| This standalone configuration file is the Jakarta EE web profile certified configuration and the default configuration that JBoss EAP uses when you start your standalone server. This configuration contains all information about the server, including subsystems, networking, deployments, socket bindings, and other configurable details for Jakarta EE web profile. This configuration does not provide the subsystems required for messaging or high availability. |
|
|
This standalone configuration file is the Jakarta EE web profile certified configuration with high availability and includes all of the default subsystems and adds the |
|
|
This standalone configuration file is the Jakarta EE Full platform certified configuration and includes all of the default subsystems and adds the |
|
| This standalone configuration file is the Jakarta EE Full platform certified configuration and includes support for every possible subsystem, including those for messaging and high availability. |
|
| This standalone configuration file includes the minimum subsystems necessary to use the built-in mod_cluster front-end load balancer to load balance other JBoss EAP instances. |
By default, starting JBoss EAP as a standalone server uses the standalone.xml file. To start JBoss EAP with a different configuration, use the --server-config argument. For example,
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --server-config=standalone-full.xml
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --server-config=standalone-full.xmlUpdate a standalone server using YAML files
Using YAML files to configure your standalone server externalizes the customization process and improves the rate of server upgrades. When using this feature, the server starts in read-only mode. This means that changes to the configuration do not persist after the server is restarted.
YAML configuration is not supported for servers in a managed domain.
Users can modify various resources in the YAML files. The following elements are supported in YAML files:
-
core-service -
interface -
socket-binding-group -
subsystem -
system-property
The following elements are not supported in YAML files:
-
extension: Add an extension to the server. This element is not supported because it might require modules that are missing. -
deployment: Add deployments to the server. This element is not supported because it requires more extensive changes in addition to configuration. -
deployment-overlay: Add deployment-overlays to the server. This element is not supported because it requires more extensive changes in addition to configuration. -
path: Already defined when the YAML files are parsed.
The YAML root node is wildfly-configuration. You can follow the model tree to modify resources. If a resource already exists (it was created by the XML configuration file or a previous YAML file), you can update it using the model tree. If the resource does not exist, you can create it using the model tree.
Example YAML configuration file defining a new PostGresql datasource
The above example defines a jdbc-driver called postgresql and a data-source called PostgreSQLDS.
You cannot use the YAML configuration file to manage modules. Instead, you need to create or provision the org.postgresql.jdbc module manually or using the management CLI.
3.5.1.1. YAML file operations using tags
You can perform several operations on YAML configuration files using tags.
!undefine: undefine an attributeUndefine
CONSOLElogger level YAML configuration file exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow !remove: remove the resourceRemove embedded Artemis broker and connect to a remote broker YAML configuration file example
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow !list-add: Add an element to a list (with an optional index)Add a
RemoteTransactionPermissionto a permissions list YAML configuration file exampleCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf an
indexattribute is not defined, the entry is appended to the end of the list.
3.5.1.2. Starting a standalone server using YAML files
You can start a standalone server using YAML configuration files.
Procedure
- Open your terminal.
Use the following command to start a standalone server with YAML files:
./standalone.sh -y=/home/ehsavoie/dev/wildfly/config2.yml:config.yml -c standalone-full.xml
./standalone.sh -y=/home/ehsavoie/dev/wildfly/config2.yml:config.yml -c standalone-full.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
--yamlor-yargument allows you to pass a list of YAML files. You must separate each YAML file path using a semicolon (;) for Windows Server or a colon (:) for Mac and Unix-based operating systems. You can use an absolute path, a path relative to the current execution directory, or a path relative to the standalone configuration directory.The operations are applied in the order that the files are defined and after the initial operations are defined by the XML configuration.
3.5.2. Managed domain configuration files
The managed domain configuration files are located in the EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/ directory. These are example configuration files that you can modify using the management CLI when you start JBoss EAP.
| Configuration file | Purpose |
|---|---|
|
| This is the main configuration file for a managed domain. Only the domain controller reads this file. This file contains the configurations for all of the profiles (default, ha, full, full-ha, load-balancer). |
|
|
This file includes configuration details specific to a physical host in a managed domain, such as network interfaces, socket bindings, the name of the host, and other host-specific details. The |
|
|
This file includes only the configuration details necessary to run a server as the managed domain controller. The |
|
|
This file includes only the configuration details necessary to run a server as a managed domain host controller. It does not define a domain controller and you must configure a domain controller address for |
By default, starting JBoss EAP in a managed domain uses the host.xml file. To start JBoss EAP with a different configuration, use the --host-config argument. For example,
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-primary.xml
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-primary.xml3.5.3. Backing up configuration data
To restore your JBoss EAP server configuration, you must back up your data in the following locations:
EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/- Back up the entire directory to save user data, server configuration, and logging settings for standalone servers.
EAP_HOME/standalone/data- Back up data for managed deployments that are confined in the data/content directory.
EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments- Back up deployments for standalone servers.
EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/- Back up the entire directory to save user and profile data, domain and host configuration, and logging settings for managed domains.
EAP_HOME/domain/data- Back up data for managed domains and deployments in managed domains that are confined in the data/content directory.
EAP_HOME/modules/- Back up any custom modules.
EAP_HOME/welcome-content/- Back up any custom welcome content.
EAP_HOME/bin/- Back up any custom scripts or startup configuration files.
3.5.4. Configuration file snapshots
To assist in the maintenance and management of the server, JBoss EAP creates a timestamped version of the original configuration file at the time of startup.
Any additional configuration changes made by management operations will result in the original file being automatically backed up, and a working copy of the instance being preserved for reference and rollback. Additionally, configuration snapshots can be taken, which are point-in-time copies of the current server configuration. These snapshots can be saved and loaded by an administrator.
The following examples use the standalone.xml file, but the same process applies to the domain.xml and host.xml files.
Take a snapshot
Use the management CLI to take a snapshot of the current configurations.
:take-snapshot
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => "EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/standalone_xml_history/snapshot/20151022-133109702standalone.xml"
}
:take-snapshot
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => "EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/standalone_xml_history/snapshot/20151022-133109702standalone.xml"
}List snapshots
Use the management CLI to list all snapshots.
Delete a snapshot
Use the management CLI to delete a snapshot.
:delete-snapshot(name=20151022-133109702standalone.xml)
:delete-snapshot(name=20151022-133109702standalone.xml)3.5.5. Starting the server with a snapshot
You can start a server using a snapshot or an automatically-saved version of the configuration.
Prerequisites
- You have installed JBoss EAP.
- You have taken a snapshot of the configuration file.
Procedure
-
Navigate to the
EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/standalone_xml_historydirectory and identify the snapshot or saved configuration file to be loaded. Start the server and point to the selected configuration file. Pass in the file path relative to the configuration directory,
EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/.EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --server-config=standalone_xml_history/snapshot/20151022-133109702standalone.xml
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --server-config=standalone_xml_history/snapshot/20151022-133109702standalone.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
When running servers in a managed domain, use the --host-config and --domain-config=<config> arguments instead to specify the configuration file.
3.5.6. View configuration changes
You can use JBoss EAP to track configuration changes made to the running system. This allows administrators to view a history of configuration changes made by other authorized users.
Changes are stored in memory and are not persisted between server restarts. This feature is not a replacement for management audit logging.
You can enable tracking and view configuration changes from either the management CLI or the management console.
Track and view configuration changes from the management CLI
To enable tracking of configuration changes, use the following management CLI command. You can specify how many entries to store using the max-history attribute.
/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:add(max-history=20)
/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:add(max-history=20)In a managed domain, configuration changes are tracked at the host level for host and server-related modifications. Enabling configuration changes for a host controller enables it for all of its managed servers. You can track configuration changes per host using the following command.
/host=HOST_NAME/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:add(max-history=20)
/host=HOST_NAME/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:add(max-history=20)To view the list of most recent configuration changes, use the following management CLI command.
/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:list-changes
/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:list-changesIn a managed domain, you can list the configuration changes for a host using the following command.
/host=HOST_NAME/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:list-changes
/host=HOST_NAME/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:list-changesYou can list the configuration changes that affect a particular server using the following command.
/host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:list-changes
/host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME/subsystem=core-management/service=configuration-changes:list-changes
This lists each configuration change made, with the date, origin, outcome, and operation details. For example, the below output from the list-changes command shows configuration changes, with the most recent displayed first.
This example lists the details of three operations performed that impacted the configuration:
- Reloading the server from the management CLI.
-
Disabling the
ExampleDSdatasource from the management CLI. -
Removing the
ExpiryQueuequeue from the management console.
Track and view configuration changes from the management console
To enable tracking of configuration changes from the management console, select to the Runtime tab, navigate to the server or host to track changes for and select Configuration Changes from the drop down. Click Enable Configuration Changes and provide a maximum history value.
The table on this page then lists each configuration change made, with the date, origin, outcome, and operation details.
3.5.7. Property replacement
You can use expressions in JBoss EAP to define replaceable properties in place of literal values in the configuration.
Using property replacement in standalone*.xml or domain.xml configuration files will replace the property with the value found in a system property. System properties are defined in the EAP profile xml file or by typing -D command from the command line terminal.
To determine if property replacement is allowed in a given subsystem, use the following command to display a description of a subsystem configuration:
/subsystem=datasources:read-resource-description(recursive=true)
/subsystem=datasources:read-resource-description(recursive=true)
If the expressions-allowed attribute is set to true, property replacement is allowed.
Expressions use the format ${PARAMETER:DEFAULT_VALUE}. If the specified parameter is set, then the parameter’s value will be used. Otherwise, the default value provided will be used.
The supported sources for resolving expressions are system properties and environment variables. When resolving expressions using environment variables, use the format ${env.LANG}.
The following example from the standalone.xml configuration file sets the inet-address for the public interface to 127.0.0.1 unless the jboss.bind.address parameter is set.
<interface name="public">
<inet-address value="${jboss.bind.address:127.0.0.1}"/>
</interface>
<interface name="public">
<inet-address value="${jboss.bind.address:127.0.0.1}"/>
</interface>
You can use the following command to set the jboss.bind.address parameter when starting EAP as a standalone server:
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.bind.address=IP_ADDRESS
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.bind.address=IP_ADDRESS
For deployments only, the source can be properties listed in a META-INF/jboss.properties file in the deployment archive. For deployment types that support subdeployments, the resolution is scoped to all subdeployments if the properties file is in the outer deployment, for example the EAR. If the properties file is in the subdeployment, then the resolution is scoped just to that subdeployment.
3.5.8. Nested expressions
You can nest expressions, which allows for more advanced use of expressions in place of fixed values.
The format of a nested expression is like that of a normal expression, but one expression is embedded in the other, for example:
${SYSTEM_VALUE_1${SYSTEM_VALUE_2}}
${SYSTEM_VALUE_1${SYSTEM_VALUE_2}}JBoss EAP evaluates nested expressions recursively, so the inner expression is first evaluated, then the outer expression is evaluated. Expressions can also be recursive, where an expression resolves to another expression, which is then resolved. Nested expressions are permitted anywhere that expressions are permitted, with the exception of management CLI commands.
You might use a nested expression if a datasource definition password is masked, for example.
3.5.9. Deployment descriptor-based property replacement
Deployment descriptor-based property replacement substitutes properties based on descriptors, so that you can remove assumptions about the environment from the application and the build chain.
Environment-specific configurations can be specified in deployment descriptors rather than annotations or build system scripts. You can provide configuration in files or as parameters at the command line.
Application configuration, such as datasource connection parameters, typically varies between development, testing, and production environments. This variance is sometimes accommodated by build system scripts, as the Jakarta EE specification does not contain a method to externalize these configurations. With JBoss EAP, you can use descriptor-based property replacement to manage configuration externally.
The spec-descriptor-property-replacement flag controls Jakarta EE descriptor replacement, and JBoss EAP disables it by default. When it’s enabled, you can replace properties in the following deployment descriptors:
-
ejb-jar.xml -
permissions.xml -
persistence.xml -
application.xml -
web.xml
You can use the following management CLI command to enable or disable property replacement in Jakarta EE descriptors:
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name="spec-descriptor-property-replacement",value=VALUE)
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name="spec-descriptor-property-replacement",value=VALUE)
The jboss-descriptor-property-replacement flag controls JBoss-specific descriptor replacement, and JBoss EAP enables it by default. When it’s enabled, you can replace properties in the following deployment descriptors:
-
jboss-ejb3.xml -
jboss-app.xml -
jboss-web.xml -
jboss-permissions.xml -
*-jms.xml -
*-ds.xml
Use the following management CLI command to enable or disable property replacement in JBoss EAP-specific descriptors:
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name="jboss-descriptor-property-replacement",value=VALUE)
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name="jboss-descriptor-property-replacement",value=VALUE)
The annotation-property-replacement flag controls property replacement inside of annotations, and it is not enabled by default. When it’s enabled, you can replace properties in the annotation attributes inside of application classes.
Use the following management CLI command to enable or disable property replacement in annotations:
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name="annotation-property-replacement",value=VALUE)
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name="annotation-property-replacement",value=VALUE)
You can set annotation-property-replacement to true to enable property replacement in your annotations when a system property value is set. For example, you can set a system property to replace the maxSession value on a Message Driven Bean:
You could set -DexampleMDB.maxSession system property to 100. If this system property is not set, the value will default to 20.
3.5.10. Using Git to manage configuration data
You can use Git to manage and persist your server configuration data, properties files, and deployments. This not only allows you to manage the version history for these files, but it also allows you to share server and application configurations across multiple servers and nodes using one or more Git repositories. This feature only works for standalone servers that use the default configuration directory layout.
You can choose to use configuration data in a local Git repository or you can pull the data from a remote Git repository. The Git repository is configured in the jboss.server.base.dir directory, which is the base directory for standalone server content. Once the jboss.server.base.dir directory is configured to use Git, JBoss EAP automatically commits every update you make to the configuration using the management CLI or management console. Any changes made outside of the server by manually editing the configuration files are not committed or persisted; however, you can use the Git CLI to add and commit manual changes. You can also use the Git CLI to view the commit history, manage branching, and manage the content.
To use this feature, pass one or more of the following arguments on the command line when you start the server.
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| --git-repo |
The location of the Git repository that is used to manage and persist server configuration data. This can be |
| --git-branch | The branch or tag name in the Git repository to use. This argument should name an existing branch or tag name as it will not be created if it does not exist. If you use a tag name, you put the repository in a detached HEAD state, meaning future commits are not attached to any branches. Tag names are read-only and are normally used when you need to replicate a configuration across several nodes. |
| --git-auth |
The URL to an Elytron configuration file that contains the credentials to be used when connecting to a remote Git repository. This argument is required if your remote Git repository requires authentication. Elytron does not support SSH. Therefore, only default SSH authentication is supported using private keys without a password. This argument is not used with a |
Using a local Git repository
To use a local Git repository, start the server with the --git-repo=local argument. You can also specify an optional branch or tag name in the remote repository by adding the --git-branch=GIT_BRANCH_NAME argument when you start the server. This argument should name an existing branch or tag name as it will not be created if it does not exist. If you use a tag name, you put the repository in a detached HEAD state, meaning future commits are not attached to any branches.
The following is an example of a command to start the server using the 1.0.x branch of the local repository.
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --git-repo=local --git-branch=1.0.x
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --git-repo=local --git-branch=1.0.x
If you start the server with the argument to use a local Git repository, JBoss EAP checks whether the jboss.server.base.dir directory is already configured for Git. If not, JBoss EAP creates and initializes the Git repository in the jboss.server.base.dir directory using the existing configuration content. JBoss EAP checks out a branch name passed by the --git-branch argument. If that argument is not passed, it checks out the master branch. After initialization, you should see a .git/ directory and a .gitignore file in the base directory for standalone server content.
Using a remote Git repository
To use a remote Git repository, start the server with the --git-repo=REMOTE_REPO argument. The value of the argument can be a URL or a remote alias that you have manually added to the local Git configuration.
You can also specify an optional branch or tag name in the remote repository by adding the --git-branch=GIT_BRANCH_NAME argument when you start the server. This argument should name an existing branch or tag name as it will not be created if it does not exist. If you use a tag name, you put the repository in a detached HEAD state, meaning future commits are not attached to any branches.
If your Git repository requires authentication, you must also add the --git-auth=AUTH_FILE_URL argument when you start the server. This argument should be the URL to an Elytron configuration file containing the credentials required to connect to the Git repository. The following is an example of a WildFly Client configuration file specifying an Elytron configuration that can be used for authentication.
Elytron does not support SSH. Therefore, only default SSH authentication is supported using private keys without a password.
The following is an example of a command to start the server with the full profile, using the 1.0.x branch of the remote eap-configuration repository, and passing the URL to an Elytron configuration file containing authentication credentials.
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --git-repo=https://github.com/MY_GIT_ID/eap-configuration.git --git-branch=1.0.x --git-auth=file:///home/USER_NAME/github-wildfly-config.xml --server-config=standalone-full.xml
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh --git-repo=https://github.com/MY_GIT_ID/eap-configuration.git --git-branch=1.0.x --git-auth=file:///home/USER_NAME/github-wildfly-config.xml --server-config=standalone-full.xml
If you start the server with the argument to use a remote Git repository, JBoss EAP checks whether the jboss.server.base.dir directory is already configured for Git. If not, JBoss EAP deletes the existing configuration files in the jboss.server.base.dir directory and replaces them with the remote Git configuration data. JBoss EAP checks out a branch name passed by the --git-branch argument. If that argument is not passed, it checks out the master branch. Once this process is complete, you should see a .git/ directory and a .gitignore file in the base directory for standalone server content.
If you later start the server passing a different --git-repo URL or --git-branch name than was originally used, you will see the error message java.lang.RuntimeException: WFLYSRV0268: Failed to pull the repository GIT_REPO_NAME when you attempt to start the server. This is because JBoss EAP attempts to pull configuration data from a different repository and branch than the one that is currently configured in the jboss.server.base.dir directory and the Git pull results in conflicts.
Publishing remote configuration data when using Git
You can push your Git repository changes to the remote repository using the management CLI publish-configuration operation. Because JBoss EAP pulls the configuration from the remote Git repository during the boot process when you start the server, this allows you to share the configuration data across multiple servers. You can only use this operation with a remote repository. It does not work for a local repository.
The following management CLI operation publishes the configuration data to the remote eap-configuration repository.
:publish-configuration(location="=https://github.com/MY_GIT_ID/eap-configuration.git")
{"outcome" => "success"}
:publish-configuration(location="=https://github.com/MY_GIT_ID/eap-configuration.git")
{"outcome" => "success"}Using snapshots with Git
In addition to using the Git commit history to track configuration changes, you can also take snapshots to preserve a configuration at a specific point in time. You can list the snapshots and delete them.
Taking snapshots when using Git
Snapshots are stored as tags in Git. You specify the snapshot tag name and commit message as arguments on the take-snapshot operation.
The following management CLI operation takes a snapshot and names the tag "snapshot-01".
:take-snapshot(name="snapshot-01", comment="1st snapshot")
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => "1st snapshot"
}
:take-snapshot(name="snapshot-01", comment="1st snapshot")
{
"outcome" => "success",
"result" => "1st snapshot"
}Listing snapshots When using Git
You can list all of the snapshot tags using the list-snapshots operation.
The following management CLI operation lists the snapshot tags.
Deleting snapshots when using Git
You can delete a specific snapshot by passing the tag name on the delete-snapshot operation.
The following management CLI operation deletes the snapshot with the tag name "snapshot-01".
:delete-snapshot(name="snapshot-01")
{"outcome" => "success"}
:delete-snapshot(name="snapshot-01")
{"outcome" => "success"}3.6. File system paths
JBoss EAP uses logical names for file system paths. Other areas of the configuration can then reference the paths using their logical name, avoiding the need to use absolute paths for each instance and allowing specific host configurations to resolve to universal logical names.
For example, the default logging subsystem configuration declares jboss.server.log.dir as the logical name for the server log directory.
Example: Relative path example for the server log directory
<file relative-to="jboss.server.log.dir" path="server.log"/>
<file relative-to="jboss.server.log.dir" path="server.log"/>JBoss EAP automatically provides a number of standard paths without any need for the user to configure them in a configuration file.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| java.home | The Java installation directory |
| jboss.controller.temp.dir |
A common alias for standalone servers and managed domains. The directory to be used for temporary file storage. Equivalent to |
| jboss.domain.base.dir | The base directory for domain content. |
| jboss.domain.config.dir | The directory that contains the domain configuration. |
| jboss.domain.data.dir | The directory that the domain will use for persistent data file storage. |
| jboss.domain.log.dir | The directory that the domain will use for persistent log file storage. |
| jboss.domain.temp.dir | The directory that the domain will use for temporary file storage. |
| jboss.domain.deployment.dir | The directory that the domain will use for storing deployed content. |
| jboss.domain.servers.dir | The directory that the domain will use for storing outputs of the managed domain instances. |
| jboss.home.dir | The root directory of the JBoss EAP distribution. |
| jboss.server.base.dir | The base directory for standalone server content. |
| jboss.server.config.dir | The directory that contains the standalone server configuration. |
| jboss.server.data.dir | The directory the standalone server will use for persistent data file storage. |
| jboss.server.log.dir | The directory the standalone server will use for log file storage. |
| jboss.server.temp.dir | The directory the standalone server will use for temporary file storage. |
| jboss.server.deploy.dir | The directory that the standalone server will use for storing deployed content. |
| user.dir | The user’s current working directory. |
| user.home | The user home directory. |
You can override a standard path or add a custom path.
3.6.1. View file system paths
Use the following management CLI command to list the file system paths:
ls /path
ls /pathIn a managed domain, you can list the file system paths for a specific server using the following management CLI command:
ls /host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME/path
ls /host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME/pathUse the following management CLI command to read the value of a file system path:
/path=PATH_NAME:read-resource
/path=PATH_NAME:read-resourceIn a managed domain, you can read the value of a file system path for a specific server using the following management CLI command:
/host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME/path=PATH_NAME:read-resource
/host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME/path=PATH_NAME:read-resource3.6.2. Override a standard path
You can override the default locations of the standard paths that begin with jboss.server.* or jboss.domain.*. This can be done in one of two ways:
Pass in the command-line argument when you start the server. For example:
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.server.log.dir=/var/log
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.server.log.dir=/var/logCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the
JAVA_OPTSvariable in the server configuration file, eitherstandalone.confordomain.conf, to contain the new location. For example:JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djboss.server.log.dir=/var/log"
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djboss.server.log.dir=/var/log"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Overriding standard paths in a managed domain
In this example, the objective is to store domain files in the /opt/jboss_eap/domain_data directory, and give each top-level directory a custom name. The default directory grouping, by-server, is used.
-
Log files are to be stored in the
all_logssubdirectory -
Data files are to be stored in the
all_datasubdirectory -
Temporary files are to be stored in the
all_tempsubdirectory -
Servers' files are to be stored in the
all_serverssubdirectory
To achieve this configuration, you would override several system properties when starting JBoss EAP.
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh -Djboss.domain.temp.dir=/opt/jboss_eap/domain_data/all_temp -Djboss.domain.log.dir=/opt/jboss_eap/domain_data/all_logs -Djboss.domain.data.dir=/opt/jboss_eap/domain_data/all_data -Djboss.domain.servers.dir=/opt/jboss_eap/domain_data/all_servers
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh -Djboss.domain.temp.dir=/opt/jboss_eap/domain_data/all_temp -Djboss.domain.log.dir=/opt/jboss_eap/domain_data/all_logs -Djboss.domain.data.dir=/opt/jboss_eap/domain_data/all_data -Djboss.domain.servers.dir=/opt/jboss_eap/domain_data/all_serversThe resulting path structure will be as follows:
3.6.3. Add a custom path
You can add a custom file system path using the management CLI or the management console.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
From the management CLI, you can add a new path using the following management CLI command.
/path=my.custom.path:add(path=/my/custom/path)
/path=my.custom.path:add(path=/my/custom/path)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - From the management console, you can configure file system paths by navigating to the Configuration tab, selecting Paths, and clicking View. From there, you can add, modify, and remove paths.
You can then use this custom path in your configuration. For example, the below log handler uses a custom path for its relative path.
3.7. Directory grouping
In a managed domain, each server’s files are stored in the EAP_HOME/domain directory. You can specify how to organize the subdirectories for servers using the host controller’s directory-grouping attribute. Directories can be grouped either by server or by type. By default, directories are grouped by server.
Directory grouping by server
By default, directories are grouped by server. If your administration is server-centric, this configuration is recommended. For example, it allows backups and log file handling to be configured per server instance.
If JBoss EAP is installed using the ZIP installation method, the default directory structure (grouped by server) will be as follows.
To group domain directories by server, enter the following management CLI command:
/host=HOST_NAME:write-attribute(name=directory-grouping,value=by-server)
/host=HOST_NAME:write-attribute(name=directory-grouping,value=by-server)
This will update the host controller’s host.xml configuration file:
Directory grouping by type
Instead of grouping directories by server, you can instead group by file type. If your administration is file type-centric, this configuration is recommended. For example, this would allow you to easily back up only data files.
If JBoss EAP is installed using the ZIP installation method and the domain’s files are grouped by type, the directory structure will be as follows.
To group domain directories by type, enter the following management CLI command:
/host=HOST_NAME:write-attribute(name=directory-grouping,value=by-type)
/host=HOST_NAME:write-attribute(name=directory-grouping,value=by-type)
This will update the host controller’s host.xml configuration file:
3.8. System properties
You can use Java system properties to configure many JBoss EAP options, as well as set any name-value pair for use within the application server.
System properties can be used to override default values in the JBoss EAP configuration. For example, the following XML configuration for the public interface bind address shows that it can be set by the jboss.bind.address system property, but if the system property is not provided, it will default to 127.0.0.1.
<inet-address value="${jboss.bind.address:127.0.0.1}"/>
<inet-address value="${jboss.bind.address:127.0.0.1}"/>There are a few ways you can set system properties in JBoss EAP, including:
If you use a JBoss EAP managed domain, system properties can be applied to either the whole domain, a specific server group, a specific host and all its server instances, or just to one specific server instance. As with most other JBoss EAP domain settings, a system property set at a more specific level will override a more abstract one. See the Domain Management chapter for more information.
Passing a system property to the startup script
You can pass a system property to the JBoss EAP startup script by using the -D argument. For example:
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.bind.address=192.168.1.2
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.bind.address=192.168.1.2This method of setting the system property is especially useful for JBoss EAP options that need to be set before JBoss EAP starts.
Setting a system property using the management CLI
Using the management CLI, you can set a system property using the following syntax:
/system-property=PROPERTY_NAME:add(value=PROPERTY_VALUE)
/system-property=PROPERTY_NAME:add(value=PROPERTY_VALUE)For example:
/system-property=jboss.bind.address:add(value=192.168.1.2)
/system-property=jboss.bind.address:add(value=192.168.1.2)
When setting system properties using the management CLI, some JBoss EAP options, including the above example of jboss.bind.address, will only take effect after the next server restart.
For a managed domain, the above example configures a system property for the entire domain, but you can also set or override system properties at more specific levels of the domain configuration.
Setting a system property using the management console
- For a standalone JBoss EAP server, you can configure system properties in the management console under the Configuration tab. Select System Properties, and click the View button.
For a managed domain:
- Domain-level system properties can be set in the Configuration tab. Select System Properties, and click the View button.
- Server group and server-level system properties can be set in the Runtime tab. Select the server group or server you want to configure, click the View button next to the server group or server name, and select the System Properties tab.
- Host-level system properties can be set in the Runtime tab. Select the host you want to configure, then using the drop-down menu next to the host name, select Properties.
Setting a system property using JAVA_OPTS
System properties can also be configured using the JAVA_OPTS environment variable. There are many ways to modify JAVA_OPTS, but JBoss EAP provides a configuration file for setting JAVA_OPTS that is used by the JBoss EAP process.
For a standalone server, this file is EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.conf, or, for a managed domain, it is EAP_HOME/bin/domain.conf. For Microsoft Windows systems these files have a .bat extension.
For an RPM installation, the RPM service configuration file is the preferred location to modify JAVA_OPTS to configure system properties. For more information, see Configure RPM Service Properties.
Add your system property definition to JAVA_OPTS in the relevant configuration file. The examples below demonstrate setting the bind address on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux system.
For
standalone.conf, add yourJAVA_OPTSsystem property definition at the end of the file. For example:... # Set the bind address JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djboss.bind.address=192.168.1.2"
... # Set the bind address JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Djboss.bind.address=192.168.1.2"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For
domain.conf,JAVA_OPTSmust be set before the process controllerJAVA_OPTSsetting. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
3.9. Management audit logging
You can enable audit logging for the management interfaces, which will log all operations performed using the management console, management CLI, or custom application that uses the Management API. Audit log entries are stored in JSON format. By default, audit logging is disabled.
You can configure audit logging to output to a file or to a syslog server.
Login and logout events cannot be audited as there is no authenticated session in JBoss EAP. Instead, audit messages are logged when an operation is received from the user.
3.9.1. Standalone server audit logging
Though disabled by default, the default audit logging configuration writes to a file.
This configuration can be read using the following management CLI command.
/core-service=management/access=audit:read-resource(recursive=true)
/core-service=management/access=audit:read-resource(recursive=true)See Enable audit logging to enable audit logging for a standalone server.
3.9.2. Managed domain audit logging
Though disabled by default, the default audit logging configuration writes a file for each host and for each server.
This configuration can be read using the following management CLI command.
/host=HOST_NAME/core-service=management/access=audit:read-resource(recursive=true)
/host=HOST_NAME/core-service=management/access=audit:read-resource(recursive=true)See Enable Audit Logging to enable audit logging for a managed domain.
3.9.3. Enable management audit logging
JBoss EAP is preconfigured with file handlers for audit logging, though audit logging is disabled by default. The management CLI command to enable audit logging depends on whether you are running as a standalone server or in a managed domain. See Management audit logging attributes for file handler attributes.
The following instructions enable NATIVE and HTTP audit logging. To configure JMX audit logging, see Enable JMX management audit logging.
To set up syslog audit logging, see Send management audit logging to a syslog server.
3.9.3.1. Enable standalone server audit logging
Audit logging can be enabled using the following command.
/core-service=management/access=audit/logger=audit-log:write-attribute(name=enabled,value=true)
/core-service=management/access=audit/logger=audit-log:write-attribute(name=enabled,value=true)
By default, this will write the audit log to EAP_HOME/standalone/data/audit-log.log.
3.9.3.2. Enable managed domain audit logging
The default audit logging configuration for a managed domain is preconfigured to write an audit log for each host and each server.
Audit logging for each host can be enabled using the following command.
/host=HOST_NAME/core-service=management/access=audit/logger=audit-log:write-attribute(name=enabled,value=true)
/host=HOST_NAME/core-service=management/access=audit/logger=audit-log:write-attribute(name=enabled,value=true)
By default, this will write the audit logs to EAP_HOME/domain/data/audit-log.log.
Audit logging for each server can be enabled using the following command.
/host=HOST_NAME/core-service=management/access=audit/server-logger=audit-log:write-attribute(name=enabled,value=true)
/host=HOST_NAME/core-service=management/access=audit/server-logger=audit-log:write-attribute(name=enabled,value=true)
By default, this will write the audit logs to EAP_HOME/domain/servers/SERVER_NAME/data/audit-log.log.
3.9.4. Enable JMX management audit logging
JBoss EAP is preconfigured with file handlers for JMX audit logging, though these logs are disabled by default. The management CLI command to enable audit logging depends on whether you are running as a standalone server or a managed domain.
To configure NATIVE or HTTP audit logging, see Enable management audit logging.
3.9.4.1. Enable standalone server JMX audit logging
JMX audit logging can be enabled for a standalone server using the following commands.
/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log:add() /subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log/handler=file:add()
/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log:add()
/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log/handler=file:add()
This enables JMX audit logging, and then uses the defined file handler to write these logs to EAP_HOME/standalone/data/audit-log.log.
3.9.4.2. Enable managed domain JMX audit logging
JMX audit logging can be enabled for each host and profile in a managed domain.
Enable JMX audit logging for a host
Enable audit logging in the host’s
jmxsubsystem./host=HOST_NAME/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log:add()
/host=HOST_NAME/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log:add()Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Once audit logging for the
jmxsubsystem has been enabled, a handler can be defined for the host with the following command./host=HOST_NAME/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log/handler=host-file:add()
/host=HOST_NAME/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log/handler=host-file:add()Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By default, this will write the JMX audit logs to
EAP_HOME/domain/data/audit-log.log.
Enable JMX audit logging for a profile
Enable audit logging in the profile’s
jmxsubsystem./profile=PROFILE_NAME/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log:add()
/profile=PROFILE_NAME/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log:add()Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Once audit logging for the
jmxsubsystem has been enabled, a handler can be defined for the profile with the following command./profile=PROFILE_NAME/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log/handler=server-file:add()
/profile=PROFILE_NAME/subsystem=jmx/configuration=audit-log/handler=server-file:add()Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By default, this will write the JMX audit logs to
EAP_HOME/domain/servers/SERVER_NAME/data/audit-log.log.
3.9.5. Send management audit logging to a syslog server
A syslog handler specifies the parameters by which audit log entries are sent to a syslog server, specifically the syslog server’s host name and the port on which the syslog server is listening. Sending audit logging to a syslog server provides more security options than logging to a local file or local syslog server. Multiple syslog handlers can be defined and be active at the same time.
By default, audit logging is preconfigured to output to a file when enabled. Use the following steps to set up and enable audit logging to a syslog server. See Management Audit Logging Attributes for syslog handler attributes.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Add a syslog handler.
Create the syslog handler, specifying the host and port of the syslog server. In a managed domain, you must precede the
/core-servicecommands with/host=HOST_NAME.batch /core-service=management/access=audit/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:add(formatter=json-formatter) /core-service=management/access=audit/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME/protocol=udp:add(host=HOST_NAME,port=PORT) run-batch
batch /core-service=management/access=audit/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:add(formatter=json-formatter) /core-service=management/access=audit/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME/protocol=udp:add(host=HOST_NAME,port=PORT) run-batchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe parameters to pass in differ depending on the protocol specified.
To configure the handler to use TLS to communicate securely with the syslog server, you must also configure the authentication, for example:
/core-service=management/access=audit/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME/protocol=tls/authentication=truststore:add(keystore-path=PATH_TO_TRUSTSTORE,keystore-password=TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD)
/core-service=management/access=audit/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME/protocol=tls/authentication=truststore:add(keystore-path=PATH_TO_TRUSTSTORE,keystore-password=TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a reference to the syslog handler.
In a managed domain, you must precede this command with
/host=HOST_NAME./core-service=management/access=audit/logger=audit-log/handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:add
/core-service=management/access=audit/logger=audit-log/handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable audit logging.
See Enable Management Audit Logging to enable audit logging.
Enabling audit logging to a syslog server in JBoss EAP will not work unless logging is enabled in the operating system as well.
For more information on rsyslog configurations on Red Hat Enterprise Linux, see the Basic Configuration of Rsyslog section of the System Administrator’s Guide for Red Hat Enterprise Linux at https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en/red-hat-enterprise-linux/.
3.9.6. Read audit log entries
Audit log entries output to files are best viewed with a text viewer, while those output to a syslog server are best viewed using a syslog viewer application.
Using a text editor for viewing log files is not recommended as some may prevent further log entries being written to the log file.
The audit log entries are stored in JSON format. Each log entry begins with an optional timestamp, followed by the fields in the below table.
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| access | This can have one of the following values:
|
| booting |
Has the value |
| domainUUID | An ID to link together all operations as they are propagated from the domain controller to its servers, secondary host controllers, and secondary host controller servers. |
| ops | The operations being executed. This is a list of the operations serialized to JSON. At boot, this is the operations resulting from parsing the XML. Once booted, the list typically contains a single entry. |
| r/o |
Has the value |
| remote-address | The address of the client executing this operation. |
| success |
Has the value |
| type |
This can have the value |
| user |
The username of the authenticated user. If the operation occurred using the management CLI on the same machine as the running server, the special user |
| version | The version number of the JBoss EAP instance. |
3.10. Server lifecycle event notifications
You can set up notifications for server lifecycle events using the JBoss EAP core-management subsystem or JMX. A change in server runtime configuration state or server running state will trigger a notification.
The server runtime configuration states for JBoss EAP are STARTING, RUNNING, RELOAD_REQUIRED, RESTART_REQUIRED, STOPPING, and STOPPED.
The server running states for JBoss EAP are STARTING, NORMAL, ADMIN_ONLY, PRE_SUSPEND, SUSPENDING, SUSPENDED, STOPPING, and STOPPED.
3.10.1. Monitor server lifecycle events using the core management subsystem
You can register a listener to the JBoss EAP core-management subsystem to monitor for server lifecycle events. The following steps show how to create and register an example listener that logs the events to a file.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Create the listener.
Create an implementation of
org.wildfly.extension.core.management.client.ProcessStateListener, like the example below.Example: Listener class
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteKeep the following in mind when implementing the listener.
- In the event of a server reload, listeners stop listening while the server attempts to stop, and the listeners are reloaded when the server starts. Because of this, implementations must ensure that they can be loaded, initialized, and removed properly several times inside the same JVM.
- Notifications to the listeners are blocking to allow reactions to server state changes. Implementations must ensure that they do not block or deadlock.
- Each listener instance is executed in its own thread and the order is not guaranteed.
Compile the class and package it into a JAR.
Note that to compile, you need to depend on the
org.wildfly.core:wildfly-core-management-clientMaven module.Add the JAR as a JBoss EAP module.
Use the following management CLI command and provide the module name and path to the JAR.
module add --name=org.simple.lifecycle.events.listener --dependencies=org.wildfly.extension.core-management-client --resources=/path/to/simple-listener-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
module add --name=org.simple.lifecycle.events.listener --dependencies=org.wildfly.extension.core-management-client --resources=/path/to/simple-listener-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jarCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the listener.
Add the listener to the
core-managementsubsystem using the following management CLI command. Specify the class, module, and file location to log the server lifecycle events./subsystem=core-management/process-state-listener=my-simple-listener:add(class=org.simple.lifecycle.events.listener.SimpleListener, module=org.simple.lifecycle.events.listener,properties={file=/path/to/my-listener-output.txt})/subsystem=core-management/process-state-listener=my-simple-listener:add(class=org.simple.lifecycle.events.listener.SimpleListener, module=org.simple.lifecycle.events.listener,properties={file=/path/to/my-listener-output.txt})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Now, server lifecycle events will be logged to the my-listener-output.txt file based on the SimpleListener class above. For example, issuing a :suspend command in the management CLI will output the following to the my-listener-output.txt file.
Running state change for STANDALONE_SERVER: normal to suspending Running state change for STANDALONE_SERVER: suspending to suspended
Running state change for STANDALONE_SERVER: normal to suspending
Running state change for STANDALONE_SERVER: suspending to suspended
This shows that the running state changed from normal to suspending, and then from suspending to suspended.
3.10.2. Monitor server lifecycle events using JMX notifications
You can register a JMX notification listener to monitor for server lifecycle events. The following steps show how to create and add an example listener that logs events to a file.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Create the listener.
Create an implementation of
java.management.NotificationListener, like the example below.Example: Listener Class
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Register the notification listener.
Add the notification listener to the
MBeanServer.Example: Add a notification listener
MBeanServer server = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer(); server.addNotificationListener(ObjectName.getInstance("jboss.root:type=state"), new StateNotificationListener(), null, null);MBeanServer server = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer(); server.addNotificationListener(ObjectName.getInstance("jboss.root:type=state"), new StateNotificationListener(), null, null);Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Package and deploy to JBoss EAP.
Server lifecycle events are now logged to a file based on the StateNotificationListener class above. For example, issuing a :suspend command in the management CLI outputs the following to the running-notifications.txt file.
jmx.attribute.change 5 jboss.root:type=state The attribute 'RunningState' has changed from 'normal' to 'suspending' jmx.attribute.change 6 jboss.root:type=state The attribute 'RunningState' has changed from 'suspending' to 'suspended'
jmx.attribute.change 5 jboss.root:type=state The attribute 'RunningState' has changed from 'normal' to 'suspending'
jmx.attribute.change 6 jboss.root:type=state The attribute 'RunningState' has changed from 'suspending' to 'suspended'
This shows that the running state changed from normal to suspending, and then from suspending to suspended.
Chapter 4. Network and Port Configuration
4.1. Interfaces
JBoss EAP references named interfaces throughout the configuration. This allows the configuration to reference individual interface declarations with logical names, rather than requiring the full details of the interface at each use.
This also allows for easier configuration in a managed domain, where network interface details can vary across multiple machines. Each server instance can correspond to a logical name group.
The standalone.xml, domain.xml, and host.xml files all include interface declarations. There are several preconfigured interface names, depending on which default configuration is used. The management interface can be used for all components and services that require the management layer, including the HTTP management endpoint. The public interface can be used for all application-related network communications. The unsecure interface is used for IIOP sockets in the standard configuration. The private interface is used for JGroups sockets in the standard configuration.
4.1.1. Default interface configurations
The following interface configurations are set by default:
JBoss EAP binds these interfaces to 127.0.0.1, but these values can be overridden at runtime by setting the appropriate property. For example, the inet-address of the public interface can be set when starting JBoss EAP as a standalone server with the following command.
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.bind.address=IP_ADDRESS
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.bind.address=IP_ADDRESS
Alternatively, you can use the -b switch on the server start command line.
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -b IP_ADDRESS
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -b IP_ADDRESS
In the above command, -b IP_ADDRESS is equivalent to -Djboss.bind.address=IP_ADDRESS.
You can also use the -b switch to set the inet-address of the management interface.
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -bmanagement=IP_ADDRESS
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -bmanagement=IP_ADDRESS
If you only want to set a single variable, you can change jboss.bind.address.management to jboss.bind.address. When you set -b switch or -Djboss.bind.address, the public and management interfaces will share the same IP_ADDRESS.
For more information about server start options, see Server Runtime Arguments.
If you modify the default network interfaces or ports that JBoss EAP uses, you must also remember to change any scripts that use the modified interfaces or ports. These include JBoss EAP service scripts, as well as remembering to specify the correct interface and port when accessing the management console or management CLI.
4.1.2. Configuring interfaces
Network interfaces are declared by specifying a logical name and selection criteria for the physical interface. The selection criteria can reference a wildcard address or specify a set of one or more characteristics that an interface or address must have in order to be a valid match. For a listing of all available interface selection criteria, see the Interface Attributes section.
Interfaces can be configured using the management console or the management CLI. Below are several examples of adding and updating interfaces. The management CLI command is shown first, followed by the corresponding configuration XML.
Add an interface with a NIC value
Add a new interface with a NIC value of eth0.
/interface=external:add(nic=eth0)
/interface=external:add(nic=eth0)<interface name="external"> <nic name="eth0"/> </interface>
<interface name="external">
<nic name="eth0"/>
</interface>Add an interface with several conditional values
Add a new interface that matches any interface/address on the correct subnet if it is up, supports multicast, and is not point-to-point.
/interface=default:add(subnet-match=192.168.0.0/16,up=true,multicast=true,not={point-to-point=true})
/interface=default:add(subnet-match=192.168.0.0/16,up=true,multicast=true,not={point-to-point=true})Update an interface attribute
Update the public interface’s default inet-address value, keeping the jboss.bind.address property to allow for this value to be set at runtime.
/interface=public:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address:192.168.0.0}")
/interface=public:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address:192.168.0.0}")<interface name="public">
<inet-address value="${jboss.bind.address:192.168.0.0}"/>
</interface>
<interface name="public">
<inet-address value="${jboss.bind.address:192.168.0.0}"/>
</interface>Add an interface to a server in a managed domain
/host=HOST_NAME/server-config=SERVER_NAME/interface=INTERFACE_NAME:add(inet-address=127.0.0.1)
/host=HOST_NAME/server-config=SERVER_NAME/interface=INTERFACE_NAME:add(inet-address=127.0.0.1)4.2. Socket bindings
Socket bindings and socket binding groups allow you to define network ports and their relationship to the networking interfaces required for your JBoss EAP configuration. A socket binding is a named configuration for a socket. A socket binding group is a collection of socket binding declarations that are grouped under a logical name.
This allows other sections of the configuration to reference socket bindings by their logical name, rather than requiring the full details of the socket configuration at each use.
The declarations for these named configurations can be found in the standalone.xml and domain.xml configuration files. A standalone server contains only one socket binding group, while a managed domain can contain multiple groups. You can create a socket binding group for each server group in the managed domain, or share a socket binding group between multiple server groups.
The ports JBoss EAP uses by default depend on which socket binding groups are used and the requirements of your individual deployments.
There are three types of socket bindings that can be defined in a socket binding group in the JBoss EAP configuration:
- Inbound socket bindings
The
socket-bindingelement is used to configure inbound socket bindings for the JBoss EAP server. The default JBoss EAP configurations provide several preconfiguredsocket-bindingelements, for example, for HTTP and HTTPS traffic. Another example can be found in the Broadcast groups section of Configuring Messaging for JBoss EAP.Attributes for this element can be found in the Inbound socket binding attributes table.
- Remote outbound socket bindings
The
remote-destination-outbound-socket-bindingelement is used to configure outbound socket bindings for destinations that are remote to the JBoss EAP server. The default JBoss EAP configurations provide an example remote destination socket binding that can be used for a mail server. Another example can be found in the Using the Integrated Artemis resource adapter for remote connections section of Configuring Messaging for JBoss EAP.Attributes for this element can be found in the Remote outbound socket binding attributes table.
- Local outbound socket bindings
The
local-destination-outbound-socket-bindingelement is used to configure outbound socket bindings for destinations that are local to the JBoss EAP server. This type of socket binding is not expected to be commonly used.Attributes for this element can be found in the Local outbound socket binding attributes table.
4.2.1. Management ports
Management ports were consolidated in JBoss EAP 7. By default, JBoss EAP 8.0 uses port 9990 for both native management, used by the management CLI, and HTTP management, used by the web-based management console. Port 9999, which was used as the native management port in JBoss EAP 6, is no longer used but can still be enabled if desired.
If HTTPS is enabled for the management console, then port 9993 is used by default.
4.2.2. Default socket bindings
JBoss EAP ships with a socket binding group for each of the five predefined profiles (default, ha, full, full-ha, load-balancer).
For detailed information about the default socket bindings, such as default ports and descriptions, see the Default socket bindings groups section.
If you modify the default network interfaces or ports that JBoss EAP uses, you must also remember to change any scripts that use the modified interfaces or ports. These include JBoss EAP service scripts, as well as remembering to specify the correct interface and port when accessing the management console or management CLI.
Standalone server
When running as a standalone server, only one socket binding group is defined per configuration file. Each standalone configuration file (standalone.xml, standalone-ha.xml, standalone-full.xml, standalone-full-ha.xml, standalone-load-balancer.xml) defines socket bindings for the technologies used by its corresponding profile.
For example, the default standalone configuration file (standalone.xml) specifies the below socket bindings.
Managed domain
When running in a managed domain, all socket binding groups are defined in the domain.xml file. There are five predefined socket binding groups:
-
standard-sockets -
ha-sockets -
full-sockets -
full-ha-sockets -
load-balancer-sockets
Each socket binding group specifies socket bindings for the technologies used by its corresponding profile. For example, the full-ha-sockets socket binding group defines several jgroups socket bindings, which are used by the full-ha profile for high availability.
The socket configuration for the management interfaces is defined in the domain controller’s host.xml file.
4.2.3. Configuring socket bindings
When defining a socket binding, you can configure the port and interface attributes, as well as multicast settings such as multicast-address and multicast-port. For details on all available socket bindings attributes, see the Socket binding attributes section.
Socket bindings can be configured using the management console or the management CLI. The following steps go through adding a socket binding group, adding a socket binding, and configuring socket binding settings using the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a new socket binding group.
NoteThis step cannot be performed when running as a standalone server.
/socket-binding-group=new-sockets:add(default-interface=public)
/socket-binding-group=new-sockets:add(default-interface=public)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a socket binding.
/socket-binding-group=new-sockets/socket-binding=new-socket-binding:add(port=1234)
/socket-binding-group=new-sockets/socket-binding=new-socket-binding:add(port=1234)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Change the socket binding to use an interface other than the default, which is set by the socket binding group.
/socket-binding-group=new-sockets/socket-binding=new-socket-binding:write-attribute(name=interface,value=unsecure)
/socket-binding-group=new-sockets/socket-binding=new-socket-binding:write-attribute(name=interface,value=unsecure)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The following example shows how the XML configuration may look after the above steps have been completed.
4.2.4. Viewing socket bindings and open ports for a server
You can view the socket binding name and the open ports for a server from the management console.
Prerequisites
Socket binding names and open ports are only visible when the server is in one of the following states:
-
running -
reload-required -
restart-required
Procedure
- Access the management console and navigate to Runtime.
- Click the server to view the socket binding name and the open ports in the right pane.
4.2.5. Port offsets
A port offset is a numeric offset value added to all port values specified in the socket binding group for that server. This allows the server to inherit the port values defined in its socket binding group, with an offset to ensure that it does not conflict with any other servers on the same host. For instance, if the HTTP port of the socket binding group is 8080, and a server uses a port offset of 100, then its HTTP port is 8180.
Below is an example of setting a port offset of 250 for a server in a managed domain using the management CLI.
/host=primary/server-config=server-two/:write-attribute(name=socket-binding-port-offset,value=250)
/host=primary/server-config=server-two/:write-attribute(name=socket-binding-port-offset,value=250)Port offsets can be used for servers in a managed domain and for running multiple standalone servers on the same host.
You can pass in a port offset when starting a standalone server using the jboss.socket.binding.port-offset property.
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.socket.binding.port-offset=100
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.socket.binding.port-offset=1004.3. IPv6 Addresses
By default, JBoss EAP is configured to run using IPv4 addresses. The steps below show how to configure JBoss EAP to run using IPv6 addresses.
4.3.1. Configure the JVM stack for IPv6 addresses
Update the startup configuration to prefer IPv6 addresses.
Procedure
Open the startup configuration file.
-
When running as a standalone server, edit the
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.conffile (orstandalone.conf.batfor Windows Server). -
When running in a managed domain, edit the
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.conffile (ordomain.conf.batfor Windows Server).
-
When running as a standalone server, edit the
Set the
java.net.preferIPv4Stackproperty tofalse.-Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=false
-Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=falseCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Append the
java.net.preferIPv6Addressesproperty and set it totrue.-Djava.net.preferIPv6Addresses=true
-Djava.net.preferIPv6Addresses=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The following example shows how the JVM options in the startup configuration file may look after making the above changes.
4.3.2. Update interface declarations for IPv6 addresses
The default interface values in the configuration can be changed to IPv6 addresses. For example, the below management CLI command sets the management interface to the IPv6 loopback address (::1).
/interface=management:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address.management:[::1]}")
/interface=management:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address.management:[::1]}")The following example shows how the XML configuration may look after running the above command.
Chapter 5. Overview of JBoss EAP class loading
JBoss EAP uses a modular class loading system for controlling the classpaths of deployed applications. This system provides more flexibility and control than the traditional system of hierarchical class loaders. Developers have fine-grained control of the classes available to their applications, and can configure a deployment to ignore classes provided by the application server in favor of their own.
The modular class loader separates all Java classes into logical groups called modules. Each module can define dependencies on other modules to include the classes from that module in its own class path. Because each deployed Java Archive (JAR) and Web Archive (WAR) file is treated as a module, developers can control the contents of their application’s class path by adding module configuration.
5.1. Types of modules in JBoss EAP
A module is a logical grouping of classes used for class loading and dependency management. JBoss EAP identifies two different types of modules:
- Static modules
- Dynamic modules
The main difference between the two is how they are packaged.
JBoss EAP also provides a set of predefined modules.
5.1.1. Static modules in JBoss EAP
Static modules are defined in the EAP_HOME/modules/ directory of the application server. Each module exists as a subdirectory, for example, EAP_HOME/modules/com/mysql/. Each module directory then contains a slot subdirectory, which defaults to main and contains the module.xml configuration file and any required Java Archive (JAR) files. All the application server-provided APIs are provided as static modules, including the Jakarta EE APIs as well as other APIs.
Example: MySQL JDBC Driver module.xml File
The MySQL driver JAR name, mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar, is provided only as an example. For information about the tested MySQL version, see Tested databases.
The module name, com.mysql, must match the directory structure for the module, excluding the slot name, main.
Creating custom static modules can be useful if many applications are deployed on the same server that use the same third-party libraries. Instead of bundling those libraries with each application, a module containing these libraries can be created and installed by an administrator. The applications can then declare an explicit dependency on the custom static modules.
The modules provided in JBoss EAP distributions are located in the system directory within the EAP_HOME/modules directory. This keeps them separate from any modules provided by third parties. Any Red Hat provided products that layer on top of JBoss EAP also install their modules within the system directory.
Users must ensure that custom modules are installed into the EAP_HOME/modules directory, using one directory per module. This ensures that custom versions of modules that already exist in the system directory are loaded instead of the shipped versions. In this way, user-provided modules will take precedence over system modules.
If you use the JBOSS_MODULEPATH environment variable to change the locations in which JBoss EAP searches for modules, then the product will look for a system subdirectory structure within one of the locations specified. A system structure must exist somewhere in the locations specified with JBOSS_MODULEPATH.
The use of absolute paths in the resource-root path element of the module.xml file is also supported. This way, your resource libraries can be made accessible without needing to move them to the EAP_HOME/modules directory.
Example: Absolute Path in the module.xml File
5.1.2. Dynamic modules in JBoss EAP
Dynamic modules are created and loaded by the application server for each Java Archive (JAR) or Web Archive (WAR) deployment, or for each subdeployment in an Enterprise Archive (EAR). The name of a dynamic module is derived from the name of the deployed archive. Because deployments are loaded as modules, they can configure dependencies and be used as dependencies by other deployments.
Modules are loaded only when required, usually when an application with explicit or implicit dependencies is deployed.
5.1.3. Predefined modules in JBoss EAP
A set of predefined modules is available to you when you use the default module loader in the application server. The special module, org.jboss.modules, which includes all of the JBoss Modules API, is always available and is provided by JBoss Modules. The standard Java Platform Module System (JPMS) modules are also available by their standard names.
For a list of platform modules available on Java 9 or later, see the appropriate JDK documentation.
5.2. Module dependencies in JBoss EAP
A module dependency is a declaration that one module requires the classes of one or more other modules to function. When JBoss EAP loads a module, the modular class loader parses the dependencies of that module and adds the classes from each dependency to its class path. If a specified dependency cannot be found, the module will fail to load.
Deployed applications, such as a Java Archive (JAR) or Web Archive (WAR), are loaded as dynamic modules and make use of dependencies to access the APIs provided by JBoss EAP.
There are two types of dependencies: explicit, and implicit.
- Explicit dependencies
-
Explicit dependencies are declared by the developer in a configuration file. A static module can declare dependencies in its
module.xmlfile. A dynamic module can declare dependencies in the deployment’sMANIFEST.MF, orjboss-deployment-structure.xmldeployment descriptor. - Implicit dependencies
- Implicit dependencies are added automatically by JBoss EAP when certain conditions or metadata are found in a deployment. The Jakarta EE APIs supplied with JBoss EAP are examples of modules that are added by detection of implicit dependencies in deployments.
Deployments can also be configured to exclude specific implicit dependencies by using the jboss-deployment-structure.xml deployment descriptor file. This can be useful when an application bundles a specific version of a library that JBoss EAP will attempt to add as an implicit dependency.
Optional Dependencies
Explicit dependencies can be specified as optional. Failure to load an optional dependency will not cause a module to fail to load. However, if the dependency becomes available later it will not be added to the module’s class path. Dependencies must be available when the module is loaded.
Exported dependency
A module’s class path contains only its own classes and that of its immediate dependencies. A module is not able to access the classes of the dependencies of one of its dependencies. However, a module can specify that an explicit dependency is exported. An exported dependency is provided to any module that depends on the module that exports it.
For example, Module A depends on Module B, and Module B depends on Module C. Module A can access the classes of Module B, and Module B can access the classes of Module C. Module A cannot access the classes of Module C unless:
- Module A declares an explicit dependency on Module C, or
- Module B exports its dependency on Module C.
Global modules
A global module is a module that JBoss EAP provides as a dependency to every application. Any module can be made global by adding it to JBoss EAP’s list of global modules. It does not require changes to the module.
For more information, see Global modules in JBoss EAP.
5.3. Creating custom modules for JBoss EAP
Creating custom modules can be useful if many applications are deployed on the same server that use the same third-party libraries. Instead of bundling those libraries with each application, a module containing these libraries can be created and installed by an administrator.
You can create custom modules in the following ways:
5.3.1. Creating a custom module manually
You can create a module from Java Archive (JAR) or other resource files to make them available to applications in JBoss EAP.
Prerequisites
- You have the JAR or resource files required by the module.
Procedure
Create the appropriate directory structure in the
EAP_HOME/modules/directory.Example: create MySQL JDBC driver directory structure
cd EAP_HOME/modules/ mkdir -p com/mysql/main
$ cd EAP_HOME/modules/ $ mkdir -p com/mysql/mainCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the JAR files or other necessary resources to the
main/subdirectory.Example: copy MySQL JDBC driver JAR
cp /path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar EAP_HOME/modules/com/mysql/main/
$ cp /path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar EAP_HOME/modules/com/mysql/main/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe MySQL driver JAR name, mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar, is provided only as an example. For information about the tested MySQL version, see Tested databases.
Create a
module.xmlfile in themain/subdirectory, specifying the appropriate resources and dependencies in the file.Example: MySQL JDBC driver
module.xmlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe MySQL driver JAR name, mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar, is provided only as an example. For information about the tested MySQL version, see Tested databases.
5.3.2. Creating a custom module by using the management CLI
You can create a module from Java Archive (JAR) or other resource files to make them available to applications in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI.
Using the module management CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment. For more information, see:
Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Prerequisites
- You have the JAR or resource files required for by the module.
Procedure
- Start the JBoss EAP server.
Launch the management CLI.
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
module addmanagement CLI command to add the new core module.Syntax
module add --name=<MODULE_NAME> --resources=<PATH_TO_RESOURCE> --dependencies=<DEPENDENCIES>
module add --name=<MODULE_NAME> --resources=<PATH_TO_RESOURCE> --dependencies=<DEPENDENCIES>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example: Create a MySQL Module
module add --name=com.mysql --resources=</path/to>/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.mysql --resources=</path/to>/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe MySQL driver JAR name, mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar, is provided only as an example. For information about the tested MySQL version, see Tested databases.
5.4. Adding a module as a dependency
To access a module’s resources, your application must have the module added as a dependency.
- See the Add an Explicit Module Dependency to a Deployment section of the JBoss EAP Development Guide for adding application-specific dependencies using deployment descriptors.
- See the Global modules in JBoss EAP section for instructions on adding modules as dependencies to all applications.
As an example, the following steps add a JAR file containing several properties files as a module and define a global module, so that an application can then load these properties.
Procedure
Add the JAR file as a core module.
module add --name=myprops --resources=</path/to>/properties.jar
module add --name=myprops --resources=</path/to>/properties.jarCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Define this module as a global module so that it is made available to all deployments.
/subsystem=ee:list-add(name=global-modules,value={name=myprops})/subsystem=ee:list-add(name=global-modules,value={name=myprops})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Verify that your application can retrieve the properties from one of the properties files contained within the Java archive (JAR).
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("my.properties");Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("my.properties");Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.5. Removing custom modules from JBoss EAP
You can remove any unnecessary modules from JBoss EAP in the following ways:
5.5.1. Removing a custom module manually
Before manually removing a module, ensure that it is not required by deployed applications or elsewhere in the server configuration, such as by a datasource.
Procedure
Remove the module’s directory under
EAP_HOME/modules/, which includes itsmodule.xmlfile and associated JAR files or other resources.For example, remove the
EAP_HOME/modules/com/mysql/main/directory to remove a custom MySQL JDBC driver module in themainslot.
5.5.2. Removing a custom module by using the management CLI
You can remove a custom module using the module remove management CLI command.
Removing a custom module by using the management CLI command is provided as Technology Preview only. Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Launch the management CLI.
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
module removemanagement CLI command to remove the custom module.Syntax
module remove --name=MODULE_NAME
module remove --name=MODULE_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Use the
--slotargument if the module to remove is in a slot other thanmain.
Example: remove MySQL module
module remove --name=com.mysql
module remove --name=com.mysqlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Use the
Execute module --help for more details on using this command to add and remove modules.
5.6. Global modules in JBoss EAP
You can define a list of global modules for JBoss EAP to add as dependencies to all JBoss EAP deployments.
You must know the name of the modules that are to be configured as global modules. For the complete listing of the included modules and whether they are supported, see Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 8.0 Included Modules on the Red Hat Customer Portal. See the Dynamic module naming conventions for JBoss EAP section for naming conventions for modules in deployments.
Use the following management CLI command to define the list of global modules:
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=global-modules,value=[{name=<MODULE_NAME_1>},{name=<MODULE_NAME_2>}]
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=global-modules,value=[{name=<MODULE_NAME_1>},{name=<MODULE_NAME_2>}]Use the following management CLI command to add a single module to the list of existing global modules:
/subsystem=ee:list-add(name=global-modules,value={name=<MODULE_NAME>})
/subsystem=ee:list-add(name=global-modules,value={name=<MODULE_NAME>})Global modules can also be added and removed using the management console by navigating to the EE subsystem from the Configuration tab and selecting the Global Modules section.
If you want a global module to be accessible by external dependencies, you must explicitly make it available. The following options are available to make the services in a global module available externally:
-
Add
services="import"to the module in yourjboss-deployment-structure.xml Add
services="true"to the global module definition./subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=global-modules,value=[{name=module1,services=true}]/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=global-modules,value=[{name=module1,services=true}]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Or, when adding multiple modules:
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=global-modules,value=[{name=module1,services=true},{name=module2,services=false}]/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=global-modules,value=[{name=module1,services=true},{name=module2,services=false}]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To add a new module to an existing list:
/subsystem=ee:list-add(name=global-modules,value={name=module1,services=true})/subsystem=ee:list-add(name=global-modules,value={name=module1,services=true})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
When defining the global module using the management console, make sure that the value of the Services property is
On.
5.7. Creating a global directory
A global directory offers a better alternative to the global module approach. For example, if you want to change the name of a library listed in a global module, you must remove the global module, change the library’s name, and then add the library to a new global module. If you change the name of a library that is listed in the global directory, you only need to reload the server to make the library name change available for all deployments.
Using a global directory, you can do the following:
- Share multiple libraries across deployed applications.
- Maintain libraries by moving common frameworks, usually added to application libraries, to a common location.
When you create a global directory, the EE subsystem configures a global directory and then scans the directory to create a JBoss Modules module dependency. The module dependency includes the global directory libraries and JAR files. This module dependency also contains the following resource loaders:
- The path resource loader provides files as a resource to an application.
- The resource loader provides classes, contained in a JAR file, to an application.
The EE subsystem adds a module dependency as a system dependency on each deployed application.
Prerequisites
Create a standard directory on your operating system. This standard directory must contain all the JAR files and resources you need deployed to applications. This creates a directory tree.
Example of a common directory showing a list of common libraries that were copied to applications:
/my-common-libs/log4j2.xml /my-common-libs/libs/log4j-api-2.14.1.jar /my-common-libs/libs/log4j-core-2.14.1.jar
/my-common-libs/log4j2.xml /my-common-libs/libs/log4j-api-2.14.1.jar /my-common-libs/libs/log4j-core-2.14.1.jarCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteSince the server deploys an application and loads the global directory, you cannot configure the global directory to override the server’s library versions. A global directory cannot replace libraries shipped with the server.
Procedure
Depending on your server setup, create a global directory. You can use the optional
relative-toattribute to set the global directory with a relative path.Example of creating a global directory on a standalone server:
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] /subsystem=ee/global-directory=my-common-libs:add(path=my-common-libs, relative-to=jboss.home.dir)
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] /subsystem=ee/global-directory=my-common-libs:add(path=my-common-libs, relative-to=jboss.home.dir)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example of creating a global directory on a server in a managed domain:
[domain@localhost:9990 /] /profile=default/subsystem=ee/global-directory=my-common-libs:add(path=my-common-libs, relative-to=jboss.server.data.dir)
[domain@localhost:9990 /] /profile=default/subsystem=ee/global-directory=my-common-libs:add(path=my-common-libs, relative-to=jboss.server.data.dir)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For a server in a managed domain, you can add the global directory under a JBoss EAP profile, which is defined in
domain.xml, by using therelative-pathattribute. You can specify either a system path or a custom system path to thisrelative-toattribute.NoteWhen running a server in managed domain, you must ensure the contents of the global directory are consistent across all server instances. For example, each host must contain a local file system directory that includes the global directory contents.
Reload your server instance to activate the global directory.
You must reload the server, so the server can scan the contents of the directory tree alphabetically, including each subdirectory level, starting from the root directory. The server adds files from each directory level to the JBoss Modules module dependency in alphabetic order.
If you change the contents of the global directory, or you change or add JAR files in a global directory, you must reload the server to make the changes available to the deployed applications. For example, if you replace a JAR library in a global directory, reload the server to ensure it re-scans the global directory and updates the deployed applications with the changed JAR library.
5.8. Reading the current values of a global directory configuration
You can read the current values of a global directory configuration by using the read-resource operation.
Procedure
Depending on your server setup, use the
read-resourceoperation to read the current values of your global directory configuration.Example output of reading the current values of a global directory configuration on a standalone server.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example output of reading the current values of a global directory configuration on a server in a managed domain.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.9. Removing a global directory
You can remove a global directory from your server configuration. This action removes only the global directory resource from the server configuration file and does not affect the underlying directory or its files.
Procedure
To remove a global directory from your standalone server, use the following command:
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] /subsystem=ee/global-directory=my-common-libs:remove()
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] /subsystem=ee/global-directory=my-common-libs:remove()Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To remove a global directory on a server in a managed domain, use the following command:
[domain@localhost:9990 /] /profile=default/subsystem=ee/global-directory=my-common-libs:remove()
[domain@localhost:9990 /] /profile=default/subsystem=ee/global-directory=my-common-libs:remove()Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
5.10. Subdeployment isolation configuration in JBoss EAP
Each subdeployment in an Enterprise Archive (EAR) is a dynamic module with its own class loader. Subdeployments always have an implicit dependency on the parent module, which gives them access to classes in EAR/lib. By default, a subdeployment can access the resources of other subdeployments within that EAR.
If you do not want a subdeployment to be allowed to access classes belonging to other subdeployments, then strict subdeployment isolation can be enabled in JBoss EAP. This setting will affect all deployments.
5.10.1. Enabling subdeployment module isolation for all deployments
Subdeployment isolation can be enabled or disabled using the management console or the management CLI from the ee subsystem. By default, subdeployment isolation is set to false, which allows the subdeployments to access resources of other subdeployments within an Enterprise Archive (EAR) deployment.
Procedure
Use the following management CLI command to enable EAR subdeployment isolation:
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=ear-subdeployments-isolated,value=true)
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=ear-subdeployments-isolated,value=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Subdeployments in an EAR will no longer be able to access resources from other subdeployments.
5.11. Defining an external JBoss EAP module directory
The default directory for JBoss EAP modules is EAP_HOME/modules. You can specify a different directory for JBoss EAP modules using the JBOSS_MODULEPATH variable. Follow the below steps to set this variable in the JBoss EAP startup configuration file.
You can also set JBOSS_MODULEPATH as an environment variable instead of setting this in the JBoss EAP startup configuration files.
Procedure
Edit the startup configuration file.
-
When running as a standalone server, edit the
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.conffile, orstandalone.conf.batfor Windows Server. -
When running in a managed domain, edit the
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.conffile, ordomain.conf.batfor Windows Server.
-
When running as a standalone server, edit the
Set the
JBOSS_MODULEPATHvariable, for example:JBOSS_MODULEPATH="/path/to/modules/directory/"
JBOSS_MODULEPATH="/path/to/modules/directory/"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To specify a list of directories use a colon (
:) to delimit the list of directories.NoteFor Windows Server, use the following syntax to set the
JBOSS_MODULEPATHvariable:set "JBOSS_MODULEPATH /path/to/modules/directory/"
set "JBOSS_MODULEPATH /path/to/modules/directory/"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To specify a list of directories use a semicolon (
;) to delimit the list of directories.
5.12. Dynamic module naming conventions for JBoss EAP
JBoss EAP loads all deployments as modules, which are named according to the following conventions.
Deployments of Web Archive (WAR) and Java Archive (JAR) files are named using the following format:
deployment.DEPLOYMENT_NAME
deployment.DEPLOYMENT_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example,
inventory.warandstore.jarwill have the module names ofdeployment.inventory.waranddeployment.store.jarrespectively.Subdeployments within an Enterprise Archive (EAR) are named using the following format:
deployment.EAR_NAME.SUBDEPLOYMENT_NAME
deployment.EAR_NAME.SUBDEPLOYMENT_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the subdeployment of
reports.warwithin the enterprise archiveaccounts.earwill have the module name ofdeployment.accounts.ear.reports.war.
Chapter 6. Managing application deployments
JBoss EAP features a range of application deployment and configuration options to cater to both administrators and developers. For administrators, the management console and the management CLI offer ideal graphical and command-line interfaces to manage application deployment in a production environment. For developers, the range of application deployment testing options include a configurable file system deployment scanner, the HTTP API, an IDE such as Red Hat CodeReady Studio, and Maven.
When deploying applications, you may want to enable validation for deployment descriptors by setting the org.jboss.metadata.parser.validate system property to true. This can be done one of the following ways:
While starting the server.
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Dorg.jboss.metadata.parser.validate=true
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Dorg.jboss.metadata.parser.validate=trueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By adding it to the server configuration with the following management CLI command.
/system-property=org.jboss.metadata.parser.validate:add(value=true)
/system-property=org.jboss.metadata.parser.validate:add(value=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.1. Managing application deployment using the management CLI
Deploying applications using the management CLI gives you the benefit of a single command-line interface with the ability to create and run deployment scripts. You can use this scripting ability to configure specific application deployment and management scenarios. You can manage the deployments for a single server when running as a standalone server, or an entire network of servers when running in a managed domain.
6.1.1. Managing application deployments in a standalone server
6.1.1.1. Deploying an application to a standalone server using the management CLI
You can deploy an application a standalone server using the management CLI by using the deployment deploy-file command.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Deploy an application packaged as a Web Archive (war) from the management CLI.
Syntax
deployment deploy-file <path_to_the_application>/<application_name>.war
deployment deploy-file <path_to_the_application>/<application_name>.warCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment deploy-file /my-applications/test-application.war
deployment deploy-file /my-applications/test-application.warCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A successful deployment does not produce any output to the management CLI, but the server log displays deployment messages such as the following output:
WFLYSRV0027: Starting deployment of "test-application.war" (runtime-name: "test-application.war") WFLYUT0021: Registered web context: /test-application WFLYSRV0010: Deployed "test-application.war" (runtime-name : "test-application.war")
WFLYSRV0027: Starting deployment of "test-application.war" (runtime-name: "test-application.war") WFLYUT0021: Registered web context: /test-application WFLYSRV0010: Deployed "test-application.war" (runtime-name : "test-application.war")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Similarly, you can use the following deployment commands:
-
Use the
deployment deploy-cli-archiveto deploy the content from a.cliarchive file. A CLI deployment archive is aJARfile with the.cliextension. It contains application archives that should be deployed and the CLI script files,deploy.scrandundeploy.scr, containing commands and operations. One script file,deploy.scr, contains the commands and operations that deploy the application archives and set up the environment; the other script file,undeploy.scr, contains the commands to undeploy the application archives and clean up the environment. -
Use the
deployment deploy-urlto deploy the content referenced by a URL.
When specifying the runtime-name attribute by using the --runtime-name option, you must include the .war extension in the name or the web context will not be registered by JBoss EAP.
6.1.1.2. Undeploying an application from a standalone server using the management CLI
You can undeploy an application from a standalone server using the management CLI by using the deployment undeploy command. Undeploying an application deletes the deployment content from the repository. If you want to retain the deployment content when while making the application unavailable, you can disable the deployment instead. For more information, see Disabling an application in a standalone server using the management CLI.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Undeploy an application by using the management CLI.
Syntax
deployment undeploy <deployment>
deployment undeploy <deployment>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment undeploy test-application.war
deployment undeploy test-application.warCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A successful undeployment does not produce any output to the management CLI, but the server log displays undeployment messages like the following output:
WFLYUT0022: Unregistered web context: /test-application WFLYSRV0028: Stopped deployment test-application.war (runtime-name: test-application.war) in 62ms WFLYSRV0009: Undeployed "test-application.war" (runtime-name: "test-application.war")
WFLYUT0022: Unregistered web context: /test-application WFLYSRV0028: Stopped deployment test-application.war (runtime-name: test-application.war) in 62ms WFLYSRV0009: Undeployed "test-application.war" (runtime-name: "test-application.war")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Similarly, you can use the deployment undeploy-cli-archive to undeploy the content from a .cli archive file. You can also undeploy all deployments using a wildcard (*).
deployment undeploy *
deployment undeploy *6.1.1.3. Disabling an application in a standalone server using the management CLI
You can disable a deployed application without removing the deployment content from the repository.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
You can disable a single application or all applications deployed to JBoss EAP by using the
deployment disablecommand from the management CLI.Disable a single deployment:
Syntax
deployment disable <deployment>
deployment disable <deployment>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment disable test-application.war
deployment disable test-application.warCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Disable all the deployments:
deployment disable-all
deployment disable-allCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.1.1.4. Enabling an application in a standalone server using the management CLI
You can enable a disabled application.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
You can enable a single application or all applications deployed to JBoss EAP by using the
deployment enablecommand from the management CLI.Enable a single deployment:
Syntax
deployment enable <deployment>
deployment enable <deployment>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment enable test-application.war
deployment enable test-application.warCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable all the deployments:
deployment enable-all
deployment enable-allCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.1.1.5. Listing deployments in a standalone server using the management CLI
You can list deployments in a standalone server and view deployment information such as the runtime name, status, and so on.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Use the
deployment infocommand to list deployment information.deployment info
deployment infoCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output will show details about each deployment, such as the runtime name, status, and whether it is enabled.
NAME RUNTIME-NAME PERSISTENT ENABLED STATUS helloworld.war helloworld.war true true OK test-application.war test-application.war true true OK
NAME RUNTIME-NAME PERSISTENT ENABLED STATUS helloworld.war helloworld.war true true OK test-application.war test-application.war true true OKCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To display deployment information by name:
deployment info helloworld.war
deployment info helloworld.warCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can also list all the deployments using the deployment list command.
6.1.2. Managing application deployments in a managed domain
6.1.2.1. Deploying an application to a managed domain using the management CLI
You can deploy an application a standalone server using the management CLI by using the deployment deploy-file command and specifying the server groups to which the application should be deployed.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running as a managed domain.
Procedure
You can deploy an application packaged as a Web Archive (war) from the management CLI to specific server groups or all the server groups.
Deploy the application to specific server groups:
Syntax
deployment deploy-file <path_to_the_application>/<application_name>.war --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>
deployment deploy-file <path_to_the_application>/<application_name>.war --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment deploy-file /my-applications/test-application.war --server-groups=main-server-group,other-server-group
deployment deploy-file /my-applications/test-application.war --server-groups=main-server-group,other-server-groupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Deploy the application to all server groups:
Syntax
deployment deploy-file <path_to_the_application>/<application_name>.war --all-server-groups
deployment deploy-file <path_to_the_application>/<application_name>.war --all-server-groupsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment deploy-file /my-applications/test-application.war --all-server-groups
deployment deploy-file /my-applications/test-application.war --all-server-groupsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A successful deployment does not produce any output to the management CLI, but the server log displays deployment messages for each affected server.
[Server:server-one] WFLYSRV0027: Starting deployment of "test-application.war" (runtime-name: "test-application.war") [Server:server-one] WFLYUT0021: Registered web context: /test-application [Server:server-one] WFLYSRV0010: Deployed "test-application.war" (runtime-name : "test-application.war")
[Server:server-one] WFLYSRV0027: Starting deployment of "test-application.war" (runtime-name: "test-application.war") [Server:server-one] WFLYUT0021: Registered web context: /test-application [Server:server-one] WFLYSRV0010: Deployed "test-application.war" (runtime-name : "test-application.war")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Similarly, you can use the following deployment commands:
-
Use the
deployment deploy-cli-archivecommand to deploy the content from a.cliarchive file. A CLI deployment archive is aJARfile with the.cliextension. It contains application archives that should be deployed and the CLI script files,deploy.scrandundeploy.scr, containing commands and operations. One script file,deploy.scr, contains the commands and operations that deploy the application archives and set up the environment; the other script file,undeploy.scr, contains the commands to undeploy the application archives and clean up the environment. -
Use the
deployment deploy-urlcommand to deploy the content referenced by a URL.
When specifying the runtime-name attribute by using the --runtime-name option, you must include the .war extension in the name or the web context will not be registered by JBoss EAP.
6.1.2.2. Undeploying an application from a managed domain using the management CLI
You can undeploy an application from JBoss EAP running as a managed domain using the management CLI by using the deployment undeploy command. Undeploying an application deletes the deployment content from the repository. If you want to retain the deployment content when while making the application unavailable, you can disable the deployment instead. For more information, see Disabling an application in a managed domain using the management CLI.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running as a managed domain.
Procedure
Undeploy an application from all server groups with that deployment from the management CLI.
Syntax
deployment undeploy <application_name>.war --all-relevant-server-groups
deployment undeploy <application_name>.war --all-relevant-server-groupsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment undeploy test-application.war --all-relevant-server-groups
deployment undeploy test-application.war --all-relevant-server-groupsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A successful undeployment does not produce any output to the management CLI, but the server log displays undeployment messages for each affected server like the following output:
[Server:server-one] WFLYUT0022: Unregistered web context: /test-application [Server:server-one] WFLYSRV0028: Stopped deployment test-application.war (runtime-name: test-application.war) in 74ms [Server:server-one] WFLYSRV0009: Undeployed "test-application.war" (runtime-name: "test-application.war")
[Server:server-one] WFLYUT0022: Unregistered web context: /test-application
[Server:server-one] WFLYSRV0028: Stopped deployment test-application.war (runtime-name: test-application.war) in 74ms
[Server:server-one] WFLYSRV0009: Undeployed "test-application.war" (runtime-name: "test-application.war")
Similarly, you can use the deployment undeploy-cli-archive command to undeploy the content from a .cli archive file. You can also undeploy all deployments using a wildcard (*).
deployment undeploy * --all-relevant-server-groups
deployment undeploy * --all-relevant-server-groups6.1.2.3. Disabling an application in a managed domain using the management CLI
You can disable a deployed application from specific server groups and retain its content in the repository for other server groups with that deployment.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running as a managed domain.
Procedure
You can disable a single application or all applications deployed to JBoss EAP by using the
deployment disablecommand from the management CLI.Disabe a single application:
Syntax
deployment disable <application_name>.war --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>
deployment disable <application_name>.war --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment disable test-application.war --server-groups=other-server-group
deployment disable test-application.war --server-groups=other-server-groupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Disable all the deployments:
Syntax
deployment disable-all --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>
deployment disable-all --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment disable-all --server-groups=other-server-group
deployment disable-all --server-groups=other-server-groupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.1.2.4. Enabling an application in a managed domain using the management CLI
Enable a disabled deployed application.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running as a managed domain.
Procedure
You can enable a single application or all applications deployed to JBoss EAP by using the
deployment enablecommand from the management CLI.Enable a single deployment:
Syntax
deployment enable <deployment> --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>
deployment enable <deployment> --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment enable test-application.war --server-groups=other-server-group
deployment enable test-application.war --server-groups=other-server-groupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable all the deployments:
deployment enable-all --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>
deployment enable-all --server-groups=<server-group_1>,..., <server-group_1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
deployment enable-all --server-groups=other-server-group
deployment enable-all --server-groups=other-server-groupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.1.2.5. Listing deployments in a managed domain using the management CLI
You can list deployments and view deployment information such as the runtime name, status, and so on.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running as a managed domain.
Procedure
Use the
deployment infocommand to list deployment information.deployment info helloworld.war
deployment info helloworld.warCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output will list the deployment and its state in each server group.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To display deployment information by server group:
deployment info --server-group=other-server-group
deployment info --server-group=other-server-groupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The output will list the deployments and their state for the specified server group.
NAME RUNTIME-NAME STATE helloworld.war helloworld.war added test-application.war test-application.war enabled
NAME RUNTIME-NAME STATE helloworld.war helloworld.war added test-application.war test-application.war enabledCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can also list all deployments in the domain using the deployment list command.
6.2. Managing application deployment using the management console
Deploying applications using the management console gives you the benefit of a graphical interface that is easy to use. You can see at a glance which applications are deployed to your server or server groups, and you can enable, disable or remove applications from the content repository as required.
6.2.1. Application deployment on a standalone server using the management console
Deployments can be viewed and managed from the Deployments tab of the JBoss EAP management console.
Deploy an Application
Click the Add (+) button. You can choose to deploy an application by uploading a deployment, adding an unmanaged deployment, or creating an empty deployment. Deployments are enabled by default.
Upload a deployment
Upload an application that will be copied to the server’s content repository and managed by JBoss EAP.
Adding an unmanaged deployment
Specify the location of a deployment. This deployment will not be copied to the server’s content repository and will not be managed by JBoss EAP.
Creating an empty deployment
Create an empty, exploded deployment. You can add files to the deployment after it has been created.
Undeploy an Application
Select the deployment and choose the Undeploy option. JBoss EAP removes the deployment from the content repository.
Disable an Application
Select the deployment and choose the Disable option to disable the application. This undeploys the deployment, but does not remove it from the content repository.
Replace an Application
Select the deployment and choose the Replace option. Select the new version of the deployment, which must have the same name as the original, and click Finish. This undeploys and removes the original version of the deployment, and then deploys the new version.
6.2.2. Managing application deployment in a managed domain using the management console
From the Deployments tab of the JBoss EAP management console, deployments can be viewed and managed by:
Content Repository
All managed and unmanaged deployments are listed in the Content Repository section. Deployments can be added and deployed to server groups here.
Server Groups
Deployments that have been deployed to one or more server groups are listed in the Server Groups section. Deployments can be enabled and added directly to a server group here.
6.2.2.1. Adding an application to the content repository using the management console
You can add an application to the content repository using the management console.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have created a user in JBoss EAP.
Procedure
Log in to the management console.
By default the management console is available on
http://localhost:9990.- From Content Repository, click the Add button.
- Choose to add an application by uploading a deployment or adding an unmanaged deployment.
Follow the prompts to deploy the application.
Note that a deployment must be deployed to a server group before it can be enabled.
6.2.2.2. Deploying an application to a server group using the management console
You can deploy an application to a server group using the management console.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have created a user in JBoss EAP.
- You have added the application to the content repository.
Procedure
Log in to the management console.
By default the management console is available on
http://localhost:9990.- From Content Repository, select a deployment and click the Deploy button.
- Select one or more server groups to which this deployment should be deployed.
- Optionally, select the option to enable the deployment on the selected server groups.
6.2.2.3. Undeploying an application from a server group using the management console
You can undeploy an application from a server group using the management console.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have created a user in JBoss EAP.
Procedure
- From Server Groups, select the appropriate server group.
- Select the desired deployment and click the Undeploy button.
Deployments can also be undeployed from multiple server groups at once by selecting the Undeploy button for the deployment in Content Repository.
6.2.2.4. Removing an application from a managed domain using the management console
You can remove an application from a managed domain using the management console.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have created a user in JBoss EAP.
Procedure
- If the deployment is still deployed to any server groups, be sure to undeploy the deployment.
- From Content Repository, select the deployment and click the Remove button.
This removes the deployment from the content repository.
6.2.2.5. Disabling an application in a managed domain using the management console
You can disable an application in a managed domain using the management console. Disabling an application only undeploys it from the server but does not remove it from the content repository.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have created a user in JBoss EAP.
Procedure
- From Server Groups, select the appropriate server group.
- Select the desired deployment and click the Disable button.
This undeploys the deployment, but does not remove it from the content repository.
6.2.2.6. Replacing an application in a managed domain using the management console
You can replace an application deployment with its newer version in a managed domain using the management console.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have created a user in JBoss EAP.
Procedure
- From Content Repository, select the deployment and click the Replace button.
- Select the new version of the deployment, which must have the same name as the original, and click Replace.
This undeploys and removes the original version of the deployment, and then deploys the new version.
6.3. Application deployment using the deployment scanner
The deployment scanner monitors the deployment directory for applications to deploy. By default, the deployment scanner scans the EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/ directory every five seconds for changes. Marker files are used to indicate the status of a deployment and to trigger actions against deployments, such as undeploying or redeploying.
While it is recommended to use the management console or management CLI for application deployment in a production environment, deploying using the deployment scanner is provided for the convenience of developers. This allows users to build and test applications in a manner suited for rapid development cycles. Additionally, the deployment scanner should not be used in conjunction with other deployment methods.
The deployment scanner is only available when running JBoss EAP as a standalone server.
6.3.1. Application deployment management in a standalone server using the deployment scanner
The deployment scanner can be configured to allow or disallow automatic deployment of XML, zipped, and exploded content. If automatic deployment is disabled, you must manually create marker files to trigger deployment actions. For more information about the available marker file types and their purposes, see the Deployment Scanner Marker Files section.
By default, automatic deployment for XML and zipped content is enabled. For details on configuring automatic deployment for each content type, see Configure the Deployment Scanner.
Deploying using the deployment scanner is provided for the convenience of developers and is not recommended for use in a production environment. It should also not be used in conjunction with other deployment methods.
Deploy an Application
Copy the content to the deployment folder.
cp /path/to/test-application.war EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/
$ cp /path/to/test-application.war EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/
If auto-deployment is enabled, this file will be picked up automatically, deployed, and a .deployed marker file will be created. If auto-deployment is not enabled, then you will need to manually add a .dodeploy marker file to trigger deployment.
touch EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/test-application.war.dodeploy
$ touch EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/test-application.war.dodeployUndeploy an Application
Trigger an undeployment by removing the .deployed marker file.
rm EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/test-application.war.deployed
$ rm EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/test-application.war.deployed
If auto-deployment is enabled, you can also remove the test-application.war file, which will trigger the undeployment. Note that this does not apply for exploded deployments.
Redeploy an Application
Create a .dodeploy marker file to initiate redeployment.
touch EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/test-application.war.dodeploy
$ touch EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/test-application.war.dodeploy6.3.2. Deployment scanner configuration
The deployment scanner can be configured using the management console or the management CLI. You can configure the deployment scanner’s behavior, such as the scan interval, deployment folder location, and autodeployment of certain application file types. You can also disable the deployment scanner entirely.
For details on all available deployment scanner attributes, see the Deployment Scanner Attributes section.
Use the below management CLI commands to configure the default deployment scanner.
Disable the Deployment Scanner
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=scan-enabled,value=false)
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=scan-enabled,value=false)
This disables the default deployment scanner.
Change the Scan Interval
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=scan-interval,value=10000)
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=scan-interval,value=10000)
This updates the scan interval time from 5000 milliseconds (five seconds) to 10000 milliseconds (ten seconds).
Change the Deployment Folder
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=path,value=/path/to/deployments)
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=path,value=/path/to/deployments)
This changes the location of the deployment folder from the default location of EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments to /path/to/deployments.
The path value will be treated as an absolute path unless the relative-to attribute is specified, in which case it will be relative to that path.
Enable the Automatic Deployment of Exploded Content
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=auto-deploy-exploded,value=true)
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=auto-deploy-exploded,value=true)This enables the automatic deployment of exploded content, which is disabled by default.
Disable the Automatic Deployment of Zipped Content
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=auto-deploy-zipped,value=false)
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=auto-deploy-zipped,value=false)This disables the automatic deployment of zipped content, which is enabled by default.
Disable the Automatic Deployment of XML Content
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=auto-deploy-xml,value=false)
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=default:write-attribute(name=auto-deploy-xml,value=false)This disables the automatic deployment of XML content, which is enabled by default.
6.3.3. Custom deployment scanner
A new deployment scanner can be added using the management CLI or by navigating to the Deployment Scanners subsystem from the Configuration tab in the management console. This will define a new directory to scan for deployments. The default deployment scanner monitors EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments. See Deployment scanner configuration for details on configuring an existing deployment scanner.
The following management CLI command adds a new deployment scanner that will check EAP_HOME/standalone/new_deployment_dir every five seconds for deployments.
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=new-scanner:add(path=new_deployment_dir,relative-to=jboss.server.base.dir,scan-interval=5000)
/subsystem=deployment-scanner/scanner=new-scanner:add(path=new_deployment_dir,relative-to=jboss.server.base.dir,scan-interval=5000)The specified directory must already exist or this command will fail with an error.
A new deployment scanner has been defined and the specified directory will be monitored for deployments.
6.4. Managing application deployment using Maven
Deploying applications using Apache Maven allows you to easily incorporate deployment to JBoss EAP into your existing development workflow.
You can use Maven to deploy applications to JBoss EAP using the WildFly Maven Plugin, which provides simple operations to deploy and undeploy applications to the application server.
6.4.1. Managing application deployment on a standalone server using Maven
You can deploy and undeploy applications to JBoss EAP running as a standalone server by using the WildFly Maven Plugin.
6.4.1.1. Deploying an application to a standalone server using Maven
The following instructions show how to undeploy the JBoss EAP helloworld quickstart to a standalone server using Maven.
See Using the Quickstart Examples in the JBoss EAP Getting Started Guide for more information on the JBoss EAP quickstarts.
Procedure
Initialize the WildFly Maven Plugin in your Maven
pom.xmlfile. This should already be configured in the JBoss EAP quickstartpom.xmlfiles.<plugin> <groupId>org.wildfly.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>wildfly-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${version.wildfly.maven.plugin}</version> </plugin><plugin> <groupId>org.wildfly.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>wildfly-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${version.wildfly.maven.plugin}</version> </plugin>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the
helloworldquickstart directory, execute the following Maven command.mvn clean install wildfly:deploy
$ mvn clean install wildfly:deployCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After issuing the Maven command to deploy, the terminal window shows the following output indicating a successful deployment.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
The deployment can also be confirmed by viewing the server log of the active server instance.
WFLYSRV0027: Starting deployment of "helloworld.war" (runtime-name: "helloworld.war") WFLYUT0021: Registered web context: /helloworld WFLYSRV0010: Deployed "helloworld.war" (runtime-name : "helloworld.war")
WFLYSRV0027: Starting deployment of "helloworld.war" (runtime-name: "helloworld.war") WFLYUT0021: Registered web context: /helloworld WFLYSRV0010: Deployed "helloworld.war" (runtime-name : "helloworld.war")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.4.1.2. Undeploying an application from a standalone server using Maven
The following instructions show how to undeploy the JBoss EAP helloworld quickstart to a standalone server using Maven.
Prerequisites
-
You have initialized the WildFly Maven Plugin in your Maven
pom.xmlfile.
Procedure
From the
helloworldquickstart directory, execute the following Maven command.mvn wildfly:undeploy
$ mvn wildfly:undeployCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After issuing the Maven command to undeploy, the terminal window shows the following output indicating a successful undeployment.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
The undeployment can also be confirmed by viewing the server log of the active server instance.
WFLYUT0022: Unregistered web context: /helloworld WFLYSRV0028: Stopped deployment helloworld.war (runtime-name: helloworld.war) in 27ms WFLYSRV0009: Undeployed "helloworld.war" (runtime-name: "helloworld.war")
WFLYUT0022: Unregistered web context: /helloworld WFLYSRV0028: Stopped deployment helloworld.war (runtime-name: helloworld.war) in 27ms WFLYSRV0009: Undeployed "helloworld.war" (runtime-name: "helloworld.war")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.4.2. Managing application deployment on a managed domain using Maven
You can deploy and undeploy applications to JBoss EAP running as a managed domain by using the WildFly Maven Plugin.
6.4.2.1. Deploying an application to a managed domain using Maven
The following instructions show how to deploy the JBoss EAP helloworld quickstart in a managed domain using Maven.
See Using the Quickstart Examples in the JBoss EAP Getting Started Guide for more information on the JBoss EAP quickstarts.
Procedure
Specify the server groups to which the application should be deployed in the Maven
pom.xmlfile. The following configuration in thepom.xmlinitializes the WildFly Maven Plugin and specifiesmain-server-groupas the server group to which the application should be deployed.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow From the
helloworldquickstart directory, execute the following Maven command.mvn clean install wildfly:deploy
$ mvn clean install wildfly:deployCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After issuing the Maven command to deploy, the terminal window shows the following output indicating a successful deployment.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Verification
The deployment can also be confirmed by viewing the server log of the active server instance.
WFLYSRV0027: Starting deployment of "helloworld.war" (runtime-name: "helloworld.war") WFLYUT0021: Registered web context: /helloworld WFLYSRV0010: Deployed "helloworld.war" (runtime-name : "helloworld.war")
WFLYSRV0027: Starting deployment of "helloworld.war" (runtime-name: "helloworld.war") WFLYUT0021: Registered web context: /helloworld WFLYSRV0010: Deployed "helloworld.war" (runtime-name : "helloworld.war")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.4.2.2. Undeploying an application from a managed domain using Maven
The following instructions show how to deploy the JBoss EAP helloworld quickstart in a managed domain using Maven.
Prerequisites
- You have initialized the WildFly Maven Plugin.
Procedure
From the
helloworldquickstart directory, execute the following Maven command.mvn wildfly:undeploy
$ mvn wildfly:undeployCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After issuing the Maven command to undeploy, the terminal window shows the following output indicating a successful undeployment.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
- The undeployment can also be confirmed by viewing the server log of the active server instance.
WFLYUT0022: Unregistered web context: /helloworld WFLYSRV0028: Stopped deployment helloworld.war (runtime-name: helloworld.war) in 106ms WFLYSRV0009: Undeployed "helloworld.war" (runtime-name: "helloworld.war")
WFLYUT0022: Unregistered web context: /helloworld
WFLYSRV0028: Stopped deployment helloworld.war (runtime-name: helloworld.war) in 106ms
WFLYSRV0009: Undeployed "helloworld.war" (runtime-name: "helloworld.war")6.5. Managing application deployment using the HTTP API
Applications can be deployed to JBoss EAP using the HTTP API with the curl command. For more information on using the HTTP API, see the HTTP API section.
6.5.1. Application deployment management on a standalone server using the HTTP API
By default, the HTTP API is accessible at http://HOST:PORT/management, for example, http://localhost:9990/management.
Deploy an Application
curl --digest -L -D - http://HOST:PORT/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u USER:PASSWORD -d '{"operation" : "composite", "address" : [], "steps" : [{"operation" : "add", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}, "content" : [{"url" : "file:/path/to/test-application.war"}]},{"operation" : "deploy", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}}],"json.pretty":1}'
$ curl --digest -L -D - http://HOST:PORT/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u USER:PASSWORD -d '{"operation" : "composite", "address" : [], "steps" : [{"operation" : "add", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}, "content" : [{"url" : "file:/path/to/test-application.war"}]},{"operation" : "deploy", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}}],"json.pretty":1}'Undeploy an Application
curl --digest -L -D - http://HOST:PORT/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u USER:PASSWORD -d '{"operation" : "composite", "address" : [], "steps" : [{"operation" : "undeploy", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}},{"operation" : "remove", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}}],"json.pretty":1}'
$ curl --digest -L -D - http://HOST:PORT/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u USER:PASSWORD -d '{"operation" : "composite", "address" : [], "steps" : [{"operation" : "undeploy", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}},{"operation" : "remove", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}}],"json.pretty":1}'See this Red Hat Knowledgebase article to learn more about programmatically generating the JSON requests.
6.5.2. Application deployment management on a managed domain using the HTTP API
You can deploy and undeploy applications on a managed domain using the HTTP API.
6.5.2.1. Deploying an application in a managed domain using the HTTP API
By default, the HTTP API is accessible at http://HOST:PORT/management, for example, http://localhost:9990/management.
Procedure
Add the deployment to the content repository.
curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "add", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}, "content" : [{"url" : "file:</path/to>/test-application.war"}],"json.pretty":1}'$ curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "add", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}, "content" : [{"url" : "file:</path/to>/test-application.war"}],"json.pretty":1}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the deployment to the desired server group.
curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "add", "address" : {"server-group" : "main-server-group","deployment":"test-application.war"},"json.pretty":1}'$ curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "add", "address" : {"server-group" : "main-server-group","deployment":"test-application.war"},"json.pretty":1}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Deploy the application to the server group.
curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "deploy", "address" : {"server-group" : "main-server-group","deployment":"test-application.war"},"json.pretty":1}'$ curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "deploy", "address" : {"server-group" : "main-server-group","deployment":"test-application.war"},"json.pretty":1}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.5.2.2. Undeploying an application in a managed domain using the HTTP API
By default, the HTTP API is accessible at http://HOST:PORT/management, for example, http://localhost:9990/management.
Procedure
Remove the deployment from all server groups to which it is assigned.
curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "remove", "address" : {"server-group" : "main-server-group","deployment":"test-application.war"},"json.pretty":1}'$ curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "remove", "address" : {"server-group" : "main-server-group","deployment":"test-application.war"},"json.pretty":1}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Remove the deployment from the content repository.
curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "remove", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}, "json.pretty":1}'$ curl --digest -L -D - http://<HOST>:<PORT>/management --header "Content-Type: application/json" -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -d '{"operation" : "remove", "address" : {"deployment" : "test-application.war"}, "json.pretty":1}'Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.6. Customizing deployment behavior
6.6.1. Custom directory for deployment content
You can define a custom location for JBoss EAP to store deployed content.
Define a Custom Directory for a Standalone Server
By default, deployed content for a standalone server is stored in the EAP_HOME/standalone/data/content directory. This location can be changed by passing in the -Djboss.server.deploy.dir argument when starting the server.
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.server.deploy.dir=/path/to/new_deployed_content
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Djboss.server.deploy.dir=/path/to/new_deployed_contentThe chosen location should be unique among JBoss EAP instances.
The jboss.server.deploy.dir property specifies the directory to be used for storing content that has been deployed using the management console or management CLI. To define a custom deployment directory to be monitored by the deployment scanner, see Deployment scanner configuration.
Define a Custom Directory for a Managed Domain
By default, deployed content for a managed domain is stored in the EAP_HOME/domain/data/content directory. This location can be changed by passing in the -Djboss.domain.deployment.dir argument when starting the domain.
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh -Djboss.domain.deployment.dir=/path/to/new_deployed_content
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh -Djboss.domain.deployment.dir=/path/to/new_deployed_contentThe chosen location should be unique among JBoss EAP instances.
6.6.2. Control the order of deployments
JBoss EAP offers fine-grained control over the order of deployments when the server is started. Strict order of the deployment of applications present in multiple EAR files can be specified along with persistence of the order after a restart.
You can use the jboss-all.xml deployment descriptor to declare dependencies between top-level deployments.
For example, if you have an app.ear that depends on framework.ear being deployed first, then you can create an app.ear/META-INF/jboss-all.xml file as shown below.
<jboss xmlns="urn:jboss:1.0">
<jboss-deployment-dependencies xmlns="urn:jboss:deployment-dependencies:1.0">
<dependency name="framework.ear" />
</jboss-deployment-dependencies>
</jboss>
<jboss xmlns="urn:jboss:1.0">
<jboss-deployment-dependencies xmlns="urn:jboss:deployment-dependencies:1.0">
<dependency name="framework.ear" />
</jboss-deployment-dependencies>
</jboss>
You can use the deployment’s runtime name as the dependency name in the jboss-all.xml file.
This ensures that framework.ear is deployed before app.ear.
If you create a jboss-all.xml file in app.ear and you do not deploy framework.ear, the server attempts to deploy app.ear and fails.
6.6.3. Overriding deployment content
6.6.3.1. About deployment overlay
A deployment overlay can be used to overlay content into an existing deployment without physically modifying the contents of the deployment archive. It allows you to override deployment descriptors, library JAR files, classes, Jakarta Server Pages pages, and other files at runtime without rebuilding the archive.
This can be useful if you need to adapt a deployment for different environments that need different configurations or settings. For example, when moving a deployment through the application lifecycle from development, to testing, to stage, and finally into production, you might want to swap deployment descriptors, modify static web resources to change the branding of the application, or even replace JAR libraries with different versions depending on the target environment. It is also a useful feature for installations that need to change a configuration but can not modify or crack an archive due to policy or security restrictions.
When defining a deployment overlay, you specify the file on a file system that will replace the file in the deployment archive. You must also specify which deployments should be affected by the deployment overlay. Any affected deployments must be redeployed in order for the changes to take effect.
Parameters
You can use any of the following parameters to configure your deployment overlay:
-
name: The name of the deployment overlay. -
content: A comma-separated list that maps the file on the file system to the file in the archive that it replaces. The format for each entry isARCHIVE_PATH=FILESYSTEM_PATH. -
deployments: Comma-separated list of deployments to which this overlay is linked. -
redeploy-affected: Redeploys all affected deployments.
For full usage details, execute deployment-overlay --help.
6.6.3.2. Defining a deployment overlay
You can define a deployment overlay to overlay content into an existing deployment without physically modifying the contents of the deployment archive.
Procedure
Use the
deployment-overlay addmanagement CLI command to add a deployment overlay:deployment-overlay add --name=new-deployment-overlay --content=WEB-INF/web.xml=/path/to/other/web.xml --deployments=test-application.war --redeploy-affected
deployment-overlay add --name=new-deployment-overlay --content=WEB-INF/web.xml=/path/to/other/web.xml --deployments=test-application.war --redeploy-affectedCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIn a managed domain, specify the applicable server groups by using
--server-groupsor specify all server groups with--all-server-groups.- After you created a deployment overlay, you can add content to an existing overlay, link the overlay to a deployment, or remove the overlay.
Optional: You can specify an overlay configuration to link to an external directory that contains static web resources, such as HTML, images, or videos, using the
<overlay>element.The
<overlay>element specifies static files that overlay the static files of a web application, similar to the procedure of JAR overlays. This element is located in the application filejboss-web.xml. With this element configuration, you do not need to repackage the application.The following example shows system property substitution in the
<overlay>element, where{example.path.to.overlay}defines the/PATH/TO/STATIC/WEB/CONTENTlocation.Example:
<overlay>element in ajboss-web.xmlfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can specify a system property in the
<overlay>element ifjboss-descriptor-property-replacementis set totrue, which is the default value for the descriptor property.To configure
jboss-descriptor-property-replacement, use the following management CLI command:/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=jboss-descriptor-property-replacement,value=true)
/subsystem=ee:write-attribute(name=jboss-descriptor-property-replacement,value=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command adds the following XML content to the
eesubsystem in the JBoss EAP configuration:<subsystem xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:ee:4.0"> <jboss-descriptor-property-replacement>true</jboss-descriptor-property-replacement> </subsystem><subsystem xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:ee:4.0"> <jboss-descriptor-property-replacement>true</jboss-descriptor-property-replacement> </subsystem>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe
<overlay>element does not override deployment files that already exist in your EAP project. If multiple<overlay>elements include the same file, the precedence order is determined based on the sequence of the overlay elements in the applicationjboss-web.xmlfile.
6.6.4. Using rollout plans
In a managed domain, operations targeted at domain or host level resources can potentially impact multiple servers. Such operations can include a roll out plan detailing the sequence in which the operation would be applied to the servers, as well as the policies for detailing whether the operation could be reverted if it fails to execute successfully on some servers. If no rollout plan is specified, the default rollout plan is used.
6.6.4.1. Example rollout plan
Below is an example rollout plan involving five server groups. Operations can be applied to server groups serially, in-series, or concurrently, concurrent-groups. For more information, see Rollout plan syntax.
Looking at the example above, applying the operation to the servers in the domain is done in three phases. If the policy for any server group triggers a rollback of the operation across the server group, all other server groups will be rolled back as well.
- Server groups group-A and group-B will have the operation applied concurrently. The operation will be applied to the servers in group-A in series, while all servers in group-B will handle the operation concurrently. If more than 20% of the servers in group-A fail to apply the operation, it will be rolled back across that group. If any servers in group-B fail to apply the operation it will be rolled back across that group.
- Once all servers in group-A and group-B are complete, the operation will be applied to the servers in group-C. Those servers will handle the operation concurrently. If more than one server in group-C fails to apply the operation it will be rolled back across that group.
- Once all servers in group-C are complete, server groups group-D and group-E will have the operation applied concurrently. The operation will be applied to the servers in group-D in series, while all servers in group-E will handle the operation concurrently. If more than 20% of the servers in group-D fail to apply the operation, it will be rolled back across that group. If any servers in group-E fail to apply the operation it will be rolled back across that group.
6.6.4.2. Rollout plan syntax
You can specify a rollout plan in either of the following ways.
-
By defining the rollout plan in the
deploycommand operation headers. See Deploying an application using a stored rollout plan for details. -
By storing the rollout plan using the
rollout-plancommand and then referencing the plan name in thedeploycommand operation headers. See Deploying an application using a stored rollout plan for details.
Although each method has a different initial command, both methods use the rollout operation header to define the rollout plan. This uses the following syntax.
rollout (id=PLAN_NAME | SERVER_GROUP_LIST) [rollback-across-groups]
rollout (id=PLAN_NAME | SERVER_GROUP_LIST) [rollback-across-groups]-
PLAN_NAMEis the name for the rollout plan that was stored using therollout-plancommand. SERVER_GROUP_LISTis the list of server groups. Use a comma (,) to separate multiple server groups to indicate that operations should be performed on each server group sequentially. Use a caret (^) separator to indicate that operations should be performed on each server group concurrently.For each server group, set any of the following policies in parentheses. Use a comma to separate multiple policies.
-
rolling-to-servers: A boolean that, if set totrue, applies the operation to each server in the group in series. If the value isfalseor not specified, the operation will be applied to the servers in the group concurrently. -
max-failed-servers: An integer which takes the maximum number of servers in the group that can fail to apply the operation before it should be reverted on all servers in the group. The default value if not specified is0, meaning that a failure on any server will trigger rollback across the group. max-failure-percentage: An integer between0and100that represents the maximum percentage of the total number of servers in the group that can fail to apply the operation before it should be reverted on all servers in the group. The default value if not specified is0, meaning that a failure on any server will trigger rollback across the group.NoteIf both
max-failed-serversandmax-failure-percentageare set to non-zero values,max-failure-percentagetakes precedence.
-
-
rollback-across-groups: A boolean that indicates whether the need to rollback the operation on all the servers in one server group triggers a rollback across all the server groups. This defaults tofalse.
6.6.4.3. Deploy an application using a rollout plan
You can provide the full details of a rollout plan directly to the deploy command by passing the rollout settings into the headers argument. See the Rollout Plan Syntax for more information on the format.
The following management CLI command deploys an application to the main-server-group server group using a deployment plan that specifies rolling-to-servers=true for serial deployment.
deploy /path/to/test-application.war --server-groups=main-server-group --headers={rollout main-server-group(rolling-to-servers=true)}
deploy /path/to/test-application.war --server-groups=main-server-group --headers={rollout main-server-group(rolling-to-servers=true)}6.6.4.4. Deploying an application using a stored rollout plan
Since rollout plans can be complex, you have the option to store the details of a rollout plan. This allows you to reference the rollout plan name when you want to use it instead of requiring the full details of the rollout plan each time.
Procedure
Use the
rollout-planmanagement CLI command to store a rollout plan. See the Rollout plan syntax for more information on the format.rollout-plan add --name=my-rollout-plan --content={rollout main-server-group(rolling-to-servers=false,max-failed-servers=1),other-server-group(rolling-to-servers=true,max-failure-percentage=20) rollback-across-groups=true}rollout-plan add --name=my-rollout-plan --content={rollout main-server-group(rolling-to-servers=false,max-failed-servers=1),other-server-group(rolling-to-servers=true,max-failure-percentage=20) rollback-across-groups=true}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This creates the following deployment plan.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the stored rollout plan name when deploying the application.
The following management CLI command deploys an application to all server groups using the
my-rollout-planstored rollout plan.deploy /path/to/test-application.war --all-server-groups --headers={rollout id=my-rollout-plan}deploy /path/to/test-application.war --all-server-groups --headers={rollout id=my-rollout-plan}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
6.6.4.5. Stored rollout plan removal
You can remove a stored rollout plan using the rollout-plan management CLI command by specifying the name of the rollout plan to remove.
rollout-plan remove --name=my-rollout-plan
rollout-plan remove --name=my-rollout-plan6.6.4.6. Default rollout plan
All operations that impact multiple servers will be executed with a rollout plan. If no rollout plan is specified in the operation request, a default rollout plan will be generated. The plan will have the following characteristics.
- There will only be a single high-level phase. All server groups affected by the operation will have the operation applied concurrently.
- Within each server group, the operation will be applied to all servers concurrently.
- Failure on any server in a server group will cause rollback across the group.
- Failure of any server group will result in rollback of all other server groups.
6.7. Manage exploded deployments
You can manage exploded deployments using the management interfaces. This allows you to change the contents of an exploded application without deploying a new version of the application.
Updates to static files in a deployment, such as JavaScript and CSS files, take effect immediately. Changes to other files, such as Java classes, might require an application redeployment for the changes to take effect.
You can either start with an empty deployment or explode an existing archive deployment and then add or remove content.
See Viewing Deployment Content to browse the files in a deployment or read the contents of the files.
Create an Empty Exploded Deployment
You can create an empty exploded deployment to which you can later add content as necessary. Use the following management CLI command to create an empty exploded deployment.
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME.war:add(content=[{empty=true}])
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME.war:add(content=[{empty=true}])
The empty=true option is required to confirm that you intended to create an empty deployment.
Explode an Existing Archive Deployment
You can explode an existing archive deployment to be able to update its contents. Note that a deployment must be disabled before it can be exploded. Use the following management CLI command to explode a deployment.
/deployment=ARCHIVE_DEPLOYMENT_NAME.ear:explode
/deployment=ARCHIVE_DEPLOYMENT_NAME.ear:explodeYou can now add or remove content from this deployment.
You can also explode an existing archive deployment from the management console. From the Deployments tab, select the deployment and select the Explode drop down option.
Add Content to an Exploded Deployment
To add content to a deployment, use the add-content management CLI operation. Provide the path to the location in the deployment where the content should be added, and provide the content to be uploaded. The content to upload can be provided as a local file stream, URL, hash of content that already exists in the JBoss EAP content repository, or a byte array of the content. The following management CLI command uses the input-stream-index option to upload the contents of a local file to the deployment.
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME.war:add-content(content=[{target-path=/path/to/FILE_IN_DEPLOYMENT, input-stream-index=/path/to/LOCAL_FILE_TO_UPLOAD}]
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME.war:add-content(content=[{target-path=/path/to/FILE_IN_DEPLOYMENT, input-stream-index=/path/to/LOCAL_FILE_TO_UPLOAD}]
When adding content to a deployment using the add-content operation, content in the deployment is overwritten by default. You can change this behavior by setting the overwrite option to false.
Remove Content from an Exploded Deployment
To remove content from a deployment, use the remove-content management CLI operation and provide the path of the content in the deployment to remove.
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME.war:remove-content(paths=[/path/to/FILE_1, /path/to/FILE_2])
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME.war:remove-content(paths=[/path/to/FILE_1, /path/to/FILE_2])6.8. Viewing deployment content
You can browse information about files in a managed deployment and read the contents of the files using the JBoss EAP management interfaces.
6.8.1. Browse files in a deployment
Use the browse-content operation to view the files and directories in a managed deployment. Provide no arguments to return the entire deployment structure or use the path argument to provide the path to a specific directory.
You can also browse contents of a deployment from the management console by navigating to the Deployments tab, selecting the deployment, and selecting View from the drop down.
/deployment=helloworld.war:browse-content(path=META-INF/)
/deployment=helloworld.war:browse-content(path=META-INF/)
This displays the files and directories in the META-INF/ directory of the helloworld.war deployment.
You can also specify the following arguments to the browse-content operation.
- archive
- Whether to only return archive files.
- depth
- Specify the depth of files to return.
6.8.2. Read deployment content
You can read the contents of a file in a managed deployment using the read-content operation. Provide no arguments to return the entire deployment or use the path argument to provide the path to a specific file. For example:
/deployment=helloworld.war:read-content(path=META-INF/MANIFEST.MF)
/deployment=helloworld.war:read-content(path=META-INF/MANIFEST.MF)This returns a file stream, which can be displayed in the management CLI or saved to the file system.
6.8.2.1. Display the Contents of a File
Use the attachment display command to read the contents of the MANIFEST.MF file.
attachment display --operation=/deployment=helloworld.war:read-content(path=META-INF/MANIFEST.MF)
attachment display --operation=/deployment=helloworld.war:read-content(path=META-INF/MANIFEST.MF)
This displays the contents of the MANIFEST.MF file from the helloworld.war deployment to the management CLI.
6.8.2.2. Save the Contents of a File
Use the attachment save command to save the contents of the MANIFEST.MF file to the file system.
attachment save --operation=/deployment=helloworld.war:read-content(path=META-INF/MANIFEST.MF) --file=/path/to/MANIFEST.MF
attachment save --operation=/deployment=helloworld.war:read-content(path=META-INF/MANIFEST.MF) --file=/path/to/MANIFEST.MF
This saves the MANIFEST.MF file from the helloworld.war deployment to the file system at path/to/MANIFEST.MF. If you do not specify a file path using the --file argument, the file will be named using its unique attachment ID and saved in the working directory of the management CLI, which by default is EAP_HOME/bin/.
Chapter 7. Configuring JBoss EAP managed domains
The managed domain operating mode allows for the management of multiple JBoss EAP instances from a single control point.
Centrally-managed JBoss EAP server collections are known as members of a domain. All JBoss EAP instances in a domain share a common management policy.
A domain consists of one domain controller, one or more host controllers, and zero or more server groups per host.
- Domain controller
- A domain controller is the central point from which the domain is controlled. It ensures that each server is configured according to the management policy of the domain. The domain controller is also a host controller.
- Host controller
- A host controller is a physical or virtual host that interacts with the domain controller to control the lifecycle of the application server instances running on its host and to assist the domain controller to manage them. Each host can contain multiple server groups.
- Server group
- A server group is a set of server instances that have JBoss EAP installed on them and are managed and configured as one. The domain controller manages the configuration of and applications deployed on server groups. Consequently, each server in a server group shares the same configuration and deployments.
Host controllers are tied to specific physical, or virtual, hosts. You can run multiple host controllers on the same hardware if you use different configurations, ensuring their ports and other resources do not conflict. It is possible for a domain controller, a single host controller, and multiple servers to run within the same JBoss EAP instance, on the same physical system.
7.1. The role of a domain controller in a managed domain
A domain controller is the JBoss EAP server instance that acts as a central management point for a domain. One host controller instance is configured to act as a domain controller.
The primary responsibilities of the domain controller are:
- Maintain the domain’s central management policy.
- Ensure all host controllers are aware of its current contents.
- Assist the host controllers in ensuring that all running JBoss EAP server instances are configured in accordance with this policy.
By default, the central management policy is stored in the EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/domain.xml file. This file is required in the directory of the host controller that is set to run as the domain controller.
The domain.xml file contains profile configurations available for use by the servers in the domain. A profile contains the detailed settings of the various subsystems available in that profile. The domain configuration also includes the definition of socket groups and the server group definitions. For more information about profiles, see About profiles.
7.2. The role of a host controller in a managed domain
The primary responsibility of a host controller is server management. It delegates domain management tasks and is responsible for starting and stopping the individual application server processes that run on its host.
It interacts with the domain controller to help manage the communication between the servers and the domain controller. Multiple host controllers of a domain can interact with only a single domain controller. Hence, all the host controllers and server instances running on a single domain mode have a single domain controller and must belong to the same domain.
By default, each host controller reads its configuration from the EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/host.xml file located in the extracted JBoss EAP installation file on its host’s file system. The host.xml file contains the following configuration information that is specific to the particular host:
- The names of the server instances meant to run from this installation.
-
Configurations specific to the local physical installation. For example, named interface definitions declared in
domain.xmlcan be mapped to an actual machine-specific IP address inhost.xml. And abstract path names in domain.xml can be mapped to actual file system paths inhost.xml. Any of the following configurations:
- How the host controller contacts the domain controller to register itself and access the domain configuration.
- How to find and contact a remote domain controller.
- Whether the host controller is to act as the domain controller
7.3. The role of a process controller in a managed domain
A process controller is a small, lightweight process that is responsible for spawning the host controller process and monitoring its lifecycle. If the host controller crashes, the process controller will restart it. It also starts server processes as directed by the host controller; however, it will not automatically restart server processes that crash.
The process controller logs to the EAP_HOME/domain/log/process-controller.log file. You can set JVM options for the process controller in the EAP_HOME/bin/domain.conf file using the PROCESS_CONTROLLER_JAVA_OPTS variable.
7.4. About server groups in a managed domain
A server group is a collection of server instances that are managed and configured as one. In a managed domain, every application server instance belongs to a server group, even if it is the only member. The server instances in a group share the same profile configuration and deployed content.
A domain controller and a host controller enforce the standard configuration on all server instances of every server group in its domain.
A domain can consist of multiple server groups. Different server groups can be configured with different profiles and deployments. For example, a domain can be configured with different server tiers providing different services.
Different server groups can also have the same profile and deployments. This can, for example, allow for rolling application upgrades where the application is upgraded on one server group and then updated on a second server group, avoiding a complete service outage.
7.5. About servers in a managed domain
A server represents an application server instance. In a managed domain, all server instances are members of a server group. The host controller launches each server instance in its own Java Virtual Machine (JVM) process. For more information, see Server configuration in a managed domain.
7.7. Managed domain configuration
7.7.1. Launching JBoss EAP as a managed domain
Domain and host controllers can be started using the domain.sh or domain.bat script provided with JBoss EAP. For a complete listing of all available startup script arguments and their purposes, use the --help argument or see the Server runtime arguments and switches section.
The domain controller must be started before any secondary servers in any server groups in the domain. Start the domain controller first, then start any other associated host controllers in the domain.
Prerequisites
JBoss EAP is installed.
For more information, see Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform Installation Methods.
Procedure
Start the domain controller with the
host-primary.xmlconfiguration file, which is preconfigured for a dedicated domain controller.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-primary.xml
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-primary.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the host controller with the
host-secondary.xmlconfiguration file, which is preconfigured for a secondary host controller.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Depending on your domain setup, you will need to make additional configurations connect to, and not conflict with, the domain controller. Also see the following example domain setups:
7.7.2. Configuring a domain controller
You must configure one host in the domain as the domain controller.
Configuring multiple domain or host controllers on the same machine is not supported when JBoss EAP is installed using the RPM installation method.
Procedure
Configure a host as the domain controller by adding the
<local/>element in the<domain-controller>declaration. The<domain-controller>element should include no other content.<domain-controller> <local/> </domain-controller>
<domain-controller> <local/> </domain-controller>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expose a management interface that should be accessible to other hosts in the domain. The HTTP interface is the standard management interface.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The sample minimal domain controller configuration file, EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/host-primary.xml, includes these configuration settings.
7.7.3. Configuring a host controller
A host controller must be configured to connect to the domain controller so that the host controller can register itself with the domain.
Configuring multiple domain or host controllers on the same machine is not supported when JBoss EAP is installed using the RPM installation method.
Procedure
Use the
<domain-controller>element of the configuration to configure a connection to the domain controller.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The sample minimal host controller configuration file, EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/host-secondary.xml, includes the configuration settings to connect to a domain controller. The configuration assumes that you provide the jboss.domain.primary.address property when starting the host controller.
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Djboss.domain.primary.address=<ip_address>
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Djboss.domain.primary.address=<ip_address>Depending on your domain setup, you may also need to provide authentication for the host controller to be authenticated by the domain controller. See Setting up a managed domain on two machines for details on generating a management user with a secret value and updating the host controller configuration with that value.
7.7.4. Host name configuration for a managed domain
Every host running in a managed domain must have a unique host name. To ease administration and allow for the use of the same host configuration files on multiple hosts, the server uses the following precedence for determining the host name.
-
If set, the host element name attribute in the
host.xmlconfiguration file. -
The value of the
jboss.host.namesystem property. -
The value that precedes the first period (
.) character in thejboss.qualified.host.namesystem property, or the entire value if there is no final period (.) character. -
The value that precedes the period (
.) character in theHOSTNAMEenvironment variable for POSIX-based operating systems, theCOMPUTERNAMEenvironment variable for Microsoft Windows, or the entire value if there is no final period (.) character.
A host controller’s name is configured in the host element at the top of the relevant host.xml configuration file, for example:
<host xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:default:20.0" name="host1">
<host xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:default:20.0" name="host1">7.7.5. Updating the name of a host in a managed domain
Use the following procedure to update the host name using the management CLI.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running as a managed domain.
Procedure
Launch the management CLI, connecting to the domain controller.
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --controller=<domain_controller_ip_address>
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --controller=<domain_controller_ip_address>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the following command to set a new host name.
/host=<existing_host_name>:write-attribute(name=name,value=<new_host_name>)
/host=<existing_host_name>:write-attribute(name=name,value=<new_host_name>)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This modifies the host name attribute in the
host-secondary.xmlfile as follows:<host name="<new_host_name>" xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:default:20.0">
<host name="<new_host_name>" xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:default:20.0">Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the host controller in order for the changes to take effect.
reload --host=<existing_host_name>
reload --host=<existing_host_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If a host controller does not have a name set in the configuration file, you can also pass in the host name at runtime.
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Djboss.host.name=<host_name>
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Djboss.host.name=<host_name>7.8. Server groups configuration
Server groups can be configured using the management CLI or from the management console Runtime tab.
The following is an example of a server group definition:
Server groups CLI commands
Add a Server Group
/server-group=<server_group_name>:add(profile=<profile_name>,socket-binding-group=<socket_binding_group_name>)
/server-group=<server_group_name>:add(profile=<profile_name>,socket-binding-group=<socket_binding_group_name>)Update a Server Group
/server-group=<server_group_name>:write-attribute(name=<attribute_name>,value=<value>)
/server-group=<server_group_name>:write-attribute(name=<attribute_name>,value=<value>)Remove a Server Group
/server-group=<server_group_name>:remove
/server-group=<server_group_name>:remove7.9. Server configuration in a managed domain
Servers can be configured using the management CLI or from the management console Runtime tab.
The default host.xml configuration file defines three servers:
- 1
- The server instance named
server-oneis associated withmain-server-groupand inherits the subsystem configuration and socket bindings specified by that server group. - 2
- The server instance named
server-twois also associated withmain-server-group, but also defines a socket bindingport-offsetvalue, so as not to conflict with the port values used byserver-one. - 3
- A server instance named
server-threeis associated withother-server-groupand uses that group’s configurations. It also defines aport-offsetvalue and setsauto-starttofalseso that this server does not start when the host controller starts.
Server configuration CLI commands
Add a server
/host=<host_name>/server-config=<server_name>:add(group=<server_group_name>)
/host=<host_name>/server-config=<server_name>:add(group=<server_group_name>)Update a server
/host=<host_name>/server-config=<server_name>:write-attribute(name=<attribute_name>,value=<value>)
/host=<host_name>/server-config=<server_name>:write-attribute(name=<attribute_name>,value=<value>)Remove a server
/host=<host_name>/server-config=<server_name>:remove
/host=<host_name>/server-config=<server_name>:remove7.10. Server operations in a managed domain
You can perform operations on servers, such as starting, stopping, and reloading, from the management console by navigating to the Runtime tab and selecting the appropriate host or server group.
Start servers
You can start a single server on a particular host.
/host=<host_name>/server=<server_name>:start
/host=<host_name>/server=<server_name>:startYou can start all servers in a specified server group.
/server-group=<server_group_name>:start-servers
/server-group=<server_group_name>:start-serversStop servers
You can stop a single server on a particular host.
/host=<host_name>/server=<server_name>:stop
/host=<host_name>/server=<server_name>:stopYou can stop all servers in a specified server group.
/server-group=<server_group_name>:stop-servers
/server-group=<server_group_name>:stop-serversReload servers
You can reload a single server on a particular host.
/host=<host_name>/server=<server_name>:reload
/host=<host_name>/server=<server_name>:reloadYou can reload all servers in a specified server group.
/server-group=<server_group_name>:reload-servers
/server-group=<server_group_name>:reload-serversKill servers
You can kill all server processes in a specified server group.
/server-group=<server_group_name>:kill-servers
/server-group=<server_group_name>:kill-servers7.11. Domain controller discovery and failover configuration
When setting up a managed domain, each host controller must be configured with information needed to contact the domain controller. In JBoss EAP, each host controller can be configured with multiple options for finding the domain controller. Host controllers iterate through the list of options until one succeeds.
A backup host controller can be promoted to domain controller if there is a problem with the primary domain controller. This allows host controllers to automatically fail over to the new domain controller once it has been promoted. For more information, see Promoting a host controller to act as domain controller.
7.11.1. Domain discovery options
The following is an example of how to configure a host controller with multiple options for finding the domain controller.
Example: A host controller with multiple domain controller options
A static discovery option includes the following required attributes:
- name
- The name for this domain controller discovery option.
- host
- The remote domain controller’s host name.
- port
- The remote domain controller’s port.
In the example above, the first discovery option is the one expected to succeed. The second can be used in failover situations.
7.11.2. Host controller with a cached domain configuration
A host controller can be started without a connection to the domain controller by using the --cached-dc option; however, the host controller must have previously cached its domain configuration locally from the domain controller. Starting a host controller with this --cached-dc option will cache the host controller’s domain configuration from the domain controller.
Example
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml --cached-dc
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml --cached-dc
This creates a domain.cached-remote.xml file in the EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/ directory that contains the information necessary for this host controller to temporarily manage its current servers without a domain controller connection.
By default, using the --cached-dc option only caches configuration used by this host controller, which means that it cannot be promoted to domain controller for the entire domain. See Promoting a host controller to act as domain controller for information on caching the entire domain configuration to allow a host controller to act as the domain controller.
If the domain controller is unavailable when starting this host controller with --cached-dc, the host controller will start using the cached configuration saved in the domain.cached-remote.xml file. Note that this file must exist or the host controller will fail to start.
While in this state, the host controller cannot modify the domain configuration, but can launch servers and manage deployments.
Once started with the cached configuration, the host controller will continue to attempt to reconnect to the domain controller. Once the domain controller becomes available, the host controller will automatically reconnect to it and synchronize the domain configuration. Note that some configuration changes may require you to reload the host controller to take effect. A warning will be logged on the host controller if this occurs.
7.11.3. Promoting a host controller to act as domain controller
You can promote a host controller to act as the domain controller if a problem arises with the primary domain controller. The host controller must first cache the domain configuration locally from the domain controller before it can be promoted.
Procedure
Use the
--backupoption for any host controller that you might want to become the domain controller.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml --backup
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml --backupCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This creates a
domain.cached-remote.xmlfile in theEAP_HOME/domain/configuration/directory that contains a copy of the entire domain configuration. This configuration will be used if the host controller is reconfigured to act as the domain controller.NoteThe
ignore-unused-configurationattribute is used to determine how much configuration to cache for a particular host. A value oftruemeans that only the configuration relevant to this host controller is cached, which would not allow it to take over as domain controller. A value offalsemeans that the entire domain configuration is cached.The
--backupargument defaults this attribute tofalseto cache the entire domain. However, if you set this attribute in thehost.xmlfile, that value is used.You can also use the
--cached-dcoption alone to create a copy of the domain configuration, but must setignore-unused-configurationtofalsein thehost.xmlto cache the entire domain. For example:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Promote a host controller to be the domain controller.
- Ensure the original domain controller is stopped.
- Use the management CLI to connect to the host controller that is to become the new domain controller.
Execute the following command to configure the host controller to act as the new domain controller.
/host=backup:write-attribute(name=domain-controller.local, value={})/host=backup:write-attribute(name=domain-controller.local, value={})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Execute the following command to reload the host controller.
reload --host=<host_name>
reload --host=<host_name>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
This host controller will now act as the domain controller.
7.12. Setting up a managed domain on a single machine
You can run multiple host controllers on a single machine by using the jboss.domain.base.dir property.
Configuring more than one JBoss EAP host controller as a system service on a single machine is not supported.
Procedure
Copy the
EAP_HOME/domaindirectory for the domain controller.cp -r EAP_HOME/domain <path_to>/domain1
$ cp -r EAP_HOME/domain <path_to>/domain1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the
EAP_HOME/domaindirectory for a host controller.cp -r EAP_HOME/domain <path_to>/host1
$ cp -r EAP_HOME/domain <path_to>/host1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the domain controller using
<path_to>/domain1.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-primary.xml -Djboss.domain.base.dir=<path_to>/domain1
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-primary.xml -Djboss.domain.base.dir=<path_to>/domain1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Start the host controller using
<path_to>/host1.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Djboss.domain.base.dir=<path_to>/host1 -Djboss.domain.primary.address=<ip_adress> -Djboss.management.http.port=<port>
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Djboss.domain.base.dir=<path_to>/host1 -Djboss.domain.primary.address=<ip_adress> -Djboss.management.http.port=<port>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen starting a host controller, you must specify the address of the domain controller using the
jboss.domain.primary.addressproperty.Additionally, since this host controller is running on the same machine as the domain controller, you must change the management interface so that it does not conflict with the domain controller’s management interface. This command sets the
jboss.management.http.portproperty.
Each instance started in this manner will share the rest of the resources in the base installation directory, for example, EAP_HOME/modules/, but use the domain configuration from the directory specified by jboss.domain.base.dir.
7.13. Setting up a managed domain on two machines
You can create managed domain on two machines, where one machine is a domain controller and the other machine is a host. For more information, see The role of a domain controller in a managed domain.
-
<IP1>= IP address of the domain controller (Machine 1) -
<IP2>= IP address of the host (Machine 2)
You may need to configure your firewall to run this example.
Procedure
On Machine 1
Add a management user so that the host can be authenticated by the domain controller.
Use the
add-user.shscript to add the management user for the host controller,HOST_NAME.Start the domain controller.
Specify the
host-primary.xmlconfiguration file, which is preconfigured for a dedicated domain controller. Also, set thejboss.bind.address.managementproperty to make the domain controller visible to other machines.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-primary.xml -Djboss.bind.address.management=<IP1>
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-primary.xml -Djboss.bind.address.management=<IP1>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
On Machine 2
Update the host configuration as follows:
Add the following configuration to the
elytronsubsystem:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantThis example uses a clear text password "MGMT_USER_PASSWORD". In production environments, either use a reference to a credential store or use an encrypted expression, instead of using a clear text password for better security. For more information, see Secure storage of credentials in JBoss EAP.
Add the authentication context to the domain controller:
<domain-controller> <remote authentication-context="secondary-hc-auth-context"> ... </domain-controller>
<domain-controller> <remote authentication-context="secondary-hc-auth-context"> ... </domain-controller>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Start the host controller.
Specify the
host-secondary.xmlconfiguration file, which is preconfigured for a secondary host controller. Also, set thejboss.domain.primary.addressproperty to connect to the domain controller and thejboss.bind.addressproperty to set the host controller bind address.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Djboss.domain.primary.address=<IP1> -Djboss.bind.address=<IP2>
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Djboss.domain.primary.address=<IP1> -Djboss.bind.address=<IP2>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can now manage the domain from the management CLI by specifying the domain controller address with the --controller parameter when launching.
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --controller=<IP1>
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --controller=<IP1>
Or you can manage the domain from the management console at http://<IP1>:9990.
7.14. Configuring a JBoss EAP 8.0 domain controller to administer JBoss EAP 7.4 instances
A JBoss EAP 8.0 domain controller can manage hosts and servers running JBoss EAP 7.4, if the hosts and servers are running JBoss EAP 7.4 or later.
7.14.1. Adding the JBoss EAP 7.4 configuration to the JBoss EAP 8.0 domain controller
To allow the domain controller to manage your JBoss EAP 7.4 servers, you must provide the JBoss EAP 7.4 configuration details in the JBoss EAP 8.0 domain configuration. You can do this by copying the JBoss EAP 7.4 profiles, socket binding groups, and server groups to the JBoss EAP 8.0 domain.xml configuration file.
You will need to rename resources if there is any conflict between the existing names in the JBoss EAP 7.4 configuration. There are also some additional adjustments to make to ensure the proper behavior.
The following procedure uses the JBoss EAP 7.4 default profile, standard-sockets socket binding group, and main-server-group server group.
Procedure
-
Edit the JBoss EAP 8.0
domain.xmlconfiguration file. It is recommended to back up this file before editing. Copy the applicable JBoss EAP 7.4 profiles to the JBoss EAP 8.0
domain.xmlfile.This procedure assumes that the JBoss EAP 7.4
defaultprofile was copied and renamed toeap74-default.JBoss EAP 7.4
domain.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the necessary extensions used by this profile.
If your JBoss EAP 7.4 profile uses subsystems that are no longer present in JBoss EAP 8.0, you must add the appropriate extensions to the JBoss EAP domain configuration.
JBoss EAP 8.0
domain.xml<extensions> ... <extension module="org.jboss.as.jsr77"/> <extension module="org.jboss.as.security"/> <extensions>
<extensions> ... <extension module="org.jboss.as.jsr77"/> <extension module="org.jboss.as.security"/> <extensions>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the applicable JBoss EAP 7.4 socket binding groups to the JBoss EAP 8.0
domain.xmlfile.This procedure assumes that the JBoss EAP 7.4
standard-socketssocket binding group was copied and renamed toeap74-standard-sockets.JBoss EAP 8.0
domain.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the applicable JBoss EAP 7.4 server groups to the JBoss EAP 8.0
domain.xmlfile.This procedure assumes that the JBoss EAP 7.4
main-server-groupserver group was copied and renamed toeap74-main-server-group. You must also update this server group to use the JBoss EAP 7.4 profile,eap74-default, and the JBoss EAP 7.4 socket binding group,eap74-standard-sockets.JBoss EAP 8.0
domain.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.14.2. Updating the behavior of the JBoss EAP 7.4 version profiles
Additional updates to the profiles used by your JBoss EAP 7.4 instances are necessary depending on the JBoss EAP version and desired behavior. You may require additional changes depending on the subsystems and configuration that your existing JBoss EAP 7.4 instances use. The following procedure assumes that the JBoss EAP 7.4 profile is eap74-default.
Procedure
- Start the JBoss EAP 8.0 domain controller and launch its management CLI to perform the following updates.
Set CDI 1.0 behavior.
This is only necessary if you want CDI 1.0 behavior for your JBoss EAP 7.4 servers, as opposed to behavior of later CDI versions used in JBoss EAP 8.0. If you want CDI 1.0 behavior, make the following updates to the
weldsubsystem.JBoss EAP 8.0 Domain Controller CLI
/profile=eap74-default/subsystem=weld:write-attribute(name=require-bean-descriptor,value=true) /profile=eap74-default/subsystem=weld:write-attribute(name=non-portable-mode,value=true)
/profile=eap74-default/subsystem=weld:write-attribute(name=require-bean-descriptor,value=true) /profile=eap74-default/subsystem=weld:write-attribute(name=non-portable-mode,value=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
7.14.3. Setting the server group for JBoss EAP 7.4 server
If you renamed the server groups, you need to update the JBoss EAP 7.4 host configuration to use the new server groups specified in the JBoss EAP 8.0 configuration. This example uses the eap74-main-server-group server group specified in the JBoss EAP 8.0 domain.xml configuration file.
Procedure
Update the host configuration.
JBoss EAP 7.4 host-secondary.xml
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
A host cannot use features or configuration settings that were introduced in a newer version of JBoss EAP than the one the host is running.
7.14.4. Prevent JBoss EAP 7.4 instances from receiving JBoss EAP 8.0 server updates
The domain controller in a managed domain forwards configuration updates to its host controllers. You must use the host-exclude configuration to specify the resources that should be hidden from particular versions. Choose the appropriate preconfigured host-exclude option for your JBoss EAP 7.4 version: EAP74.
The active-server-groups attribute of the host-exclude configuration specifies the list of server groups that are used by a particular version. These server groups and their associated profiles, socket binding groups, and deployment resources will be available to hosts of this version, but all others will be hidden from these hosts.
This example assumes that the version is JBoss EAP 7.4 and adds the JBoss EAP 7.4 server group eap74-main-server-group as an active server group.
JBoss EAP 8.0 Domain Controller CLI
/host-exclude=EAP74:write-attribute(name=active-server-groups,value=[eap74-main-server-group])
/host-exclude=EAP74:write-attribute(name=active-server-groups,value=[eap74-main-server-group])
If necessary, you can specify additional socket binding groups used by your servers using the active-socket-binding-groups attribute. This is only required for socket binding groups that are not associated with the server groups specified in active-server-groups.
7.15. JBoss EAP profiles management
7.15.1. About profiles
JBoss EAP uses profiles as a way to organize which subsystems are available to a server. A profile consists of a collection of available subsystems along with each subsystem’s specific configuration. A profile with a large number of subsystems results in a server with a large set of capabilities. A profile with a small, focused set of subsystems will have fewer capabilities but a smaller footprint.
JBoss EAP comes with five predefined profiles that should satisfy most use cases:
- default
-
Includes commonly used subsystems, such as
logging,security,datasources,infinispan,webservices,ee,ejb3,transactions, and so on. - ha
-
Includes the subsystems provided in the default profile with the addition of the
jgroupsandmodclustersubsystems for high availability. - full
-
Includes the subsystems provided in the default profile with the addition of the
messaging-activemqandiiop-openjdksubsystems. - full-ha
-
Includes the subsystems provided in the full profile with the addition of the
jgroupsandmodclustersubsystems for high availability. - load-balancer
- Includes the minimum subsystems necessary to use the built-in mod_cluster front-end load balancer to load balance other JBoss EAP instances.
7.15.2. Cloning a profile
JBoss EAP allows you to create a new profile in a managed domain by cloning an existing profile. This will create a copy of the original profile’s configuration and subsystems.
Procedure
Clone a profile by using the
cloneoperation on the desired profile to clone./profile=full-ha:clone(to_profile=<cloned_profile>)
/profile=full-ha:clone(to_profile=<cloned_profile>)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can also clone a profile from the management console by selecting the desired profile to clone and clicking Clone.
7.15.3. Hierarchical profiles in a managed domain
In a managed domain, you can create a hierarchy of profiles. This allows you to create a base profile with common extensions that other profiles can inherit.
The managed domain defines several profiles in domain.xml. If multiple profiles use the same configuration for a particular subsystem, you can configure it in just one place instead of different profiles. The values in parent profiles cannot be overridden.
In addition, each profile must be self-sufficient. If an element or subsystem is referenced, then it must be defined in the profile where it is referenced.
A profile can include other profiles in a hierarchy using the management CLI by using the list-add operation and providing the profile to include.
/profile=new-profile:list-add(name=includes, value=<profile_name>)
/profile=new-profile:list-add(name=includes, value=<profile_name>)Chapter 8. Configuring JVM settings
You can configure Java Virtual Machine (JVM) settings for a standalone JBoss EAP server, or a JBoss EAP server in a managed domain.
For a standalone JBoss EAP server instance, the server startup processes pass JVM settings to the JBoss EAP server at startup. These can be declared from the command line before launching JBoss EAP, or using the System Properties page under Configuration in the management console.
In a managed domain, JVM settings are declared in the host.xml and domain.xml configuration files, and can be configured at host, server group, or server levels.
Configure system properties in JAVA_OPTS if they need to be read by the JVM itself, or JBoss EAP modules (such as the logging manager), during the initial phase of startup of a standalone server, or a managed domain host controller.
8.1. Configuring JVM settings for a standalone server
You can define the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) settings for standalone JBoss EAP server instances at runtime by setting the JAVA_OPTS environment variable before starting the server. Alternatively, you can add the JVM settings to the standalone.conf or standalone.bat configuration file, and also by setting system properties. If system properties are set using multiple ways, the values in the JBoss EAP configuration file standalone*.xml override the other values.
Procedure
Setting the
JAVA_OPTSenvironment variable:Linux
export JAVA_OPTS="-Xmx1024M"
$ export JAVA_OPTS="-Xmx1024M"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Microsoft Windows
set JAVA_OPTS="Xmx1024M"
set JAVA_OPTS="Xmx1024M"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Alternatively, JVM settings can be added to the
standalone.conffile, orstandalone.conf.batfor Windows Server, in theEAP_HOME/binfolder, which contains examples of options to pass to the JVM. Besides setting the
JAVA_OPTSenvironment variable, you can set system properties using one of the following alternative ways:Execute the following command:
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Dmyproperty=value
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh -Dmyproperty=valueCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Edit the JBoss EAP configuration file,
standalone*.xml.
If system properties are set using multiple ways, the values in the JBoss EAP configuration file standalone*.xml override the other values, which may cause JBoss EAP startup issues. For example, if you have defined system settings in the JAVA_OPTS environment variable and in the JBoss EAP configuration file, the values in JBoss EAP configuration override the values in JAVA_OPTS.
8.2. Configuring JVM settings for a managed domain
In a JBoss EAP managed domain, you can define JVM settings at multiple levels. You can define custom JVM settings on a particular host, and then apply those settings to server groups, or to individual server instances.
By default, server groups and individual servers will inherit the JVM settings from their parent, but you can choose to override JVM settings at each level.
The JVM settings in domain.conf, or domain.conf.bat for Windows Server, are applied to the Java process of the JBoss EAP host controller, and not the individual JBoss EAP server instances controlled by that host controller.
8.2.1. Defining JVM settings on a host controller
You can define Java Virtual Machine (JVM) settings on a host controller, and apply those settings to server groups or individual servers. JBoss EAP comes with a default JVM setting, but the following procedure demonstrates creating a new JVM setting named production_jvm with some custom JVM settings and options. These settings are stored within the <jvm> tag in host.xml.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running as a managed domain.
Procedure
Define JVM settings by using the management CLI.
Syntax
/host=<HOST_NAME>/jvm=<SETTING_NAME>:add(heap-size=<HEAP_SIZE>, max-heap-size=<MAX_HEAP_SIZE>, max-permgen-size=<MAX_PERMANENT_GENERATION_SIZED>, stack-size=<STACK_SIZE>, jvm-options=["<JVM_OPTIONS>"])
/host=<HOST_NAME>/jvm=<SETTING_NAME>:add(heap-size=<HEAP_SIZE>, max-heap-size=<MAX_HEAP_SIZE>, max-permgen-size=<MAX_PERMANENT_GENERATION_SIZED>, stack-size=<STACK_SIZE>, jvm-options=["<JVM_OPTIONS>"])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
/host=exampleHost1/jvm=production_jvm:add(heap-size=2048m, max-heap-size=2048m, max-permgen-size=512m, stack-size=1024k, jvm-options=["-XX:-UseParallelGC"])
/host=exampleHost1/jvm=production_jvm:add(heap-size=2048m, max-heap-size=2048m, max-permgen-size=512m, stack-size=1024k, jvm-options=["-XX:-UseParallelGC"])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow See Managed Domain JVM Configuration Attributes for descriptions of all available options.
Define JVM settings by using the management console.
- Navigate to Runtime → Hosts in the management console.
- Choose a host and click View.
- Select the JVMs tab to define the settings.
8.2.2. Applying JVM settings to a server group
When creating a server group, you can specify a JVM configuration that all servers in the group will use. These settings for a server group are stored in domain.xml.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running as a managed domain.
You have defined JVM settings for a host controller.
For more information, see Defining JVM settings on a host controller.
Procedure
Applying JVM settings to a server group by using the management CLI.
Create a server group name
exampleGroupAthat uses theproduction_jvmJVM settings./server-group=exampleGroupA:add(profile=default,socket-binding-group=standard-sockets) /server-group=exampleGroupA/jvm=production_jvm:add
/server-group=exampleGroupA:add(profile=default,socket-binding-group=standard-sockets) /server-group=exampleGroupA/jvm=production_jvm:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also override specific JVM settings at the server group level. For example, to set a different heap size, you can use the following command:
/server-group=exampleGroupA/jvm=production_jvm:write-attribute(name=heap-size,value="1024m")
/server-group=exampleGroupA/jvm=production_jvm:write-attribute(name=heap-size,value="1024m")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow After applying the above command, the server group
groupAwill inherit the JVM settings fromproduction_jvm, except for the heap size which has an overridden value of1024m.Applying JVM settings to a server group by using the management console.
- Navigate to Runtime → Server Groups.
- Choose a server group and click View.
- Select the JVMs tab to apply the settings.
8.2.3. Applying JVM settings to an individual server in a server group
By default, an individual JBoss EAP server instance will inherit the JVM settings of the server group it belongs to. However, you can choose to override the inherited settings with another complete JVM setting definition from the host controller, or choose to override specific JVM settings. These settings for an individual server are stored in host.xml.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running as a managed domain.
You have applied JVM settings to a server group.
For more information, see Applying JVM settings to a server group.
Procedure
Applying JVM settings to an individual server by using the management CLI.
Override the JVM definition in the Applying JVM settings to a server group procedure, and set the JVM settings for
server-oneto thedefaultJVM definition:/host=exampleHost1/server-config=server-one/jvm=default:add
/host=exampleHost1/server-config=server-one/jvm=default:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Also, similar to server groups, you can override specific JVM settings at the server level. For example, to set a different heap size, you can use the following command:
/host=exampleHost1/server-config=server-one/jvm=default:write-attribute(name=heap-size,value="1024m")
/host=exampleHost1/server-config=server-one/jvm=default:write-attribute(name=heap-size,value="1024m")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Applying JVM settings to an individual server by using the management console.
- Navigate to Runtime → Hosts.
- Choose the host, and click View on the server.
- Selecting the JVMs tab to apply settings.
8.3. Viewing the JVM resource status in the management console
You can view the status of JVM resources, such as heap and thread usage, for standalone or managed domain servers from the management console. While statistics are not displayed in real time, you can click Refresh to provide an up-to-date overview of JVM resources.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
View the JVM status for a standalone JBoss EAP server:
- Navigate to the Runtime tab, select the server, and select Status.
View JVM status for a JBoss EAP server in a managed domain:
- Navigate to Runtime → Hosts, select the host and server, and select Status.
The following heap usage information is displayed:
- Max
- The maximum amount of memory that can be used for memory management.
- Used
- The amount of used memory.
- Committed
- The amount of memory that is committed for the Java Virtual Machine to use.
Other information, such as JVM uptime and thread usage, is also available.
For information about optimizing JVM performance, see JVM tuning in the Performance tuning for JBoss EAP guide.
Chapter 9. Mail subsystem
This chapter focuses on the mail subsystem, essential for integrating email functionalities into your JBoss EAP application. This section, provides detailed procedures for configuring the mail server settings, customizing transport protocols to meet your organization’s specific needs, and enhancing security through the use of a credential store for password management.
Prerequisites
- You have installed JBoss EAP 8.0.
9.1. Configuring the mail subsystem
The mail subsystem allows you to configure mail sessions in JBoss EAP, and then inject those sessions into your applications using JNDI. Additionally, it supports the use of Jakarta EE annotations like @MailSessionDefinition and @MailSessionDefinitions to streamline the configuration process.
Prerequisites
- You have JBoss EAP installed and running.
- You have network access to the SMTP server.
Procedure
Configure the SMTP server and the outbound socket binding using the following CLI commands, for example:
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=my-smtp:add(host=localhost, port=25)
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=my-smtp:add(host=localhost, port=25)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow /subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession:add(jndi-name=java:jboss/mail/MySession)
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession:add(jndi-name=java:jboss/mail/MySession)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow /subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=smtp:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-smtp, username=user, password=pass, tls=true)
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=smtp:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-smtp, username=user, password=pass, tls=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Call the configured mail session within an application:
@Resource(lookup="java:jboss/mail/MySession") private Session session;
@Resource(lookup="java:jboss/mail/MySession") private Session session;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
9.2. Configuring custom transports
When you configure a standard mail server like SMTP, POP3 or IMAP in JBoss EAP, you need to define several attributes, with the most crucial being the outbound-socket-binding-ref attribute. This attribute links your mail session to a specific host and port. However, if your setup involves multiple hosts for load balancing, standard Jakarta Mail configurations might fall short, as they don’t support multiple hosts. In such cases, you should set up custom mail transports through the management CLI. These custom transports allow for more flexible configurations and don’t require the outbound-socket-binding-ref attribute.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP installed and running.
Procedure
Add a new mail session and specify the JNDI name.
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession:add(jndi-name=java:jboss/mail/MySession)
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession:add(jndi-name=java:jboss/mail/MySession)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add an outbound socket binding and specify the host and port.
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=my-smtp-binding:add(host=localhost, port=25)
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=my-smtp-binding:add(host=localhost, port=25)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add an SMTP server and specify the outbound socket binding, username, and password.
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=smtp:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-smtp-binding, username=user, password=pass, tls=true)
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=smtp:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-smtp-binding, username=user, password=pass, tls=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can configure a POP3 or IMAP server using similar steps.
POP3 Server
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=my-pop3-binding:add(host=localhost, port=110) /subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=pop3:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-pop3-binding, username=user, password=pass)
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=my-pop3-binding:add(host=localhost, port=110)
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=pop3:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-pop3-binding, username=user, password=pass)IMAP Server
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=my-imap-binding:add(host=localhost, port=143) /subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=imap:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-imap-binding, username=user, password=pass)
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=my-imap-binding:add(host=localhost, port=143)
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=imap:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-imap-binding, username=user, password=pass)To use a custom server, create a custom mail server without an outbound socket binding. You can specify the host information in the properties definition of the custom mail server. For example:
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/custom=myCustomServer:add(username=user,password=pass, properties={"host" => "myhost", "my-property" =>"value"})
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/custom=myCustomServer:add(username=user,password=pass, properties={"host" => "myhost", "my-property" =>"value"})
If you define a custom protocol, any property name that includes a period (.) is considered a fully-qualified name and is passed directly. Any other format, such as my-property, is translated in the following format: mail.server-name.my-property.
The following XML is an example mail configuration that includes custom servers.
9.3. Using a credential store for passwords
In addition to using clear-text passwords, you can enhance security in the JBoss EAP mail subsystem by using a credential store. The elytron subsystem allows you to create and manage credential stores to securely store and access passwords. For detailed steps on how to set up and use these credential stores, you can refer to the Credential Store section of How to Configure Server Security.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP installed and running.
Use a credential store for passwords using the management CLI:
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=smtp:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-smtp-binding, username=user, credential-reference={store=exampleCS, alias=mail-session-pw}, tls=true)
/subsystem=mail/mail-session=mySession/server=smtp:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=my-smtp-binding, username=user, credential-reference={store=exampleCS, alias=mail-session-pw}, tls=true)
The following is an example of how to specify a credential-reference attribute that uses a clear-text password.
credential-reference={clear-text="MASK-Ewcyuqd/nP9;A1B2C3D4;351"}
credential-reference={clear-text="MASK-Ewcyuqd/nP9;A1B2C3D4;351"}Use a credential store for passwords using the management console:
- Access the management console. For more information, see the Management console.
- Navigate to Configuration → Subsystems → Mail.
- Select the appropriate mail session and click View.
- Select Server and choose the appropriate mail session server. You can configure the credential reference in the Credential Reference tab and edit other attributes in the Attributes tab.
Chapter 10. Logging with JBoss EAP
JBoss EAP provides highly-configurable logging facilities for both its internal use and for deployed applications. The logging subsystem is based on JBoss LogManager and supports several third-party application logging frameworks in addition to JBoss Logging.
10.1. Logging mechanisms in JBoss EAP
JBoss EAP provides a range of logging mechanisms to support monitoring, troubleshooting, and managing the server environment. Understanding these mechanisms helps in maintaining and debugging your JBoss EAP setup:
10.1.1. Server logging in JBoss EAP
In JBoss EAP, server logging is primarily managed through the server.log file, where all log entries are recorded.
The location of this log file depends on your operating mode:
-
Standalone server:
EAP_HOME/standalone/log/server.log -
Managed domain:
EAP_HOME/domain/servers/SERVER_NAME/log/server.log
This file is commonly known as the server log.
10.1.2. Bootup logging in JBoss EAP
During bootup, JBoss EAP logs information about the Java environment and the startup of each service. This log is useful for troubleshooting and is written to the server log by default.
Bootup logging is configured in the logging.properties file, which is used until the JBoss EAP logging subsystem starts.
The file location depends on your operating mode:
-
Standalone server:
EAP_HOME/standalone/configuration/logging.properties Managed domain: There is a
logging.propertiesfile for both the domain controller and each server.-
Domain controller:
EAP_HOME/domain/configuration/logging.properties Server:
EAP_HOME/domain/servers/SERVER_NAME/data/logging.propertiesWarningDo not directly edit the
logging.propertiesfile unless necessary. If you have a specific use case, consult Red Hat Customer Portal before making changes.Manual modifications to the
logging.propertiesfile are overwritten on startup.
-
Domain controller:
10.1.2.1. Viewing bootup errors
When troubleshooting JBoss EAP, checking for bootup errors is a key step. You can use this information to diagnose and resolve the errors. If needed, open a support case for assistance in troubleshooting bootup errors.
You can view bootup errors in the following ways:
-
Reviewing bootup errors in the
server.logfile - Reading bootup errors with the management CLI command
Each method has its own advantages depending on your requirements.
10.1.2.1.1. Reviewing bootup errors in server.log file
You can open the server.log file to view any errors that occurred during bootup.
This method provides error messages along with related information, helping you understand the cause of the errors. It displays error messages in plain text format.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the JBoss EAP server’s file system.
-
You can access the
server.logfile for review.
Procedure
-
Open the
server.logfile in a file viewer. - Navigate to the end of the file.
-
Search backward for the
WFLYSRV0049message identifier, which indicates the start of the latest bootup sequence. Search the log from that point onward for instances of
ERROR. Each instance will include a description of the error and list the modules involved.The following is an example error description from the
server.loglog file.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.1.2.1.2. Reading bootup errors with the management CLI command
When troubleshooting JBoss EAP, you can use the read-boot-errors management CLI command to view errors reported during bootup.
This method is useful if you do not have access to the file system of the server, enabling remote monitoring and error checking through scripting. With the management CLI command, you can identify and address boot errors. For example, you can write a script that starts multiple JBoss EAP instances and check for bootup errors.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Launch the management CLI.
<EAP_HOME>/bin/jboss-cli.sh
$ <EAP_HOME>/bin/jboss-cli.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Run the following management CLI command:
/core-service=management:read-boot-errors
/core-service=management:read-boot-errorsCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Review the output to see a list of any errors that occurred during bootup.
- Example output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.1.3. Garbage collection logging in JBoss EAP
Garbage collection logging records all garbage collection activity in plain text log files. These logs are useful for diagnostic purposes.
The garbage collection logs are located at EAP_HOME/standalone/log/gc.log.DIGIT.current. Each log file is limited to 3 MB, and up to five files are rotated.
It is recommended to keep garbage collection logging enabled, as it helps with troubleshooting and has minimal overhead. However, you can disable it for a standalone server by setting the GC_LOG variable to false before starting the server. For example:
export GC_LOG=false EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh
$ export GC_LOG=false
$ EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.sh10.1.4. Default log file locations in JBoss EAP
The following log files are created based on the default logging configurations. These configurations use periodic log handlers to write the server log files.
| Log File | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Contains server log messages, including startup messages. |
|
| Contains garbage collection details. |
| Log File | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Contains log messages related to the startup of the host controller. |
|
| Contains log messages related to the startup of the process controller. |
|
| Contains log messages for the named server, including startup messages. |
10.1.5. Setting the default locale of the server in JBoss EAP
You can configure the default locale for JBoss EAP by setting JVM properties to the startup configuration file. The startup configuration file is EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.conf for a standalone server or EAP_HOME/bin/domain.conf for a managed domain.
For Windows server, the JBoss EAP startup configuration files are standalone.conf.bat and domain.conf.bat.
Log messages that have been internationalized and localized will use this default locale.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the startup configuration file for your server mode.
Procedure
Set the language by adding the
user.languageproperty to theJAVA_OPTSvariable. For example, to set the locale to French, add the following line to the startup configuration file:JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Duser.language=fr"
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Duser.language=fr"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the language and country by adding the
user.languageanduser.countryproperties. For example, to set the locale to Brazilian Portuguese, add the following line:JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Duser.language=pt -Duser.country=BR"
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Duser.language=pt -Duser.country=BR"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the server locale using the o`rg.jboss.logging.locale` property to specify a different locale for log messages. This overrides the default locale for logging. For example, to set the server locale to Brazilian Portuguese, add the following line:
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dorg.jboss.logging.locale=pt-BR"
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dorg.jboss.logging.locale=pt-BR"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This property affects only log messages that use JBoss Logging and its dependencies. Other dependencies, such as Jakarta Server Faces, cannot get an overridden locale.
NoteTo start JBoss EAP with a different locale than the system default, edit
EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.conffor standalone mode orEAP_HOME/bin/domain.conffor managed domain mode. Use theorg.jboss.logging.localeproperty to set the locale in BCP 47 format.
10.2. Viewing log files
Viewing server and application logs is crucial for diagnosing errors, performance issues, and other problems.
You can view logs using the following methods:
Consider the following key points regarding log access and management:
-
Logs must be located in the directory specified by the server’s
jboss.server.log.dirproperty. - Logs are defined as file, periodic rotating, size rotating, or periodic size rotating log handlers.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) limits users to viewing only the logs they are authorized to access in the management console or CLI.
10.2.1. Viewing logs from the management console
You can view logs directly from the JBoss EAP management console, which provides a graphical interface for log access.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management console.
Procedure
- Log in to the management console.
- Select the Runtime tab and choose the appropriate server.
- Select Log Files and choose a log file from the list.
Click View to open and search the log contents, or choose Download from the dropdown to save the log file to your local file system.
WarningThe management console log viewer is not designed for very large log files, for example, greater than 100MB. You will receive a confirmation prompt if you attempt to open a log file larger than 15MB. Opening a very large file in the management console may crash your browser. It is recommended to download large log files and open them in a text editor.
10.2.2. Viewing logs from the management CLI
You can read log file contents from the management CLI using the read-log-file command. By default, this displays the last 10 lines of the specified log file.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Use the following command to read the contents of a log file:
/subsystem=logging/log-file=LOG_FILE_NAME:read-log-file
/subsystem=logging/log-file=LOG_FILE_NAME:read-log-fileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIn a managed domain, precede this command with
/host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME.Customize the log output using the following parameters:
- encoding: Specify the character encoding used to read the file.
-
lines: Set the number of lines to read from the file. A value of
-1will read all log lines. The default is10. -
skip: Specify the number of lines to skip before reading. The default is
0. -
tail: Set whether to read from the end of the file. Defaults to
true.
For example, the following management CLI command reads the first 5 lines from the top of the server.log log file.
/subsystem=logging/log-file=server.log:read-log-file(lines=5,tail=false)
/subsystem=logging/log-file=server.log:read-log-file(lines=5,tail=false)This produces the following output:
10.3. Overview of logging subsystem configuration
The JBoss EAP logging subsystem uses log categories and log handlers for configuration. Log categories specify which messages to capture, while log handlers define how to handle those messages, such as writing them to disk or sending them to the console.
Application logging profiles let you create uniquely-named logging configurations that can be assigned to a deployment or multiple deployments, separate from the main logging settings. Logging profile configuration is nearly identical to that of the main logging subsystem.
10.3.1. Root logger configuration
The JBoss EAP root logger captures all log messages at the specified log level or higher that are not captured by a logger. However, if a defined logger has use-parent-handlers set to true and also has a handler defined, both the defined logger and the root logger will be used to process the message.
By default, the root logger uses a console and a periodic log handler, which writes to the server.log file. This file is commonly known as the server log.
10.3.2. Log categories in JBoss EAP
A log category defines a set of log messages to capture and one or more log handlers that will process those messages.
The log messages are determined by the specified origin and log level. Any string value may be specified. However, package names or class names are preferred. The logger name is specified using dot notation, for example, Logger.getLogger("example.logger.name"). The log manager processes each section of the name and checks for a matching configuration. If found and use-parent-handlers is set to false, the process stops. If the configuration is not defined or use-parent-handlers is set to true, by default, the log manager continues checking parent names, such as "example.logger". The logger configuration depends on how the logger is created, not the package or class name.
Although the log category is typically based on the Java package and class name, it can be any name specified by the Logger.getLogger(LOGGER_NAME) method.
A logger can have a handler assigned. If the use-parent-handlers is set to false, no higher-level loggers will process the message, even if the logger determines it is loggable. For example, if the logger name is org.jboss.as.logging and it is configured with use-parent-handlers=false, the org.jboss.as logger will not be checked.
10.3.3. Log handlers in JBoss EAP
Log handlers define how captured log messages are recorded, specifying the destination and format for entries. Understanding the different types of log handlers is essential for effective logging configuration, as each type serves distinct purposes tailored to various needs.
A log handler must be added to at least one logger to be active.
10.3.3.1. Types of log handlers
Log handlers classify into several types that determine how log entries are processed and stored. Each type has distinct features to meet various logging requirements:
-
Console: Writes log messages to either the host operating system’s standard out,
stdout, or standard error,stderr, stream. These messages are displayed when JBoss EAP runs from a command line prompt. The messages from a console log handler are not saved unless the operating system is configured to capture the standard out or standard error stream. - File: Writes log messages to a specified file.
- Periodic: Writes log messages to a named file until a specified time period elapses. After that, the file is renamed with a timestamp, and the handler continues writing to a new created log file with the original name.
- Size: Writes log messages to a named file until the file reaches a specified size. When the file reaches that size, it is renamed with a numeric suffix, and the handler continues to write into a newly created log file with the original name. Each size log handler must specify the maximum number of files to keep in this manner.
- Periodic Size: Writes log messages to a named file until the file reaches the specified size or the specified time period expires. The handler then renames the file and continues writing to a newly created log file with the original name. This handler combines the features of both periodic and size log handlers.
- Syslog: Sends messages to a remote logging server. This enables multiple applications to send their log messages to the same server for parsing.
- Socket: Sends log messages over a socket to a remote logging server. This can use either a TCP or UDP socket.
-
Custom: Enables you to configure new types of log handlers. A custom handler must be implemented as a Java class that extends
java.util.logging.Handlerand included in a module. You can also use a Log4J appender as a custom log handler. - Async: Provides asynchronous behavior for one or more other log handlers. This is useful for log handlers that might have high latency or performance issues, such as writing log files to a network file system.
10.3.4. Supported log levels in JBoss EAP
A log level is an enumerated value that indicates the nature and severity of a log message. As a developer, you can specify the level of a log message using the appropriate method of your chosen logging framework to send the message.
JBoss EAP supports all log levels used by the supported application logging frameworks. The most commonly used log levels from lowest to highest are TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, and FATAL.
Log levels help log categories and handlers limit the messages they process. Each log level has an assigned numeric value indicating its order relative to other log levels. Log categories and handlers are assigned a log level and process only log messages of that level or higher. For example, a log handler with the level of WARN records messages at the WARN, ERROR, and FATAL.
| Log Level | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | Integer.MIN_VALUE | Provides all log messages. |
| FINEST | 300 | - |
| FINER | 400 | - |
| TRACE | 400 |
|
| DEBUG | 500 |
|
| FINE | 500 | - |
| CONFIG | 700 | - |
| INFO | 800 |
|
| WARN | 900 |
|
| WARNING | 900 | - |
| ERROR | 1000 |
|
| SEVERE | 1000 | - |
| FATAL | 1100 |
|
| OFF | Integer.MAX_VALUE | Does not display any log message. |
ALL is the lowest log level and includes messages of all log levels. This provides the most amount of logging.
FATAL is the highest log level and includes only messages of that level. This provides the least amount of logging.
10.3.5. Log formatters in JBoss EAP
Log formatters are used to format a log message. You can assign a formatter to a logging handler using the named-formatter attribute.
10.3.5.1. Types of log formatters
Log formatters classify into several types that determine how log entries are formatted.
The logging subsystem includes four types of formatters:
-
Pattern formatter: Formats log messages in plain text. In addition to using the formatter as the
named-formatterattribute of log handlers, you can also use it as aformatterattribute without the need to create the formatter resource first. - JSON formatter: Formats log messages in JSON.
- XML formatter: Formats log messages in XML.
-
Custom formatter: Used with handlers. Most log records are formatted in the printf format. Formatters may require invocation of the
org.jboss.logmanager.ExtLogRecord#getFormattedMessage()for proper formatting.
10.3.6. Filter expressions for logging in JBoss EAP
Filter expressions, configured using the filter-spec attribute, record log messages based on various criteria. Filters are applied to raw, unformatted messages. You can add a filter to a logger or handler, but the logger filter takes precedence over the filter put on a handler.
A filter-spec specified for the root logger is not inherited by other loggers. Instead a filter-spec must be specified per handler.
The following table describes the available filter expressions for logging:
| Filter Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| accept | Accepts all log messages. |
| deny | Denies all log messages. |
| not[filter expression] | Returns the inverted value of a single filter expression. For example:
|
| all[filter expression] | Returns the concatenated value from a comma-separated list of filter expressions. For example:
|
| any[filter expression] | Returns one value from a comma-separated list of filter expressions. For example:
|
| levelChange[level] | Updates the log record with the specified level. For example:
|
| levels[levels] | Filters log messages with a level listed in the comma-separated list of levels. For example:
|
| levelRange[minLevel,maxLevel] |
Filters log messages within the specified level range. The
|
| match["pattern"] | Filters log messages using the provided regular expression. For example:
|
| substitute["pattern","replacement value"] | Replaces the first match to the pattern (first argument) with the replacement text (second argument). For example:
|
| substituteAll["pattern","replacement value"] | Replaces all matches of the pattern (first argument) with the replacement text (second argument). For example:
|
When configuring the filter expression using the management CLI, escape commas and quotation marks in the filter text to ensure the value is correctly processed as a string. You must precede commas and quotation marks with a backslash (\) and wrap the entire expression in quotation marks. Below is an example that properly escapes substituteAll("WFLY","YLFW").
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value="substituteAll(\"WFLY\"\,\"YLFW\")")
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value="substituteAll(\"WFLY\"\,\"YLFW\")")10.3.7. Implicit logging dependencies in JBoss EAP
By default, the JBoss EAP logging subsystem adds implicit logging API dependencies to deployments. You can manage whether these implicit dependencies are added to deployments by using the add-logging-api-dependencies attribute, which is set to true by default.
To prevent these dependencies from being added, set the add-logging-api-dependencies attribute to false using the management CLI:
/subsystem=logging:write-attribute(name=add-logging-api-dependencies, value=false)
/subsystem=logging:write-attribute(name=add-logging-api-dependencies, value=false)10.4. Configuring log categories
You can configure log categories in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Categories.
You can perform the following tasks to configure a log category:
If you configure this log category for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
10.4.1. Adding and configuring a log category using the management CLI
The log category name is typically the Java package of origin. However, a logger can use any string name based on your requirements. For more information, see the Java logging API documentation. Messages from classes in that package are captured if they meet other settings, such as the log level.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a log category by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:add
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can set one or more of the following log category attributes based on your needs:
Set the log level for the log category by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.Set whether this category should use the log handlers of the root logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:write-attribute(name=use-parent-handlers,value=USE_PARENT_HANDLERS)
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:write-attribute(name=use-parent-handlers,value=USE_PARENT_HANDLERS)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By default, log categories use the handlers of the root logger in addition to their own. Set the
use-parent-handlersattribute tofalseto ensure the log category uses only its assigned handlers.Set the filter expression by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the expression to filter log messages for the log category. Escape any commas and quotation marks, and surround the expression with quotation marks. For example, replace the
FILTER_EXPRESSIONvariable with"not(match(\"WFLY\"))"to set a filter expression ofnot(match("WFLY")).
10.4.2. Assigning log handlers and managing log categories
Log handlers in JBoss EAP control how log messages are processed and recorded for log categories. Assign a log handler to a specific log category to customize logging behavior to your application’s needs. You can also remove a log category when it is no longer needed, keeping your logging configuration organized and efficient.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Assign a log handler to the log category by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:add-handler(name=LOG_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:add-handler(name=LOG_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If needed, you can remove a log category by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:remove
/subsystem=logging/logger=LOG_CATEGORY:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log category when it is no longer required for your logging configuration.
10.5. Configuring log handlers
Log handlers define how captured log messages are recorded.
See the appropriate section to configure the specific log handler:
- Configuring a console log handler
- Configuring a file log handler
- Configuring a periodic rotating log handler
- Configuring a size rotating log handler
- Configuring a periodic size rotating log handler
- Configuring a syslog handler
- Configuring a socket log handler
- Configuring a custom log handler
- Configuring an async log handler
10.5.1. Configuring a console log handler
You can configure a console log handler in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Handler > Console Handler.
You can perform the following tasks to configure a console log handler:
- Add a new console log handler
- Configure the console log handler settings
- Assign the console log handler to a logger
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a console log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:add
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can set one or more of the following console log handler attributes based on your needs:
Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.Set the target for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=target,value=TARGET)
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=target,value=TARGET)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The target can be
System.out,System.err, orconsole. The default isSystem.out.Set the encoding for the handler, such as
utf-8, by using the following command./subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the formatter string for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the default format string is
%d{HH:mm:ss,SSS} %-5p [%c] (%t) %s%e%n. Enclose theFORMATvalue in quotation marks.NoteUse the
named-formatterattribute if you want to reference a saved formatter.Set auto flush by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify whether to automatically flush after each write. The default value is
true.Set the filter expression by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the expression to filter log messages for the handler. Escape any commas and quotation marks, and surround the expression with quotation marks. For example, replace the
FILTER_EXPRESSIONvariable with"not(match(\"WFLY\"))"to create a filter expression ofnot(match("WFLY")).
Assign the console log handler to a logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To activate the log handler, you can assign the console log handler to the root logger or any other logger.
If needed, you can remove a log handler by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:remove
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE_HANDLER_NAME:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration. However, a log handler cannot be removed if it is currently assigned to a logger or an async log handler.
Next steps
10.5.2. Configuring a file log handler
You can configure a file log handler in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Handler > File Handler.
You can perform the following tasks to configure a file log handler:
- Add a new file log handler
- Configure the file log handler settings
- Assign the file log handler to a logger
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a file log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=FILE_PATH,relative-to=RELATIVE_TO_PATH})/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=FILE_PATH,relative-to=RELATIVE_TO_PATH})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen you add a file log handler, specify the file path using the
fileattribute, which consists of thepathandrelative-toattributes. Use thepathattribute to set the log file path, including the file name, for example,my-log.log. Optionally, use therelative-toattribute to indicate that the path is relative to a named path, such asjboss.server.log.dir.You can set one or more of the following file log handler attributes based on your needs:
Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.Set the append behavior for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=append,value=APPEND)
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=append,value=APPEND)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
appendattribute tofalseto overwrite the file upon server restart. By default, JBoss EAP appends log messages to the same file when the server restarts.Set the encoding for the handler, such as
utf-8, by using the following command:/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the formatter string for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the default format string is
%d{HH:mm:ss,SSS} %-5p [%c] (%t) %s%e%n. Enclose theFORMATvalue in quotation marks.NoteUse the
named-formatterattribute if you want to reference a saved formatter.Set auto flush by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify whether to automatically flush after each write. The default value is
true.Set the filter expression by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the expression to filter log messages for the handler. Escape any commas and quotation marks, and surround the expression with quotation marks. For example, replace the
FILTER_EXPRESSIONvariable with"not(match(\"WFLY\"))"to create a filter expression ofnot(match("WFLY")).
Assign the file log handler to a logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=FILE_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=FILE_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To activate the log handler, you can assign the file log handler to the root logger or any other logger.
Assign the file log handler to a specific logger named
CATEGORYby using the following command:/subsystem=logging/logger=CATEGORY:add-handler(name=FILE_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/logger=CATEGORY:add-handler(name=FILE_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
CATEGORYwith the name of the logger to which you want to assign the file log handler.If needed, you can remove a log handler by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:remove
/subsystem=logging/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration. However, a log handler cannot be removed if it is currently assigned to a logger or an async log handler.
10.5.3. Configuring a periodic rotating log handler
You can configure a periodic rotating log handler in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Handler > Periodic Handler.
You can perform the following tasks to configure a periodic rotating log handler:
- Add a new periodic rotating log handler
- Configure the periodic rotating log handler settings
- Assign the periodic rotating log handler to a logger
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a periodic rotating log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=FILE_PATH,relative-to=RELATIVE_TO_PATH},suffix=SUFFIX)/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=FILE_PATH,relative-to=RELATIVE_TO_PATH},suffix=SUFFIX)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen you add a periodic rotating log handler, specify the file path using the
fileattribute, which consists of thepathandrelative-toattributes. Use thepathattribute to set the log file path, including the file name, for example,my-log.log. Optionally, use therelative-toattribute to indicate that the path is relative to a named path, such asjboss.server.log.dir.You must set the suffix for rotated logs by using the
suffixattribute. The suffix must follow a format thatjava.text.SimpleDateFormatcan understand, such as.yyyy-MM-dd-HH. The rotation period is automatically calculated based on this suffix.You can set one or more of the following periodic rotating log handler attributes based on your needs:
Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.Set the append behavior for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=append,value=APPEND)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=append,value=APPEND)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
appendattribute tofalseto overwrite the file upon server restart. By default, JBoss EAP appends log messages to the same file when the server restarts.Set the encoding for the handler, such as
utf-8, by using the following command./subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the formatter string for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the default format string is
%d{HH:mm:ss,SSS} %-5p [%c] (%t) %s%e%n. Enclose theFORMATvalue in quotation marks.NoteUse the
named-formatterattribute if you want to reference a saved formatter.Set auto flush by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify whether to automatically flush after each write. The default value is
true.Set the filter expression by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the expression to filter log messages for the handler. Escape any commas and quotation marks, and surround the expression with quotation marks. For example, replace the
FILTER_EXPRESSIONvariable with"not(match(\"WFLY\"))"to create a filter expression ofnot(match("WFLY")).
Assign the periodic rotating log handler to a logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To activate the log handler, you can assign the periodic rotating log handler to the root logger or any other logger.
If needed, you can remove a log handler by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:remove
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration. However, a log handler cannot be removed if it is currently assigned to a logger or an async log handler.
Next steps
10.5.4. Configuring a size rotating log handler
You can configure a size log handler in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Handler > Size Handler.
You can perform the following tasks to configure a size log handler:
- Add a new size log handler
- Configure the size log handler settings
- Assign the size log handler to a logger
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a size log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=FILE_PATH,relative-to=RELATIVE_TO_PATH})/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=FILE_PATH,relative-to=RELATIVE_TO_PATH})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen you add a size log handler, specify the file path using the
fileattribute, which consists of thepathandrelative-toattributes. Use thepathattribute to set the log file path, including the file name, for example,my-log.log. Optionally, use therelative-toattribute to indicate that the path is relative to a named path, such asjboss.server.log.dir.You can set one or more of the following size log handler attributes based on your needs:
Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.Set the suffix for rotated logs by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=suffix, value=SUFFIX)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=suffix, value=SUFFIX)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf specified, the suffix must follow a format that
java.text.SimpleDateFormatcan understand, such as.yyyy-MM-dd-HH. The suffix is optional for thesize-rotating-file-handler. It indicates when the file was rotated, not the rotation period itself.Set the encoding for the handler, such as
utf-8, by using the following command./subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the rotation size by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=rotate-size, value=ROTATE_SIZE)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=rotate-size, value=ROTATE_SIZE)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the maximum file size before rotation. The default is
2mfor 2 megabytes.Set the maximum number of backup logs to keep by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=max-backup-index, value=MAX_BACKUPS)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=max-backup-index, value=MAX_BACKUPS)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the number of backups to retain. The default is
1.NoteRotation occurs based on the size limit, not the suffix. If a suffix is defined, it is added to the rotated files, but those files will not be deleted. Only files that reach the size limit are deleted during rotation.
Set whether to rotate the log on boot by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=rotate-on-boot, value=ROTATE_ON_BOOT)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=rotate-on-boot, value=ROTATE_ON_BOOT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By default, a new log file is not created on server restart. Set this to
trueto rotate the log when the server restart.Set the append behavior for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=append,value=APPEND)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=append,value=APPEND)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
appendattribute tofalseto overwrite the file upon server restart. By default, JBoss EAP appends log messages to the same file when the server restarts.Set the encoding for the handler, such as
utf-8, by using the following command./subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the formatter string for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the default format string is
%d{HH:mm:ss,SSS} %-5p [%c] (%t) %s%e%n. Enclose theFORMATvalue in quotation marks.NoteUse the
named-formatterattribute if you want to reference a saved formatter.Set auto flush by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify whether to automatically flush after each write. The default value is
true.Set the filter expression by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the expression to filter log messages for the handler. Escape any commas and quotation marks, and surround the expression with quotation marks. For example, replace the
FILTER_EXPRESSIONvariable with"not(match(\"WFLY\"))"to create a filter expression ofnot(match("WFLY")).
Assign the size log handler to a logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To activate the log handler, you can assign the size log handler to the root logger or any other logger.
If needed, you can remove a log handler by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:remove
/subsystem=logging/size-rotating-file-handler=SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration. However, a log handler cannot be removed if it is currently assigned to a logger or an async log handler.
10.5.5. Configuring a periodic size rotating log handler
You can configure a periodic size rotating log handler in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Handler > Periodic Size Handler.
You can perform the following tasks to configure a periodic size log handler:
- Add a new periodic size log handler
- Configure the periodic size log handler settings
- Assign the periodic size log handler to a logger
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a periodic size log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=FILE_PATH,relative-to=RELATIVE_TO_PATH},suffix=SUFFIX)/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=FILE_PATH,relative-to=RELATIVE_TO_PATH},suffix=SUFFIX)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen you add a periodic size log handler, specify the file path using the
fileattribute, which consists of thepathandrelative-toattributes. Use thepathattribute to set the log file path, including the file name, for example,my-log.log. Optionally, use therelative-toattribute to indicate that the path is relative to a named path, such asjboss.server.log.dir.You must set the suffix for rotated logs by using the
suffixattribute. The suffix must follow a format thatjava.text.SimpleDateFormatcan understand, such as.yyyy-MM-dd-HH. The rotation period is automatically calculated based on this suffix.You can set one or more of the following periodic size log handler attributes based on your needs:
Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.Set the rotation size by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=rotate-size, value=ROTATE_SIZE)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=rotate-size, value=ROTATE_SIZE)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the maximum file size before rotation. The default is
2mfor 2 megabytes.Set the maximum number of backup logs to keep by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=max-backup-index, value=MAX_BACKUPS)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=max-backup-index, value=MAX_BACKUPS)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the number of backups to retain. The default is
1.NoteWhen rotated by the suffix, the rotated files will not be deleted. Only files that reach the size limit when rotated will be deleted during rotation.
Set whether to rotate the log on boot by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=rotate-on-boot, value=ROTATE_ON_BOOT)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=rotate-on-boot, value=ROTATE_ON_BOOT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow By default, a new log file is not created on server restart. Set this to
trueto rotate the log when the server restart.Set the append behavior for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=append,value=APPEND)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=append,value=APPEND)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
appendattribute tofalseto overwrite the file upon server restart. By default, JBoss EAP appends log messages to the same file when the server restarts.Set the encoding for the handler, such as
utf-8, by using the following command./subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the formatter string for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the default format string is
%d{HH:mm:ss,SSS} %-5p [%c] (%t) %s%e%n. Enclose theFORMATvalue in quotation marks.NoteUse the
named-formatterattribute if you want to reference a saved formatter.Set auto flush by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify whether to automatically flush after each write. The default value is
true.Set the filter expression by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the expression to filter log messages for the handler. Escape any commas and quotation marks, and surround the expression with quotation marks. For example, replace the
FILTER_EXPRESSIONvariable with"not(match(\"WFLY\"))"to create a filter expression ofnot(match("WFLY")).
Assign the periodic size log handler to a logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To activate the log handler, you can assign the periodic size log handler to the root logger or any other logger.
If needed, you can remove a log handler by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:remove
/subsystem=logging/periodic-size-rotating-file-handler=PERIODIC_SIZE_HANDLER_NAME:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration. However, a log handler cannot be removed if it is currently assigned to a logger or an async log handler.
Next steps
10.5.6. Configuring a syslog handler
You can configure a syslog handler in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. This handler sends messages to a remote logging server that supports the Syslog protocol, either RFC-3164 or RFC-5424. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Handler > Syslog Handler.
You can perform the following tasks to configure a syslog handler:
- Add a new syslog handler
- Configure the syslog handler settings
- Assign the syslog handler to a logger
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a syslog handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:add
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can set one or more of the following syslog handler attributes based on your needs:
Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.Set the application name for logging by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=app-name,value=APP_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=app-name,value=APP_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default application name is
java.Set the address of the syslog server by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=server-address,value=SERVER_ADDRESS)
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=server-address,value=SERVER_ADDRESS)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default address is
localhost.Set the port of the syslog server by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=port,value=PORT)
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=port,value=PORT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default port is
514.Set the syslog format according to an RFC specification by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=syslog-format,value=SYSLOG_FORMAT)
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=syslog-format,value=SYSLOG_FORMAT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default format is
RFC5424.Specify the
named-formatterattribute to format the syslog payload message by using the following command:/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=named-formatter, value=FORMATTER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=named-formatter, value=FORMATTER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Assign the syslog handler to a logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To activate the log handler, you can assign the syslog handler to the root logger or any other logger.
If needed, you can remove a log handler by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:remove
/subsystem=logging/syslog-handler=SYSLOG_HANDLER_NAME:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration. However, a log handler cannot be removed if it is currently assigned to a logger or an async log handler.
Next steps
10.5.7. Configuring a socket log handler
You can configure a socket log handler in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. The handler sends messages over a TCP or UDP socket. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Handler > Socket Handler.
If the server starts in admin-only mode, it discards log messages.
You can perform the following tasks to configure a socket log handler:
- Add a socket binding
- Add a log formatter
- Add the socket log handler
- Configure the settings
- Assign the socket log handler to a logger
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add the socket binding by using the following command:
/socket-binding-group=SOCKET_BINDING_GROUP/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=SOCKET_BINDING_NAME:add(host=HOST, port=PORT)
/socket-binding-group=SOCKET_BINDING_GROUP/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=SOCKET_BINDING_NAME:add(host=HOST, port=PORT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can define either a
remote-destination-outbound-socket-bindingorlocal-destination-outbound-socket-bindingas the socket binding to use.Add the log formatter to use, such as a JSON formatter, by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/json-formatter=FORMATTER:add
/subsystem=logging/json-formatter=FORMATTER:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the socket log handler by specifying the socket binding and formatter to use by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=SOCKET_BINDING_NAME,named-formatter=FORMATTER)
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=SOCKET_BINDING_NAME,named-formatter=FORMATTER)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can set one or more of the following socket log handler attributes based on your needs:
Set the protocol by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=protocol,value=PROTOCOL)
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=protocol,value=PROTOCOL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default protocol is
TCP.Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.NoteDuring server startup, log messages handled by a socket log handler are queued until the socket binding is configured and the
loggingsubsystem is initialized. If the log level is set low, such asTRACEorDEBUG, it can result in large memory consumption during startup.Set the encoding for the handler, such as
utf-8, by using the following command./subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set auto flush by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=autoflush,value=AUTO_FLUSH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify whether to automatically flush after each write. The default value is
true.Set the filter expression by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the expression to filter log messages for the handler. Escape any commas and quotation marks, and surround the expression with quotation marks. For example, replace the
FILTER_EXPRESSIONvariable with"not(match(\"WFLY\"))"to create a filter expression ofnot(match("WFLY")).
Assign the socket log handler to a logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To activate the log handler, you can assign the socket log handler to the root logger or any other logger.
If needed, you can remove a socket log handler by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:remove
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=SOCKET_HANDLER_NAME:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration. However, a log handler cannot be removed if it is currently assigned to a logger or an async log handler.
Next steps
10.5.7.1. Sending socket log messages over SSL/TLS
You can set up a socket log handler to send log messages over a socket by using the SSL_TCP protocol. This setup involves configuring key components in the elytron subsystem, including a keystore, trust manager, and client SSL context. This configuration ensures secure transmission of log messages from the root logger over the specified socket, with the messages formatted by a JSON formatter.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Configure the Elytron settings by following these steps:
Add the keystore by using the following command:
/subsystem=elytron/key-store=log-server-ks:add(path=/path/to/keystore.jks, type=JKS, credential-reference={clear-text=mypassword})/subsystem=elytron/key-store=log-server-ks:add(path=/path/to/keystore.jks, type=JKS, credential-reference={clear-text=mypassword})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the trust manager by using the following command:
/subsystem=elytron/trust-manager=log-server-tm:add(key-store=log-server-ks)
/subsystem=elytron/trust-manager=log-server-tm:add(key-store=log-server-ks)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the client SSL context by using the following command:
/subsystem=elytron/client-ssl-context=log-server-context:add(trust-manager=log-server-tm, protocols=["TLSv1.2"])
/subsystem=elytron/client-ssl-context=log-server-context:add(trust-manager=log-server-tm, protocols=["TLSv1.2"])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Add the socket binding by using the following command:
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=log-server:add(host=localhost, port=4560)
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=log-server:add(host=localhost, port=4560)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a JSON formatter by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/json-formatter=json:add
/subsystem=logging/json-formatter=json:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the socket log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=log-server-handler:add(named-formatter=json, level=INFO, outbound-socket-binding-ref=log-server, protocol=SSL_TCP, ssl-context=log-server-context)
/subsystem=logging/socket-handler=log-server-handler:add(named-formatter=json, level=INFO, outbound-socket-binding-ref=log-server, protocol=SSL_TCP, ssl-context=log-server-context)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Assign the log handler to the root logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=log-server-handler)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=log-server-handler)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.5.8. Configuring a custom log handler
You can configure a custom log handler in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Handler > Custom Handler.
You can perform the following tasks to configure a custom log handler:
- Add a new custom log handler
- Configure the custom log handler settings
- Assign the custom log handler to a logger
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a custom log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:add(class=CLASS_NAME,module=MODULE_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:add(class=CLASS_NAME,module=MODULE_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen you add a custom log handler, specify the Java class of the handler and the JBoss EAP module that contains it. The class must extend
java.util.logging.Handler.Ensure you have created a module containing the custom logger or this command will fail.
You can set one or more of the following custom log handler attributes based on your needs:
Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.Set the properties for the log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=properties.PROPERTY_NAME,value=PROPERTY_VALUE)
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=properties.PROPERTY_NAME,value=PROPERTY_VALUE)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The properties must be accessible using a setter method.
Set the encoding for the handler, such as
utf-8, by using the following command./subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=encoding,value=ENCODING)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the formatter string for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=formatter,value=FORMAT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For example, the default format string is
%d{HH:mm:ss,SSS} %-5p [%c] (%t) %s%e%n. Enclose theFORMATvalue in quotation marks.NoteUse the
named-formatterattribute if you want to reference a saved formatter.Set the filter expression by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the expression to filter log messages for the handler. Escape any commas and quotation marks, and surround the expression with quotation marks. For example, replace the
FILTER_EXPRESSIONvariable with"not(match(\"WFLY\"))"to create a filter expression ofnot(match("WFLY")).
Assign the custom log handler to a logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To activate the log handler, you can assign the handler to the root logger or any other logger.
Assign the custom log handler to a specific logger named
CATEGORYby using the following command:/subsystem=logging/logger=CATEGORY:add-handler(name=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/logger=CATEGORY:add-handler(name=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
CATEGORYwith the name of the logger to which you want to assign the custom log handler.If needed, you can remove a custom log handler by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:remove
/subsystem=logging/custom-handler=CUSTOM_HANDLER_NAME:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration. However, a log handler cannot be removed if it is currently assigned to a logger or an async log handler.
Next steps
10.5.9. Configuring an async log handler
You can configure an async log handler in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Handler > Async Handler.
You can perform the following tasks to configure an async log handler:
- Add a new async log handler
- Add sub-handlers to the async log handler
- Configure the async log handler settings
- Assign the async log handler to a logger
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add an async log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:add(queue-length=QUEUE_LENGTH)
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:add(queue-length=QUEUE_LENGTH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen you add an async log handler, specify the queue length, which is the maximum number of log requests that can be held in the queue at any given time.
Add a sub-handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:add-handler(name=HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:add-handler(name=HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can add one or more handlers as sub-handlers for this async log handler. The handlers must already exist in the configuration or this command will fail.
You can set one or more of the following async log handler attributes based on your needs:
Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default is
ALL.Set the overflow action by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=overflow-action,value=OVERFLOW_ACTION)
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=overflow-action,value=OVERFLOW_ACTION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The default value is
BLOCK, which means that threads will block if the queue is full. You can change this value toDISCARD, which means that the oldest log messages will be deleted to accommodate new messages in the event of a full queue.Set the filter expression by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=filter-spec, value=FILTER_EXPRESSION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Specify the expression to filter log messages for the handler. Escape any commas and quotation marks, and surround the expression with quotation marks. For example, replace the
FILTER_EXPRESSIONvariable with"not(match(\"WFLY\"))"to create a filter expression ofnot(match("WFLY")).
Assign the async log handler to a logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To activate the log handler, you can assign the async log handler to the root logger or any other logger.
If needed, you can remove an async log handler by using the
removeoperation with the following command:/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:remove
/subsystem=logging/async-handler=ASYNC_HANDLER_NAME:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration. However, a log handler cannot be removed if it is currently assigned to a logger.
10.6. Configuring the root logger
The root logger captures all log messages of the specified log level or higher sent to the server that are not captured by a log category.
You can configure the root logger in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, and selecting Root Logger.
If you configure this log handler for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Assign the log handlers to the root logger by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=LOG_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:add-handler(name=LOG_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If needed, you can remove the root handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:remove-handler(name=LOG_HANDLER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:remove-handler(name=LOG_HANDLER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can remove a log handler when it is no longer required for your logging configuration.
Set the log level for the handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)
/subsystem=logging/root-logger=ROOT:write-attribute(name=level,value=LEVEL)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.7. Configuring log formatters
A log formatter defines the appearance of log messages from the handler.
The logging subsystem lets you configure the following types of log formatters:
10.7.1. Configuring a pattern formatter
You can create a named pattern formatter to use across log handlers to format log messages.
You can configure a pattern formatter in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, selecting Formatter and then choosing the Pattern Formatter option.
If you configure this log formatter for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Create a pattern formatter by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/pattern-formatter=PATTERN_FORMATTER_NAME:add(pattern=PATTERN)
/subsystem=logging/pattern-formatter=PATTERN_FORMATTER_NAME:add(pattern=PATTERN)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow When defining a pattern formatter, provide a pattern string to format log messages. For example, the default configuration uses the following log formatter string for server log messages:
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS} %-5p [%c] (%t) %s%e%n.Example
2016-03-18 15:49:32,075 INFO [org.jboss.as] (Controller Boot Thread) WFLYSRV0051: Admin console listening on http://127.0.0.1:9990
2016-03-18 15:49:32,075 INFO [org.jboss.as] (Controller Boot Thread) WFLYSRV0051: Admin console listening on http://127.0.0.1:9990Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the color map for a pattern formatter by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/pattern-formatter=PATTERN_FORMATTER_NAME:write-attribute(name=color-map,value="LEVEL:COLOR,LEVEL:COLOR")
/subsystem=logging/pattern-formatter=PATTERN_FORMATTER_NAME:write-attribute(name=color-map,value="LEVEL:COLOR,LEVEL:COLOR")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Define a color map to assign a color to different log levels. The format is a comma-separated list of
LEVEL:COLOR.-
Valid levels:
finest,finer,fine,config,trace,debug,info,warning,warn,error,fatal,severe -
Valid colors:
black,green,red,yellow,blue,magenta,cyan,white,brightblack,brightred,brightgreen,brightblue,brightyellow,brightmagenta,brightcyan,brightwhite
-
Valid levels:
10.7.2. Configuring a JSON log formatter
You can create a JSON log formatter to format log messages in JSON.
You can configure a JSON log formatter in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, selecting Formatter and then choosing the JSON Formatter option.
If you configure this log formatter for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add a JSON log formatter.
Example
/subsystem=logging/json-formatter=JSON_FORMATTER_NAME:add(pretty-print=true, exception-output-type=formatted)
/subsystem=logging/json-formatter=JSON_FORMATTER_NAME:add(pretty-print=true, exception-output-type=formatted)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a Logstash JSON log formatter by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/json-formatter=logstash:add(exception-output-type=formatted, key-overrides=[timestamp="@timestamp"], meta-data=[@version=1])
/subsystem=logging/json-formatter=logstash:add(exception-output-type=formatted, key-overrides=[timestamp="@timestamp"], meta-data=[@version=1])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou can modify the JSON log formatter output keys and add static metadata. The primary purpose of the JSON log formatter is to format log messages in JSON. Logstash consumes this JSON output and searches for the
@timestampand@versionfields. The following example creates a JSON log formatter that formats messages for Logstash.You can use the JSON formatter attributes as follows:
-
The
key-overridesattribute overrides the names of the defined keys. -
Format exceptions as objects by setting the
exception-output-typeattribute to formatted. -
Include the exception stack trace by setting the
exception-output-typeattribute todetailed. -
Format exceptions as objects and include stack traces by setting the
exception-output-typetodetailed-and-formatted. -
Add metadata to log records using the
meta-dataattribute.
-
The
10.7.3. Configuring an XML log formatter
You can create an XML log formatter to format log messages in XML.
You can configure an XML log formatter in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration → Subsystems → Logging → Configuration, clicking View, selecting Formatter and then choosing the XML Formatter option.
If you configure this log formatter for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add an XML log formatter.
Example
/subsystem=logging/xml-formatter=XML_FORMATTER_NAME:add(pretty-print=true, exception-output-type=detailed-and-formatted)
/subsystem=logging/xml-formatter=XML_FORMATTER_NAME:add(pretty-print=true, exception-output-type=detailed-and-formatted)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a key override XML log formatter by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/xml-formatter=XML_FORMATTER_NAME:add(pretty-print=true, print-namespace=true, namespace-uri="urn:custom:1.0", key-overrides={message=msg, record=logRecord, timestamp=date}, print-details=true)/subsystem=logging/xml-formatter=XML_FORMATTER_NAME:add(pretty-print=true, print-namespace=true, namespace-uri="urn:custom:1.0", key-overrides={message=msg, record=logRecord, timestamp=date}, print-details=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can use the XML formatter attributes as follows:
-
The
key-overridesattribute overrides the names of the defined keys. -
Format exceptions as objects by setting the
exception-output-typeattribute to formatted. -
Include the exception stack trace by setting the
exception-output-typeattribute todetailed. -
Format exceptions as objects and include stack traces by setting the
exception-output-typetodetailed-and-formatted. -
Add metadata to log records using the
meta-dataattribute.
-
The
10.7.4. Configuring a custom log formatter
You can create a custom log formatter to use across log handlers to format log messages.
You can configure a custom log formatter in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Configuration, clicking View, selecting Formatter and then choosing the Custom Formatter option.
If you configure this log formatter for a logging profile, start the command with /subsystem=logging/logging-profile=LOGGING_PROFILE_NAME/ instead of /subsystem=logging/.
Additionally, if you are running in a managed domain, precede the commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add the custom log formatter by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/custom-formatter=CUSTOM_FORMATTER_NAME:add(class=CLASS_NAME, module=MODULE_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/custom-formatter=CUSTOM_FORMATTER_NAME:add(class=CLASS_NAME, module=MODULE_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen you add a custom log formatter, specify the Java class of the formatter and the JBoss EAP module that contains it. This class must extend
java.util.logging.Formatter. Ensure you have created a module containing the custom logger or this command will fail.Set the properties for the log formatter by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/custom-formatter=CUSTOM_FORMATTER_NAME:write-attribute(name=properties.PROPERTY_NAME,value=PROPERTY_VALUE)
/subsystem=logging/custom-formatter=CUSTOM_FORMATTER_NAME:write-attribute(name=properties.PROPERTY_NAME,value=PROPERTY_VALUE)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The properties must be accessible using a setter method.
Assign the custom formatter to a log handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=named-formatter, value=CUSTOM_FORMATTER_NAME)
/subsystem=logging/periodic-rotating-file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name=named-formatter, value=CUSTOM_FORMATTER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command assigns a custom formatter for use by a periodic rotating file handler.
The following example configures a custom XML formatter. It uses the java.util.logging.XMLFormatter class provided in the org.jboss.logmanager module and assigns it to the console log handler.
Example
/subsystem=logging/custom-formatter=custom-xml-formatter:add(class=java.util.logging.XMLFormatter, module=java.logging) /subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE:write-attribute(name=named-formatter, value=custom-xml-formatter)
/subsystem=logging/custom-formatter=custom-xml-formatter:add(class=java.util.logging.XMLFormatter, module=java.logging)
/subsystem=logging/console-handler=CONSOLE:write-attribute(name=named-formatter, value=custom-xml-formatter)Expected Output
10.8. Configuring application logging in JBoss EAP
You can configure logging for applications by using the JBoss EAP logging subsystem or on a per-deployment basis. The logging subsystem provides centralized management, while per-deployment logging enables custom configurations specific to each application.
10.8.1. Per-deployment logging configuration
Per-deployment logging enables developers to configure logging for their applications in advance. When the application is deployed, logging starts according to the defined configuration. The log files generated through this configuration contain information only about the behavior of the application.
When using per-deployment logging, the application does not use the logging subsystem configuration. Instead, it uses the logging configuration defined within the application’s deployment file. Each application can have custom logging settings, independent of the global configuration.
This approach has advantages and disadvantages compared to system-wide logging. An advantage is that the JBoss EAP administrator does not need to configure any logging other than server logging. A disadvantage is that the per-deployment logging configuration is read only at server startup and cannot be changed at runtime.
10.8.1.1. Disabling per-deployment logging
You can disable per-deployment logging in JBoss EAP by either setting the use-deployment-logging-config attribute or excluding the logging subsystem.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Use one of the following methods to disable per-deployment logging:
Set the
use-deployment-logging-configattribute tofalse./subsystem=logging:write-attribute(name=use-deployment-logging-config,value=false)
/subsystem=logging:write-attribute(name=use-deployment-logging-config,value=false)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
use-deployment-logging-configattribute controls whether your deployment is scanned for per-deployment logging. This defaults totrue. Set it tofalseto disable per-deployment logging.-
Exclude the
loggingsubsystem by using ajboss-deployment-structure.xmlfile.
10.8.2. Application logging profiles
Logging profiles are independent sets of logging configurations that you can assign to deployed applications. Like the regular logging subsystem, a logging profile can define handlers, categories, formatters, and a root logger. However, it cannot refer to configurations in other profiles or the main logging subsystem. The design of logging profiles resembles the logging subsystem for easier configuration.
Logging profiles enable administrators to create logging configurations specific to one or more applications without impacting other configurations. Each profile is defined in the server configuration, allowing changes to the logging setup without requiring the redeployment of affected applications.
Each logging profile can have:
- A unique name. This value is required.
- Any number of log handlers.
- Any number of log categories.
- Up to one root logger.
- Log formatters.
An application can specify the logging profile to use in its MANIFEST.MF file by setting the Logging-Profile attribute.
10.8.2.1. Configuring a logging profile
You can configure a logging profile with log handlers, categories, and a root logger. Configuring a logging profile uses the same syntax as configuring the logging subsystem, except for the following differences:
-
The root configuration path is
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=NAME. - A logging profile cannot contain other logging profiles.
The
loggingsubsystem includes the following attributes that are not available for a logging profile:-
add-logging-api-dependencies -
use-deployment-logging-config
-
You can configure a Logging profiles in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI. Alternatively, you can configure them through the management console by navigating to Configuration > Subsystems > Logging > Logging Profiles.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Create the logging profile by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME:add
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the file handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=>"LOG_NAME.log", "relative-to"=>"jboss.server.log.dir"})/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:add(file={path=>"LOG_NAME.log", "relative-to"=>"jboss.server.log.dir"})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the logging level for the file handler by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name="level", value="DEBUG")
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME/file-handler=FILE_HANDLER_NAME:write-attribute(name="level", value="DEBUG")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the logger name by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME/logger=CATEGORY_NAME:add(level=TRACE)
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME/logger=CATEGORY_NAME:add(level=TRACE)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Assign the file handler to the category by using the following command:
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME/logger=CATEGORY_NAME:add-handler(name="FILE_HANDLER_NAME")
/subsystem=logging/logging-profile=PROFILE_NAME/logger=CATEGORY_NAME:add-handler(name="FILE_HANDLER_NAME")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can then set the logging profile to use by an application in its MANIFEST.MF file.
10.8.2.2. Application logging profile configuration example
This example shows the configuration of a logging profile and the application that uses it. It includes the management CLI commands, the resulting XML, and the application’s MANIFEST.MF file.
The example logging profile has the following characteristics:
-
The name is
accounts-app-profile. -
The log category is
com.company.accounts.ejbs. -
The log level is
TRACE. -
The log handler is a file handler using the file
ejb-trace.log.
Management CLI Session
XML Configuration
Application MANIFEST.MF file
Manifest-Version: 1.0 Logging-Profile: accounts-app-profile
Manifest-Version: 1.0
Logging-Profile: accounts-app-profile10.8.3. Viewing deployment logging configuration
You can view the logging configuration of a deployment in JBoss EAP by using the management CLI.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Retrieve the logging configuration for a specific deployment by using the following command:
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=logging/configuration=CONFIG:read-resource
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=logging/configuration=CONFIG:read-resourceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
CONFIGvalue can be one of the following:-
default: If the deployment is using theloggingsubsystem, this will output the logging subsystem configuration. -
profile-PROFILE_NAME: If the deployment is using a logging profile defined in the logging subsystem, this will output the logging profile configuration. -
The path to the configuration file being used, for example,
myear.ear/META-INF/logging.properties.
-
To display the configuration for a specific logging profile, run the following command:
/deployment=mydeployment.war/subsystem=logging/configuration=profile-MYPROFILE:read-resource(recursive=true,include-runtime=true)
/deployment=mydeployment.war/subsystem=logging/configuration=profile-MYPROFILE:read-resource(recursive=true,include-runtime=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This command retrieves the configuration for the
MYPROFILElogging profile, which is used by the specified deployment.Expected output
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also perform a recursive
read-resourceoperation to retrieve the entire logging configuration and other information about a deployment, by using the following command:/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=logging:read-resource(include-runtime=true, recursive=true)
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=logging:read-resource(include-runtime=true, recursive=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
10.9. Logging subsystem performance management
You can optimize and monitor the performance of the logging subsystem to ensure efficient logging and resource management. Regular monitoring helps identify potential issues before they impact performance.
Chapter 11. Datasource management
11.1. About JBoss EAP datasources
About JDBC
The JDBC API is the standard that defines how databases are accessed by Java applications. An application configures a datasource that references a JDBC driver. Application code can then be written against the driver, rather than the database. The driver converts the code to the database language. This means that if the correct driver is installed, an application can be used with any supported database.
For more information, see the JDBC specification
Supported databases
See JBoss EAP 8.0 supported configurations for the list of JDBC-compliant databases supported by JBoss EAP 8.0.
Datasource types
The two general types of resources are referred to as datasources and XA datasources.
- Non-XA datasources
- Used for applications that do not use transactions, or applications that use transactions with a single database.
- XA datasources
- Used by applications that use multiple databases or other XA resources as part of one XA transaction. XA datasources introduce additional overhead.
You specify which type of datasource to use when creating the datasource using the JBoss EAP management interfaces.
The ExampleDS datasource
JBoss EAP ships with an example datasource configuration, ExampleDS, which is provided to demonstrate how datasources are defined. This datasource uses an H2 database, which is a lightweight, relational database management system that provides developers with the ability to quickly build applications.
The ExampleDS datasource and the H2 database should not be used in a production environment. This is a very small, self-contained datasource that supports all of the standards needed for testing and building applications, but is not robust or scalable enough for production use.
11.2. JDBC drivers
Before defining datasources in JBoss EAP for your applications to use, you must first install the appropriate JDBC driver.
11.2.1. Installing a JDBC driver as a core module
To install a JDBC driver as a core module, you must first add the JDBC driver as a core module and then register the JDBC driver in the datasources subsystem.
11.2.1.1. Add the JDBC driver as a core module
JDBC drivers can be installed as a core module using the management CLI using the following steps.
Download the JDBC driver.
Download the appropriate JDBC driver from your database vendor. See JDBC Driver Download Locations for standard download locations for JDBC drivers of common databases.
Make sure to extract the archive if the JDBC driver JAR file is contained within a ZIP or TAR archive.
- Start the JBoss EAP server.
Launch the management CLI.
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.shCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the
module addmanagement CLI command to add the new core module.[disconnected /] module add --name=MODULE_NAME --resources=PATH_TO_JDBC_JAR --dependencies=DEPENDENCIES
[disconnected /] module add --name=MODULE_NAME --resources=PATH_TO_JDBC_JAR --dependencies=DEPENDENCIESCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
The following command adds a MySQL JDBC driver module:
[disconnected /] module add --name=com.mysql --resources=/path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=jakarta.transaction.api,java.se,wildflyee.api,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom
[disconnected /] module add --name=com.mysql --resources=/path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=jakarta.transaction.api,java.se,wildflyee.api,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.domCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example
To launch the management CLI and add a new core module in a single step, use the following command:
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --command="module add --name=MODULE_NAME --resources=PATH_TO_JDBC_JAR --dependencies=DEPENDENCIES"
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --command="module add --name=MODULE_NAME --resources=PATH_TO_JDBC_JAR --dependencies=DEPENDENCIES"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Execute
module --helpfor more details on using this command to add and remove modules.
You must next register it as a JDBC driver for it to be referenced by application datasources.
11.2.1.2. Register the JDBC driver
After the driver has been installed as a core module, you must register it as a JDBC driver using the following management CLI command. When running in a managed domain, be sure to precede this command with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=DRIVER_NAME:add(driver-name=DRIVER_NAME,driver-module-name=MODULE_NAME,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=XA_DATASOURCE_CLASS_NAME, driver-class-name=DRIVER_CLASS_NAME)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=DRIVER_NAME:add(driver-name=DRIVER_NAME,driver-module-name=MODULE_NAME,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=XA_DATASOURCE_CLASS_NAME, driver-class-name=DRIVER_CLASS_NAME)
The driver-class-name parameter is only required if the JDBC driver jar defines more than one class in its /META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver file.
For example, the /META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver file in the MySQL 5.1.36 JDBC driver JAR defines two classes:
- com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
- com.mysql.fabric.jdbc.FabricMySQLDriver
For this case, you would pass in driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver.
For example, the following command registers a MySQL JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mysql:add(driver-name=mysql,driver-module-name=com.mysql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlXADataSource, driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mysql:add(driver-name=mysql,driver-module-name=com.mysql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlXADataSource, driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver)The JDBC driver is now available to be referenced by application datasources.
11.2.2. Installing a JDBC driver as a JAR deployment
JDBC drivers can be installed as a JAR deployment using either the management CLI or the management console. As long as the driver is JDBC 4-compliant, it will automatically be recognized and installed as a JDBC driver upon deployment.
The following steps describe how to install a JDBC driver using the management CLI.
The recommended installation method for JDBC drivers is to install them as a core module.
Download the JDBC driver.
Download the appropriate JDBC driver from your database vendor. See JDBC Driver Download Locations for standard download locations for JDBC drivers of common databases.
Make sure to extract the archive if the JDBC driver JAR file is contained within a ZIP or TAR archive.
- If the JDBC driver is not JDBC 4-compliant, see the steps to Update a JDBC Driver JAR to be JDBC 4-Compliant.
Deploy the JAR to JBoss EAP.
deploy PATH_TO_JDBC_JAR
deploy PATH_TO_JDBC_JARCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIn a managed domain, specify the appropriate server groups.
For example, the following command deploys a MySQL JDBC driver.
deploy /path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar
deploy /path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jarCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A message will be displayed in the JBoss EAP server log that displays the deployed driver name, which will be used when defining datasources.
WFLYJCA0018: Started Driver service with driver-name = mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar
WFLYJCA0018: Started Driver service with driver-name = mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jarCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The JDBC driver is now available to be referenced by application datasources.
Update a JDBC driver JAR to be JDBC 4-compliant
If the JDBC driver JAR is not JDBC 4-compliant, it can be made deployable using the following steps.
- Create an empty temporary directory.
-
Create a
META-INFsubdirectory. -
Create a
META-INF/servicessubdirectory. Create a
META-INF/services/java.sql.Driverfile and add one line to indicate the fully-qualified class name of the JDBC driver.For example, the below line would be added for a MySQL JDBC driver.
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.DriverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the JAR command-line tool to add this new file to the JAR.
jar \-uf jdbc-driver.jar META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver
jar \-uf jdbc-driver.jar META-INF/services/java.sql.DriverCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.2.3. JDBC driver download locations
The following table gives the standard download locations for JDBC drivers of common databases used with JBoss EAP.
These links point to third-party websites which are not controlled or actively monitored by Red Hat. For the most up-to-date drivers for your database, check your database vendor’s documentation and website.
| Vendor | Download Location |
|---|---|
| MySQL | |
| PostgreSQL | |
| Oracle | http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/features/jdbc/index-091264.html |
| IBM | |
| Sybase | The jConnect JDBC driver is part of the SDK for SAP ASE installation. Currently there is not a separate download site for this driver by itself. |
| Microsoft |
11.2.4. Access vendor-specific classes
In some cases, it is necessary for an application to use vendor-specific functionality that is not part of the JDBC API. In these cases, you can access vendor-specific APIs by declaring a dependency in that application.
This is advanced usage. Only applications that need functionality not found in the JDBC API should implement this procedure.
This process is required when using the reauthentication mechanism, and accessing vendor-specific classes.
You can define a dependency for an application using either the MANIFEST.MF file or a jboss-deployment-structure.xml file.
If you have not yet done so, install a JDBC driver as a core module.
Using the MANIFEST.MF file
-
Edit the application’s
META-INF/MANIFEST.MFfile. Add the
Dependenciesline and specify the module name.For example, the below line declares the
com.mysqlmodule as a dependency.Dependencies: com.mysql
Dependencies: com.mysqlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Using a jboss-deployment-structure.xml file
-
Create a file called
jboss-deployment-structure.xmlin theMETA-INF/orWEB-INF/folder of the application. Specify the module using the
dependencieselement.For example, the following example
jboss-deployment-structure.xmlfile declares thecom.mysqlmodule as a dependency.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The example code below accesses the MySQL API.
Follow the vendor-specific API guidelines closely, as the connection is being controlled by the IronJacamar container.
11.3. Creating datasources
Datasources can be created using the management console or the management CLI.
JBoss EAP 8.0 allows you to use expressions in datasource attribute values, such as the enabled attribute.
11.3.1. Create a non-XA datasource
You can create non-XA datasources using either the management CLI or the management console.
Defining a non-XA datasource using the management console
Navigate to datasources in standalone or domain mode.
Use the following navigation in the standalone mode:
Configuration → Subsystems → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources
Use the following navigation in the domain mode:
Configuration → Profiles → full → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources
- Click the Add (+) button and choose Add Datasource.
- It opens the Add Datasource wizard where you can choose the datasource type and click Next. This creates a template for your database. The following pages of the wizard are prefilled with values specific for the selected datasource. This makes the datasource creation process easy.
- You can test your connection on the Test Connection page before finishing the datasource creation process.
- Review the details and click Finish to create the datasource.
Defining a non-XA datasource using the management CLI
Non-XA datasources can be defined using the data-source add management CLI command.
- If you have not yet done so, install and register the appropriate JDBC Driver as a Core Module.
Define the datasource using the
data-source addcommand, specifying the appropriate argument values.data-source add --name=DATASOURCE_NAME --jndi-name=JNDI_NAME --driver-name=DRIVER_NAME --connection-url=CONNECTION_URL --user-name=USER_NAME --password=PASSWORD
data-source add --name=DATASOURCE_NAME --jndi-name=JNDI_NAME --driver-name=DRIVER_NAME --connection-url=CONNECTION_URL --user-name=USER_NAME --password=PASSWORDCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIn a managed domain, you must specify the
--profile=PROFILE_NAMEargument.See the Datasource Parameters section below for tips on these parameter values.
For detailed examples, see the Example Datasource Configurations for the supported databases.
Datasource parameters
- jndi-name
-
The JNDI name for the datasource must start with
java:/orjava:jboss/. For example,java:jboss/datasources/ExampleDS. - driver-name
The driver name value depends on whether the JDBC driver was installed as a core module or a JAR deployment.
- For a core module, the driver name value will be the name given to the JDBC driver when it was registered.
For a JAR deployment, the driver name is the name of the JAR if there is only one class listed in its
/META-INF/services/java.sql.Driverfile. If there are multiple classes listed, then the value isJAR_NAME+ "_" +DRIVER_CLASS_NAME+ "_" +MAJOR_VERSION+ "_" +MINOR_VERSION(for examplemysql-connector-java-5.1.36-bin.jar_com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver_5_1).You can also see the driver name listed in the JBoss EAP server log when the JDBC JAR is deployed.
WFLYJCA0018: Started Driver service with driver-name = mysql-connector-java-5.1.36-bin.jar_com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver_5_1
WFLYJCA0018: Started Driver service with driver-name = mysql-connector-java-5.1.36-bin.jar_com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver_5_1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- connection-url
- For details on the connection URL formats for the supported databases, see the list of Datasource Connection URLs.
For a complete listing of all available datasource attributes, see the Datasource Attributes section.
- user-name
- The user name to use when creating a new datasource connection.
- password
- The password to use when creating a new datasource connection.
11.3.2. Create an XA datasource
You can create XA datasources using either the management CLI or the management console.
Defining an XA datasource using the management console
Navigate to datasources in standalone or domain mode.
Use the following navigation in the standalone mode:
Configuration → Subsystems → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources
Use the following navigation in the domain mode:
Configuration → Profiles → full → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources
- Click the Add (+) button and choose Add XA Datasource.
- It opens the Add XA Datasource wizard where you can choose the datasource type and click Next. This creates a template for your database. The following pages of the wizard are prefilled with values specific for the selected datasource. This makes the datasource creation process easy.
- You can test your connection on the Test Connection page before finishing the datasource creation process.
- Review the details and click Finish to create the datasource.
Defining an XA datasource using the management CLI
XA datasources can be defined using the xa-data-source add management CLI command.
In a managed domain, you will need to specify the profile to use. Depending on the format of the management CLI command, you will either precede the command with /profile=PROFILE_NAME or pass in the --profile=PROFILE_NAME argument.
- If you have not yet done so, install and register the appropriate JDBC Driver as a Core Module.
Define the datasource using the
xa-data-source addcommand, specifying the appropriate argument values.xa-data-source add --name=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME --jndi-name=JNDI_NAME --driver-name=DRIVER_NAME --xa-datasource-class=XA_DATASOURCE_CLASS --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"HOST_NAME","DatabaseName"=>"DATABASE_NAME"}xa-data-source add --name=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME --jndi-name=JNDI_NAME --driver-name=DRIVER_NAME --xa-datasource-class=XA_DATASOURCE_CLASS --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"HOST_NAME","DatabaseName"=>"DATABASE_NAME"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow See the Datasource Parameters section below for tips on these parameter values.
Set XA datasource properties.
At least one XA datasource property is required when defining an XA datasource or you will receive an error when adding the datasource in the previous step. Any properties that were not set when defining the XA datasource can be set individually afterward.
Set the server name.
/subsystem=datasources/xa-data-source=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME/xa-datasource-properties=ServerName:add(value=HOST_NAME)
/subsystem=datasources/xa-data-source=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME/xa-datasource-properties=ServerName:add(value=HOST_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the database name.
/subsystem=datasources/xa-data-source=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME/xa-datasource-properties=DatabaseName:add(value=DATABASE_NAME)
/subsystem=datasources/xa-data-source=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME/xa-datasource-properties=DatabaseName:add(value=DATABASE_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
For detailed examples, see the Example Datasource Configurations for the supported databases.
Datasource parameters
- jndi-name
-
The JNDI name for the datasource must start with
java:/orjava:jboss/. For example,java:jboss/datasources/ExampleDS. - driver-name
The driver name value depends on whether the JDBC driver was installed as a core module or a JAR deployment.
- For a core module, the driver name value will be the name given to the JDBC driver when it was registered.
For a JAR deployment, the driver name is the name of the JAR if there is only one class listed in its
/META-INF/services/java.sql.Driverfile. If there are multiple classes listed, then the value isJAR_NAME+ "_" +DRIVER_CLASS_NAME+ "_" +MAJOR_VERSION+ "_" +MINOR_VERSION, for example,mysql-connector-java-5.1.36-bin.jar_com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver_5_1.You can also see the driver name listed in the JBoss EAP server log when the JDBC JAR is deployed.
WFLYJCA0018: Started Driver service with driver-name = mysql-connector-java-5.1.36-bin.jar_com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver_5_1
WFLYJCA0018: Started Driver service with driver-name = mysql-connector-java-5.1.36-bin.jar_com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver_5_1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
- xa-datasource-class
-
Specify the XA datasource class for the JDBC driver’s implementation of the
jakarta.sql.XADataSourceclass. - xa-datasource-properties
- At least one XA datasource property is required when defining an XA datasource or you will receive an error when attempting to add it. Additional properties can also be added to the XA datasource after it has been defined.
For a complete listing of all available datasource attributes, see the Datasource Attributes section.
11.4. Modifying datasources
Datasources settings can be configured using the management console or the management CLI.
JBoss EAP 8.0 allows you to use expressions in datasource attribute values, such as the enabled attribute.
11.4.1. Modify a non-XA datasource
Non-XA datasource settings can be updated using the data-source management CLI command. You can also update datasource attributes from the management console in standalone or domain mode:
- In standalone mode, navigate to Configuration → Subsystems → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources.
- In domain mode, navigate to Configuration → Profiles → full → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources.
Non-XA datasources can be integrated with Jakarta Transactions transactions. To integrate the datasource with Jakarta Transactions, ensure that the jta parameter is set to true.
Example of updating settings for a datasource
Settings for a datasource can be updated by using the following management CLI command.
data-source --name=DATASOURCE_NAME --ATTRIBUTE_NAME=ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
data-source --name=DATASOURCE_NAME --ATTRIBUTE_NAME=ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
In a managed domain, you must specify the --profile=PROFILE_NAME argument.
A server reload may be required for the changes to take effect.
11.4.2. Modify an XA datasource
XA datasource settings can be updated using the xa-data-source management CLI command. You can also update datasource attributes from the management console in standalone or domain mode:
- In standalone mode, navigate to Configuration → Subsystems → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources.
- In domain mode, navigate to Configuration → Profiles → full → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources.
Example of updating an XA datasource
Settings for an XA datasource can be updated by using the following management CLI command.
xa-data-source --name=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME --ATTRIBUTE_NAME=ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
xa-data-source --name=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME --ATTRIBUTE_NAME=ATTRIBUTE_VALUECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIn a managed domain, you must specify the
--profile=PROFILE_NAMEargument.
Example of adding an XA datasource property
An XA datasource property can be added using the following management CLI command.
/subsystem=datasources/xa-data-source=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME/xa-datasource-properties=PROPERTY:add(value=VALUE)
/subsystem=datasources/xa-data-source=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME/xa-datasource-properties=PROPERTY:add(value=VALUE)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIn a managed domain, you must precede this command with
/profile=PROFILE_NAME.
A server reload may be required for the changes to take effect.
11.5. Removing datasources
Datasources can be removed using the management console or the management CLI.
11.5.1. Remove a non-XA datasource
Non-XA datasources can be removed using the data-source remove management CLI command. You can also use the management console in standalone or domain mode to remove datasources:
- In standalone mode, navigate to Configuration → Subsystems → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources.
- In domain mode, navigate to Configuration → Profiles → full → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources.
Use the following command to remove a non-XA datasource:
data-source remove --name=DATASOURCE_NAME
data-source remove --name=DATASOURCE_NAME
In a managed domain, you must specify the --profile=PROFILE_NAME argument.
The server will require a reload after the datasource is removed.
11.5.2. Remove an XA datasource
XA datasources can be removed using the xa-data-source remove management CLI command. You can also use the management console in standalone or domain mode to remove datasources:
- In standalone mode, navigate to Configuration → Subsystems → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources.
- In domain mode, navigate to Configuration → Profiles → full → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources.
Use the following command to remove an XA datasource:
xa-data-source remove --name=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME
xa-data-source remove --name=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME
In a managed domain, you must specify the --profile=PROFILE_NAME argument.
The server will require a reload after the XA datasource is removed.
11.6. Testing datasource connections
You can use the management CLI or management console to test a datasource connection to verify that its settings are correct.
Test a datasource connection using the management CLI
The following management CLI command can be used to test a datasource’s connection.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:test-connection-in-pool
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:test-connection-in-pool
In a managed domain, you must precede this command with /host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME. If you are testing an XA datasource, replace data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME with xa-data-source=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME.
Test a datasource connection using the management console
When using the Add Datasource wizard in the management console, you have the opportunity to test the connection before creating the datasource. On the Test Connection screen of the wizard, click the Test Connection button.
When a datasource is added, you can test the connection by using the following procedure:
- Navigate to Configuration → Subsystems → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources in standalone mode or Configuration → Profiles → full → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources in domain mode.
- Select the datasource.
- Select Test Connection from the drop-down list.
11.7. Flushing datasource connections
You can flush datasource connections using the following management CLI commands.
In a managed domain, you must precede these commands with /host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME.
Flush all connections in the pool.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:flush-all-connection-in-pool
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:flush-all-connection-in-poolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Gracefully flush all connections in the pool.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:flush-gracefully-connection-in-pool
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:flush-gracefully-connection-in-poolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The server will wait until connections become idle before flushing them.
Flush all idle connections in the pool.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:flush-idle-connection-in-pool
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:flush-idle-connection-in-poolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Flush all invalid connections in the pool.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:flush-invalid-connection-in-pool
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATASOURCE_NAME:flush-invalid-connection-in-poolCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The server will flush all connections that it determines to be invalid, for example, by the
valid-connection-checker-class-nameorcheck-valid-connection-sqlvalidation mechanism discussed in Database Connection Validation.
You can also flush connections using the management console. From the Runtime tab, select the server, select Datasources, choose a datasource, and use the drop down to select the appropriate action.
11.8. XA datasource recovery
An XA datasource is a datasource that can participate in an XA global transaction, which is coordinated by the transaction manager and can span multiple resources in a single transaction. If one of the participants fails to commit its changes, the other participants abort the transaction and restore their state as it was before the transaction occurred. This is to maintain consistency and avoid potential data loss or corruption.
XA recovery is the process of ensuring that all resources affected by a transaction are updated or rolled back, even if any of the resources or transaction participants crash or become unavailable. XA recovery happens without user intervention.
Each XA resource needs to have a recovery module associated with its configuration. The recovery module is the code that is executed when recovery is being performed. JBoss EAP automatically registers recovery modules for JDBC XA resources. You can register a custom module with your XA datasource if you wish to implement custom recovery code. The recovery module must extend class com.arjuna.ats.jta.recovery.XAResourceRecovery.
11.8.1. Configuring XA recovery
For most JDBC resources, the recovery module is automatically associated with the resource. In these cases, you only need to configure the options that allow the recovery module to connect to your resource to perform recovery.
The following table describes the XA datasource parameters specific to XA recovery. Each of these configuration attributes can be set during datasource creation or afterward. You can set them using either the management console or the management CLI. See Modify an XA Datasource for information on configuring XA datasources.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| recovery-username | The user name to use to connect to the resource for recovery. Note that if this is not specified, the datasource security settings will be used. |
| recovery-password | The password to use to connect to the resource for recovery. Note that if this is not specified, the datasource security settings will be used. |
| recovery-security-domain | The security domain to use to connect to the resource for recovery. |
| recovery-plugin-class-name |
If you need to use a custom recovery module, set this attribute to the fully-qualified class name of the module. The module should extend class |
| recovery-plugin-properties |
If you use a custom recovery module which requires properties to be set, set this attribute to the list of comma-separated |
Disable XA recovery
If multiple XA datasources connect to the same physical database, then XA recovery typically needs to be configured for only one of them.
Use the following management CLI command to disable recovery for an XA datasource:
/subsystem=datasources/xa-data-source=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME:write-attribute(name=no-recovery,value=true)
/subsystem=datasources/xa-data-source=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME:write-attribute(name=no-recovery,value=true)11.8.2. Vendor-specific XA recovery
Vendor-specific configuration
Some databases require specific configurations in order to cooperate in XA transactions managed by the JBoss EAP transaction manager. For detailed and up-to-date information, see your database vendor’s documentation.
- MySQL
- No special configuration is required. For more information, see the MySQL documentation.
For automated XA recovery, MySQL 8 and later requires special configuration. For more information, see the JBoss EAP 8.0 supported configurations.
- PostgreSQL and Postgres Plus Advanced Server
-
For PostgreSQL to be able to handle XA transactions, change the configuration parameter
max_prepared_transactionsto a value greater than0and equal to or greater thanmax_connections. - Oracle
Ensure that the Oracle user,
USER, has access to the tables needed for recovery.GRANT SELECT ON sys.dba_pending_transactions TO USER; GRANT SELECT ON sys.pending_trans$ TO USER; GRANT SELECT ON sys.dba_2pc_pending TO USER; GRANT EXECUTE ON sys.dbms_xa TO USER;
GRANT SELECT ON sys.dba_pending_transactions TO USER; GRANT SELECT ON sys.pending_trans$ TO USER; GRANT SELECT ON sys.dba_2pc_pending TO USER; GRANT EXECUTE ON sys.dbms_xa TO USER;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If the Oracle user does not have the proper permissions, you may see an error such as the following:
WARN [com.arjuna.ats.jta.logging.loggerI18N] [com.arjuna.ats.internal.jta.recovery.xarecovery1] Local XARecoveryModule.xaRecovery got XA exception jakarta.transaction.xa.XAException, XAException.XAER_RMERR
WARN [com.arjuna.ats.jta.logging.loggerI18N] [com.arjuna.ats.internal.jta.recovery.xarecovery1] Local XARecoveryModule.xaRecovery got XA exception jakarta.transaction.xa.XAException, XAException.XAER_RMERRCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Microsoft SQL Server
- For more information, see the Microsoft SQL Server documentation, including Understanding XA transactions.
- IBM DB2
- No special configuration is required. For more information, see the IBM DB2 documentation.
- Sybase
Sybase expects XA transactions to be enabled on the database. Without correct database configuration, XA transactions will not work. The
enable xact coordinationparameter enables or disables Adaptive Server transaction coordination services. When this parameter is enabled, Adaptive Server ensures that updates to remote Adaptive Server data commit or roll back with the original transaction.To enable transaction coordination, use:
sp_configure 'enable xact coordination', 1
sp_configure 'enable xact coordination', 1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - MariaDB
- No special configuration is required. For more information, see the MariaDB documentation.
Known issues
These known issues with handling XA transactions are for the specific database and JDBC driver versions supported with JBoss EAP 8.0. For up-to-date information on the supported databases, see JBoss EAP 8.0 supported configurations.
- MySQL
- MySQL is not fully capable of handling XA transactions. If a client is disconnected from MySQL, then all the information about such transactions is lost. See this MySQL bug for more information. Note that this issue was fixed in MySQL 5.7.
- PostgreSQL and Postgres Plus Advanced Server
The JDBC driver returns the
XAER_RMERRXAException error code when a network failure occurs during the commit phase of two-phase commit (2PC). This error signals an unrecoverable catastrophic event to the transaction manager, but the transaction is left in thein-doubtstate on the database side and could be easily corrected after network connection is established again. The correct return code should beXAER_RMFAILorXAER_RETRY. The incorrect error code causes the transaction to be left in theHeuristicstate on the JBoss EAP side and holding locks in the database which requires manual intervention. See this PostgreSQL bug for more information.If a connection failure happens when the one-phase commit optimization is used, the JDBC driver returns
XAER_RMERR, but theXAER_RMFAILerror code should be returned. This could lead to data inconsistency if the database commits data during one-phase commit and the connection goes down at that moment, then the client is informed that transaction was rolled back.The Postgres Plus JDBC driver returns XIDs for all prepared transactions that exist in the Postgres Plus Server, so there is no way to determine the database to which the XID belongs. If you define more than one data source for the same database in JBoss EAP, an in-doubt transaction recovery attempt could be run under wrong account, which causes the recovery to fail.
- Oracle
The JDBC driver returns XIDs belonging to all users on the database instance, when the Recovery Manager calls recovery using datasource configured with some user credentials. The JDBC driver throws the exception
ORA-24774: cannot switch to specified transactionbecause it tries to recover XIDs belonging to other users.The workaround for this issue is to grant
FORCE ANY TRANSACTIONprivilege to the user whose credentials are used in recovery datasource configuration. For more information about configuring the privilege, see Manually overriding in-doubt transactions.- Microsoft SQL Server
The JDBC driver returns the
XAER_RMERRXAException error code when a network failure occurs during the commit phase of two-phase commit (2PC). This error signals an unrecoverable catastrophic event to the transaction manager, but the transaction is left in thein-doubtstate on the database side and could be easily corrected after network connection is established again. The correct return code should beXAER_RMFAILorXAER_RETRY. The incorrect error code causes the transaction to be left in theHeuristicstate on the JBoss EAP side and holding locks in the database which requires manual intervention. See this Microsoft SQL Server issue report for more information.If a connection failure happens when the one-phase commit optimization is used, the JDBC driver returns
XAER_RMERR, but theXAER_RMFAILerror code should be returned. This could lead to data inconsistency if the database commits data during one-phase commit and the connection goes down at that moment, then the client is informed that transaction was rolled back.- IBM DB2
-
If a connection failure happens during a one-phase commit, the JDBC driver returns
XAER_RETRY, but theXAER_RMFAILerror code should be returned. This could lead to data inconsistency if the database commits data during one-phase commit and the connection goes down at that moment, then the client is informed that transaction was rolled back. - Sybase
The JDBC driver returns the
XAER_RMERRXAException error code when a network failure occurs during the commit phase of two-phase commit (2PC). This error signals an unrecoverable catastrophic event to the transaction manager, but the transaction is left in thein-doubtstate on the database side and could be easily corrected after network connection is established again. The correct return code should beXAER_RMFAILorXAER_RETRY. The incorrect error code causes the transaction to be left in theHeuristicstate on the JBoss EAP side and holding locks in the database which requires manual intervention.If a connection failure happens when the one-phase commit optimization is used, the JDBC driver returns
XAER_RMERR, but theXAER_RMFAILerror code should be returned. This could lead to data inconsistency if the database commits data during one-phase commit and the connection goes down at that moment, then the client is informed that transaction was rolled back.If an XA transaction that includes an insert to a Sybase 15.7 or 16 database fails before the Sybase transaction branch is in a prepared state, then repeating the XA transaction and inserting the same record with the same primary key will fail with an error of
com.sybase.jdbc4.jdbc.SybSQLException: Attempt to insert duplicate key row. This exception will be thrown until the original unfinished Sybase transaction branch is rolled back.- MariaDB
- MariaDB is not fully capable of handling XA transactions. If a client is disconnected from MariaDB, then all the information about such transactions is lost.
- MariaDB Galera Cluster
- XA transactions are not supported in MariaDB Galera Cluster.
11.9. Database connection validation
Database maintenance, network problems, or other outage events may cause JBoss EAP to lose the connection to the database. In order to recover from these situations, you can enable database connection validation for your datasources.
To configure database connection validation, you specify the validation timing method to define when the validation occurs, the validation mechanism to determine how the validation is performed, and the exception sorter to define how exceptions are handled.
Choose one of the validation timing methods.
- validate-on-match
When the
validate-on-matchmethod is set totrue, the database connection is validated every time it is checked out from the connection pool using the validation mechanism specified in the next step.If a connection is not valid, a warning is written to the log and the next connection in the pool is retrieved. This process continues until a valid connection is found. If you prefer not to cycle through every connection in the pool, you can use the
use-fast-failoption. If a valid connection is not found in the pool, a new connection is created. If the connection creation fails, an exception is returned to the requesting application.- background-validation
When the
background-validationmethod is set totrue, connections are validated periodically in a background thread prior to use. The frequency of the validation is specified by thebackground-validation-millisproperty. The default value ofbackground-validation-millisis0, meaning that it is disabled.When determining the value of the
background-validation-millisproperty, consider the following:-
This value should not be set to the same value as your
idle-timeout-minutessetting. - The lower the value, the more frequently the pool is validated and the sooner invalid connections are removed from the pool.
- Lower values take more database resources. Higher values result in less frequent connection validation checks and use less database resources, but dead connections are undetected for longer periods of time.
-
This value should not be set to the same value as your
NoteThese validation methods are mutually exclusive as demonstrated in the following examples:
-
If
validate-on-matchis set totrue, you must setbackground-validationtofalse. -
If
background-validationis set totrue, you must setvalidate-on-matchtofalse.
For a comparison matrix for these validation methods, see Comparison of validation timing methods.
Choose one of the validation mechanisms.
- valid-connection-checker-class-name
Using
valid-connection-checker-class-nameis the preferred validation mechanism. This specifies a connection checker class that is used to validate connections for the particular database in use. JBoss EAP provides the following connection checkers:-
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ValidConnectionChecker -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLValidConnectionChecker -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLReplicationValidConnectionChecker -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.novendor.JDBC4ValidConnectionChecker -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.novendor.NullValidConnectionChecker -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleValidConnectionChecker -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLValidConnectionChecker -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseValidConnectionChecker
-
- check-valid-connection-sql
Using
check-valid-connection-sql, you provide the SQL statement that will be used to validate the connection.The following is an example SQL statement that you might use to validate Oracle connections.
select 1 from dual
select 1 from dualCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following is an example SQL statement that you might use to validate MySQL or PostgreSQL connections.
select 1
select 1Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Set the exception sorter class name.
When an exception is marked as fatal, the connection is closed immediately, even if the connection is participating in a transaction. Use the exception sorter class option to properly detect and clean up after fatal connection exceptions. Choose the appropriate JBoss EAP exception sorter for your datasource type.
-
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ExceptionSorter -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.informix.InformixExceptionSorter -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLExceptionSorter -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorter -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.novendor.NullExceptionSorter -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleExceptionSorter -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLExceptionSorter -
org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseExceptionSorter
-
11.10. Datasource security
Datasource security refers to encrypting or obscuring passwords for datasource connections. These passwords can be stored in plain text in configuration files, but this represents a security risk.
There are several methods you can use for datasource security. Examples of each are included below.
Secure a Datasource using a security domain
Use the following steps to secure a datasource using a security domain:
Create the new security domain.
/subsystem=security/security-domain=DsRealm:add(cache-type=default) /subsystem=security/security-domain=DsRealm/authentication=classic:add(login-modules=[{code=ConfiguredIdentity,flag=required,module-options={userName=sa, principal=sa, password=sa}}])/subsystem=security/security-domain=DsRealm:add(cache-type=default) /subsystem=security/security-domain=DsRealm/authentication=classic:add(login-modules=[{code=ConfiguredIdentity,flag=required,module-options={userName=sa, principal=sa, password=sa}}])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow A security domain for the datasource is defined. The following XML extract is the result of calling CLI commands.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a new datasource.
data-source add --name=securityDs --jndi-name=java:jboss/datasources/securityDs --connection-url=jdbc:h2:mem:test;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1 --driver-name=h2 --new-connection-sql="select current_user()"
data-source add --name=securityDs --jndi-name=java:jboss/datasources/securityDs --connection-url=jdbc:h2:mem:test;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1 --driver-name=h2 --new-connection-sql="select current_user()"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the security domain on the datasource.
data-source --name=securityDs --security-domain=DsRealm
data-source --name=securityDs --security-domain=DsRealmCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server for the changes to be effective.
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
If you are using a security domain with multiple datasources, disable caching on the security domain. This can be accomplished by setting the value of the cache-type attribute to none or by removing the attribute altogether; however, if caching is desired, use a separate security domain for each datasource.
The following XML extract shows the datasource secured with the DsRealm.
For more information on using Security Domains, see How to Configure Identity Management.
Secure a datasource using a password vault
Use the following steps to secure a datasource using a password vault:
Set the password vault for the ExampleDS datasource.
data-source --name=ExampleDS --password=${VAULT::ds_ExampleDS::password::N2NhZDYzOTMtNWE0OS00ZGQ0LWE4MmEtMWNlMDMyNDdmNmI2TElORV9CUkVBS3ZhdWx0}data-source --name=ExampleDS --password=${VAULT::ds_ExampleDS::password::N2NhZDYzOTMtNWE0OS00ZGQ0LWE4MmEtMWNlMDMyNDdmNmI2TElORV9CUkVBS3ZhdWx0}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to implement the changes.
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The following XML security element is added to the ExampleDS datasource secured with password vault.
<security>
<user-name>admin</user-name>
<password>${VAULT::ds_ExampleDS::password::N2NhZDYzOTMtNWE0OS00ZGQ0LWE4MmEtMWNlMDMyNDdmNmI2TElORV9CUkVBS3ZhdWx0}</password>
</security>
<security>
<user-name>admin</user-name>
<password>${VAULT::ds_ExampleDS::password::N2NhZDYzOTMtNWE0OS00ZGQ0LWE4MmEtMWNlMDMyNDdmNmI2TElORV9CUkVBS3ZhdWx0}</password>
</security>For more information on using the Password Vault, see the Password Vault section in the JBoss EAP How to Configure Server Security guide.
Secure a datasource using a credential store
You can also use a credential store to provide passwords. The elytron subsystem provides the ability to create credential stores to securely house and use your passwords throughout JBoss EAP. You can find more details on creating and using credential stores in the Credential Store section in the JBoss EAP How to Configure Server Security guide.
Adding a credential store reference to ExampleDS
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=credential-reference,value={store=exampleCS, alias=example-ds-pw})
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=credential-reference,value={store=exampleCS, alias=example-ds-pw})Secure a datasource using an authentication context
You can also use an Elytron authentication context to provide usernames and passwords.
Use the following steps to configure and use an authentication context for datasource security.
Remove
passwordanduser-name./subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:undefine-attribute(name=password) /subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:undefine-attribute(name=user-name)
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:undefine-attribute(name=password) /subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:undefine-attribute(name=user-name)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable Elytron security for the datasource.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=elytron-enabled,value=true) reload
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=elytron-enabled,value=true) reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an
authentication-configurationfor your credentials.The authentication configuration contains the credentials you want your datasource to use when making a connection. The below example uses a reference to a credential store, but you could also use an Elytron security domain.
/subsystem=elytron/authentication-configuration=exampleAuthConfig:add(authentication-name=sa,credential-reference={clear-text=sa})/subsystem=elytron/authentication-configuration=exampleAuthConfig:add(authentication-name=sa,credential-reference={clear-text=sa})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an
authentication-context./subsystem=elytron/authentication-context=exampleAuthContext:add(match-rules=[{authentication-configuration=exampleAuthConfig}])/subsystem=elytron/authentication-context=exampleAuthContext:add(match-rules=[{authentication-configuration=exampleAuthConfig}])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the datasource to use the authentication context.
The below example updates
ExampleDSto use an authentication context./subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=authentication-context,value=exampleAuthContext) reload
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=authentication-context,value=exampleAuthContext) reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteIf
authentication-contextattribute is not set andelytron-enabledattribute is set totrue, JBoss EAP will use the current context for authentication.
Secure a datasource using Kerberos
To secure a datasource using kerberos authentication, the following configuration is required:
- Kerberos is configured on the database server.
- JBoss EAP host server has a keytab entry for the database server.
To secure a datasource using kerberos:
Configure JBoss EAP to use kerberos.
/system-property=java.security.krb5.conf:add(value="/path/to/krb5.conf") /system-property=sun.security.krb5.debug:add(value="false") /system-property=sun.security.spnego.debug:add(value="false")
/system-property=java.security.krb5.conf:add(value="/path/to/krb5.conf") /system-property=sun.security.krb5.debug:add(value="false") /system-property=sun.security.spnego.debug:add(value="false")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For debugging, change the values of
sun.security.krb5.debugandsun.security.spnego.debugtotrue. In a production environment, it is recommended to set the values tofalse.Configure security.
You can use legacy security or Elytron security to secure a datasource.
To use kerberos with legacy security:
Configure infinispan cache to periodically remove expired tickets from cache.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following attributes define ticket expiration:
-
lifespan: Interval, in milliseconds, at which new certificates are requested from the KDC. Set the value of thelifespanattribute to be just smaller than the lifespan defined by the KDC. -
max-idle: Interval, in milliseconds, at which a valid ticket should be removed from the cache, if it unused. -
max-entries: The maximum number copies of the kerberos tickets to keep in cache. The value corresponds to the number of configured connections in your datasource.
-
Create a security domain.
batch /subsystem=security/security-domain=KerberosDatabase:add(cache-type=infinispan) /subsystem=security/security-domain=KerberosDatabase/authentication=classic:add /subsystem=security/security-domain=KerberosDatabase/authentication=classic/login-module="KerberosDatabase-Module":add(code="org.jboss.security.negotiation.KerberosLoginModule",module="org.jboss.security.negotiation",flag=required, module-options={ "debug" => "false", "storeKey" => "false", "useKeyTab" => "true", "keyTab" => "/path/to/eap.keytab", "principal" => "PRINCIPAL@SERVER.COM", "doNotPrompt" => "true", "refreshKrb5Config" => "true", "isInitiator" => "true", "addGSSCredential" => "true", "credentialLifetime" => "-1"}) run-batchbatch /subsystem=security/security-domain=KerberosDatabase:add(cache-type=infinispan) /subsystem=security/security-domain=KerberosDatabase/authentication=classic:add /subsystem=security/security-domain=KerberosDatabase/authentication=classic/login-module="KerberosDatabase-Module":add(code="org.jboss.security.negotiation.KerberosLoginModule",module="org.jboss.security.negotiation",flag=required, module-options={ "debug" => "false", "storeKey" => "false", "useKeyTab" => "true", "keyTab" => "/path/to/eap.keytab", "principal" => "PRINCIPAL@SERVER.COM", "doNotPrompt" => "true", "refreshKrb5Config" => "true", "isInitiator" => "true", "addGSSCredential" => "true", "credentialLifetime" => "-1"}) run-batchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
When using Microsoft JDBC driver for SQL server, add attribute and value
"wrapGSSCredential" ⇒ "true"inmodule-options. -
For debugging, change the value of the
debugattribute inmodule-optionstotrue.
-
When using Microsoft JDBC driver for SQL server, add attribute and value
To use kerberos with Elytron:
Set up a kerberos factory in Elytron.
/subsystem=elytron/kerberos-security-factory=krbsf:add(debug=false, principal=PRINCIPAL@SERVER.COM, path=/path/to/keytab, request-lifetime=-1, obtain-kerberos-ticket=true, server=false)
/subsystem=elytron/kerberos-security-factory=krbsf:add(debug=false, principal=PRINCIPAL@SERVER.COM, path=/path/to/keytab, request-lifetime=-1, obtain-kerberos-ticket=true, server=false)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For debugging, add attribute and value
debug = true.For a list of supported attributes, see the Kerberos Security Factory Attributes section in the How to Configure Server Security guide.
Create an authentication configuration to use the kerberos factory.
/subsystem=elytron/authentication-configuration=kerberos-conf:add(kerberos-security-factory=krbsf)
/subsystem=elytron/authentication-configuration=kerberos-conf:add(kerberos-security-factory=krbsf)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create an authentication context.
/subsystem=elytron/authentication-context=ds-context:add(match-rules=[{authentication-configuration=kerberos-conf}])/subsystem=elytron/authentication-context=ds-context:add(match-rules=[{authentication-configuration=kerberos-conf}])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Secure the datasource with kerberos.
If you use Elytron:
Configure the datasource to use an authentication context.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=KerberosDS:add(connection-url="URL", min-pool-size=0, max-pool-size=10, jndi-name="java:jboss/datasource/KerberosDS", driver-name=<jdbc-driver>.jar, elytron-enabled=true, authentication-context=ds-context, allow-multiple-users=false, pool-prefill=false, pool-use-strict-min=false, idle-timeout-minutes=2)
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=KerberosDS:add(connection-url="URL", min-pool-size=0, max-pool-size=10, jndi-name="java:jboss/datasource/KerberosDS", driver-name=<jdbc-driver>.jar, elytron-enabled=true, authentication-context=ds-context, allow-multiple-users=false, pool-prefill=false, pool-use-strict-min=false, idle-timeout-minutes=2)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure vendor-specific connection properties.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=KerberosDS/connection-properties=<connection-property-name>:add(value="(<kerberos-value>)")
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=KerberosDS/connection-properties=<connection-property-name>:add(value="(<kerberos-value>)")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example: connection properties for Oracle database
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=KerberosDS/connection-properties=oracle.net.authentication_services:add(value="(KERBEROS5)")
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=KerberosDS/connection-properties=oracle.net.authentication_services:add(value="(KERBEROS5)")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
When using kerberos authentication, it is recommended to use the following attributes and values for the datasource:
-
pool-prefill=false -
pool-use-strict-min=false -
idle-timeout-minutes
For a list of supported attributes, see Datasource Attributes.
11.11. Datasource statistics
When statistics collection is enabled for a datasource, you can view runtime statistics for the datasource.
11.11.1. Enabling datasource statistics
By default, datasource statistics are not enabled. You can enable datasource statistics collection using the management CLI or the management console.
11.11.1.1. Enable datasource statistics using the management CLI
The following management CLI command enables the collection of statistics for the ExampleDS datasource.
In a managed domain, precede this command with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=statistics-enabled,value=true)
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=statistics-enabled,value=true)Reload the server for the changes to take effect.
11.11.1.2. Enable datasource statistics using the management console
Use the following steps to enable statistics collection for a datasource using the management console.
Procedure
Navigate to datasources in standalone or domain mode.
Use the following navigation in the standalone mode:
Configuration → Subsystems → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources
Use the following navigation in the domain mode:
Configuration → Profiles → full → Datasources & Drivers → Datasources
- Select the datasource and click View.
- Click Edit under the Attributes tab.
- Set the Statistics Enabled field to ON and click Save. A popup appears indicating that the changes require a reload in order to take effect.
Reload the server.
- For a standalone server, click the Reload link from the popup to reload the server.
- For a managed domain, click the Topology link from the popup. From the Topology tab, select the appropriate server and select the Reload drop down option to reload the server.
11.11.2. Viewing datasource statistics
You can view runtime statistics for a datasource using the management CLI or management console.
11.11.2.1. View datasource statistics using the management CLI
The following management CLI command retrieves the core pool statistics for the ExampleDS datasource.
In a managed domain, precede these commands with /host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME.
The following management CLI command retrieves the JDBC statistics for the ExampleDS datasource.
Since statistics are runtime information, be sure to specify the `include-runtime=true` argument.
Since statistics are runtime information, be sure to specify the `include-runtime=true` argument.See Datasource Statistics for a detailed list of all available statistics.
11.11.2.2. View datasource statistics using the management console
To view datasource statistics from the management console, navigate to the Datasources subsystem from the Runtime tab, select a datasource, and click View.
See Datasource Statistics for a detailed list of all available statistics.
11.12. Datasource tuning
For tips on monitoring and optimizing performance for the datasources subsystem, see the Datasource and Resource Adapter Tuning section of the Performance tuning for JBoss EAP.
11.13. Capacity policies
JBoss EAP supports defining capacity policies for Jakarta Connectors deployments, including datasources. Capacity policies define how physical connections for a pool are created, referred to as capacity incrementing, and destroyed, referred to as capacity decrementing. The default policies are set to create one connection per request for capacity incrementing, and destroy all connections when they time out when the idle timeout is scheduled for capacity decrementing.
To configure capacity polices, you need to specify a capacity incrementer class, a capacity decrementer class, or both.
Example: Defining capacity policies
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=capacity-incrementer-class, value="org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.SizeIncrementer") /subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=capacity-decrementer-class, value="org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.SizeDecrementer")
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=capacity-incrementer-class, value="org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.SizeIncrementer")
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=capacity-decrementer-class, value="org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.SizeDecrementer")You can also configure properties on the specified capacity incrementer or decrementer class.
Example: Configuring properties for capacity policies
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=capacity-incrementer-properties.size, value=2) /subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=capacity-decrementer-properties.size, value=2)
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=capacity-incrementer-properties.size, value=2)
/subsystem=datasources/data-source=ExampleDS:write-attribute(name=capacity-decrementer-properties.size, value=2)MaxPoolSize incrementer policy
Class name: org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.MaxPoolSizeIncrementer
The MaxPoolSize incrementer policy will fill the pool to its max size for each request. This policy is useful when you want to keep the maximum number of connections available all the time.
Size incrementer policy
Class name: org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.SizeIncrementer
The Size incrementer policy will fill the pool by the specified number of connections for each request. This policy is useful when you want to increment with an additional number of connections per request in anticipation that the next request will also need a connection.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | The number of connections that should be created |
This is the default increment policy, and has a size value of 1.
Watermark incrementer policy
Class name: org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.WatermarkIncrementer
The Watermark incrementer policy will fill the pool to the specified number of connections for each request. This policy is useful when you want to keep a specified number of connections in the pool at all times.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Watermark | The watermark level for the number of connections |
MinPoolSize decrementer policy
Class name: org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.MinPoolSizeDecrementer
The MinPoolSize decrementer policy will decrement the pool to its minimum size for each request. This policy is useful when you want to limit the number of connections after each idle timeout request. The pool will operate in a First In First Out (FIFO) manner.
Size decrementer policy
Class name: org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.SizeDecrementer
The Size decrementer policy will decrement the pool by the specified number of connections for each idle timeout request.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | The number of connections that should be destroyed |
This policy is useful when you want to decrement an additional number of connections per idle timeout request in anticipation that the pool usage will lower over time.
The pool will operate in a First In First Out (FIFO) manner.
TimedOut decrementer policy
Class name: org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.TimedOutDecrementer
The TimedOut decrementer policy will remove all connections that have timed out from the pool for each idle timeout request. The pool will operate in a First In Last Out (FILO) manner.
This policy is the default decrement policy.
TimedOut/FIFO decrementer policy
Class name: org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.TimedOutFIFODecrementer
The TimedOutFIFO decrementer policy will remove all connections that have timed out from the pool for each idle timeout request. The pool will operate in a First In First Out (FIFO) manner.
Watermark decrementer policy
Class name: org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.capacity.WatermarkDecrementer
The Watermark decrementer policy will decrement the pool to the specified number of connections for each idle timeout request. This policy is useful when you want to keep a specified number of connections in the pool at all times. The pool will operate in a First In First Out (FIFO) manner.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Watermark | The watermark level for the number of connections |
11.14. Enlistment tracing
Enlistment traces can be recorded in order to help locate error situations that happen during enlistment of XAResource instances. When enlistment tracing is enabled, the jca subsystem creates an exception object for every pool operation, so that an accurate stack trace can be produced if necessary; however, this does come with performance overhead.
As of JBoss EAP 7.1, enlistment tracing is disabled by default. You can enable the recording of enlistment traces for a datasource using the management CLI by setting the enlistment-trace attribute to true.
Enable enlistment tracing for a non-XA datasource
data-source --name=DATASOURCE_NAME --enlistment-trace=true
data-source --name=DATASOURCE_NAME --enlistment-trace=trueEnable enlistment tracing for an XA datasource
xa-data-source --name=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME --enlistment-trace=true
xa-data-source --name=XA_DATASOURCE_NAME --enlistment-trace=trueEnabling enlistment tracing can cause a performance impact.
11.15. Example Datasource Configurations
11.15.1. Example MySQL datasource
This is an example of a MySQL datasource configuration with connection information, basic security, and validation options.
Example: MySQL datasource configuration
Example: MySQL JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the MySQL JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.mysql --resources=/path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.mysql --resources=/path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the MySQL JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mysql:add(driver-name=mysql,driver-module-name=com.mysql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlXADataSource, driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mysql:add(driver-name=mysql,driver-module-name=com.mysql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlXADataSource, driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the MySQL datasource.
data-source add --name=MySqlDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MySqlDS --driver-name=mysql --connection-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jbossdb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorter
data-source add --name=MySqlDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MySqlDS --driver-name=mysql --connection-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jbossdb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.2. Example MySQL XA datasource
This is an example of a MySQL XA datasource configuration with XA datasource properties, basic security, and validation options.
Example: MySQL XA datasource configuration
Example: MySQL JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the MySQL JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.mysql --resources=/path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.mysql --resources=/path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the MySQL JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mysql:add(driver-name=mysql,driver-module-name=com.mysql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlXADataSource, driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mysql:add(driver-name=mysql,driver-module-name=com.mysql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlXADataSource, driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the MySQL XA datasource.
xa-data-source add --name=MySqlXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MySqlXADS --driver-name=mysql --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorter --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"mysqldb"}xa-data-source add --name=MySqlXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MySqlXADS --driver-name=mysql --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorter --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"mysqldb"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.3. Example PostgreSQL datasource
This is an example of a PostgreSQL datasource configuration with connection information, basic security, and validation options.
Example: PostgreSQL datasource configuration
Example: PostgreSQL JDBC driver module.xml file
In the example above, make sure you replace 42.x.y with your driver version number.
Example management CLI commands
You can add the PostgreSQL JDBC driver and the PostgreSQL datasource to your JDBC API with the following CLI commands.
Add the PostgreSQL JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.postgresql --resources=/path/to/postgresql-42.x.y.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.postgresql --resources=/path/to/postgresql-42.x.y.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the example above, make sure you replace 42.x.y with your driver version number.
ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the PostgreSQL JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=postgresql:add(driver-name=postgresql,driver-module-name=com.postgresql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.postgresql.xa.PGXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=postgresql:add(driver-name=postgresql,driver-module-name=com.postgresql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.postgresql.xa.PGXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the PostgreSQL datasource.
data-source add --name=PostgresDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/PostgresDS --driver-name=postgresql --connection-url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgresdb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLExceptionSorter
data-source add --name=PostgresDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/PostgresDS --driver-name=postgresql --connection-url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgresdb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLExceptionSorterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.4. Example PostgreSQL XA datasource
This is an example of a PostgreSQL XA datasource configuration with XA datasource properties, basic security, and validation options.
Example: PostgreSQL XA datasource configuration
Example: PostgreSQL JDBC driver module.xml file
In the example above, make sure you replace 42.x.y with your driver version number.
Example management CLI commands
You can add the PostgreSQL JDBC driver and the PostgreSQL datasource to your JDBC API with the following CLI commands.
Add the PostgreSQL JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.postgresql --resources=/path/to/postgresql-42.x.y.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.postgresql --resources=/path/to/postgresql-42.x.y.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the example above, make sure you replace 42.x.y with your driver version number.
ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the PostgreSQL JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=postgresql:add(driver-name=postgresql,driver-module-name=com.postgresql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.postgresql.xa.PGXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=postgresql:add(driver-name=postgresql,driver-module-name=com.postgresql,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.postgresql.xa.PGXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the PostgreSQL XA datasource.
xa-data-source add --name=PostgresXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/PostgresXADS --driver-name=postgresql --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLExceptionSorter --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","PortNumber"=>"5432","DatabaseName"=>"postgresdb"}xa-data-source add --name=PostgresXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/PostgresXADS --driver-name=postgresql --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.postgres.PostgreSQLExceptionSorter --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","PortNumber"=>"5432","DatabaseName"=>"postgresdb"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.5. Example Oracle datasource
This is an example of an Oracle datasource configuration with connection information, basic security, and validation options.
Example: Oracle datasource configuration
Example: Oracle JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the Oracle JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.oracle --resources=/path/to/ojdbc7.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.oracle --resources=/path/to/ojdbc7.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the Oracle JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=oracle:add(driver-name=oracle,driver-module-name=com.oracle,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=oracle.jdbc.xa.client.OracleXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=oracle:add(driver-name=oracle,driver-module-name=com.oracle,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=oracle.jdbc.xa.client.OracleXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the Oracle datasource.
data-source add --name=OracleDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/OracleDS --driver-name=oracle --connection-url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleExceptionSorter
data-source add --name=OracleDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/OracleDS --driver-name=oracle --connection-url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleExceptionSorterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.6. Example Oracle XA datasource
The following settings must be applied for the user accessing an Oracle XA datasource in order for XA recovery to operate correctly. The value user is the user defined to connect from JBoss EAP to Oracle:
-
GRANT SELECT ON sys.dba_pending_transactions TO user; -
GRANT SELECT ON sys.pending_trans$ TO user; -
GRANT SELECT ON sys.dba_2pc_pending TO user; -
GRANT EXECUTE ON sys.dbms_xa TO user;
This is an example of an Oracle XA datasource configuration with XA datasource properties, basic security, and validation options.
Example: Oracle XA datasource configuration
Example: Oracle JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the Oracle JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.oracle --resources=/path/to/ojdbc7.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.oracle --resources=/path/to/ojdbc7.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the Oracle JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=oracle:add(driver-name=oracle,driver-module-name=com.oracle,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=oracle.jdbc.xa.client.OracleXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=oracle:add(driver-name=oracle,driver-module-name=com.oracle,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=oracle.jdbc.xa.client.OracleXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the Oracle XA datasource.
xa-data-source add --name=OracleXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/OracleXADS --driver-name=oracle --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --xa-datasource-properties={"URL"=>"jdbc:oracle:thin:@oracleHostName:1521:orcl"}xa-data-source add --name=OracleXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/OracleXADS --driver-name=oracle --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --xa-datasource-properties={"URL"=>"jdbc:oracle:thin:@oracleHostName:1521:orcl"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.7. Example Oracle RAC datasource
This is an example of a Real Application Cluster (RAC) datasource configuration with connection information, basic security, and validation options.
Example: Oracle RAC datasource configuration
Example: Oracle JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
To achieve this example configuration, use the following management CLI commands:
Add the Oracle JDBC driver as a core module:
module add --name=com.oracle --resources=/path/to/ojdbc7.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.oracle --resources=/path/to/ojdbc7.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Register the Oracle JDBC driver:
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=oracle:add(driver-name=oracle,driver-module-name=com.oracle,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=oracle.jdbc.xa.client.OracleXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=oracle:add(driver-name=oracle,driver-module-name=com.oracle,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=oracle.jdbc.xa.client.OracleXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the Oracle RAC datasource:
data-source add --name=OracleDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/OracleDS --driver-name=oracle --connection-url="jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(LOAD_BALANCE=on)(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host1)(PORT=1521))(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host2)(PORT=1521))" --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleExceptionSorter
data-source add --name=OracleDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/OracleDS --driver-name=oracle --connection-url="jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(LOAD_BALANCE=on)(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host1)(PORT=1521))(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host2)(PORT=1521))" --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleExceptionSorterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.8. Example Oracle RAC XA datasource
This is an example of a RAC datasource configuration with XA datasource properties, basic security, and validation options.
Example: Oracle RAC XA datasource configuration
Example: Oracle JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
To achieve this example configuration, use the following management CLI commands:
Add the Oracle JDBC driver as a core module:
module add --name=com.oracle --resources=/path/to/ojdbc7.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.oracle --resources=/path/to/ojdbc7.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Register the Oracle JDBC driver:
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=oracle:add(driver-name=oracle,driver-module-name=com.oracle,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=oracle.jdbc.xa.client.OracleXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=oracle:add(driver-name=oracle,driver-module-name=com.oracle,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=oracle.jdbc.xa.client.OracleXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the Oracle RAC XA datasource:
xa-data-source add --name=OracleXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/OracleXADS --driver-name=oracle --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --xa-datasource-properties={"URL"=>"jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(LOAD_BALANCE=on)(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host1)(PORT=1521))(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host2)(PORT=1521))"}xa-data-source add --name=OracleXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/OracleXADS --driver-name=oracle --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.oracle.OracleExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --xa-datasource-properties={"URL"=>"jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(LOAD_BALANCE=on)(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host1)(PORT=1521))(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=host2)(PORT=1521))"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.9. Example Microsoft SQL server datasource
This is an example of a Microsoft SQL Server datasource configuration with connection information, basic security, and validation options.
Example: Microsoft SQL server datasource configuration
Example: Microsoft SQL server JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the Microsoft SQL Server JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.microsoft --resources=/path/to/sqljdbc42.jar --dependencies=java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,jakarta.xml.bind.api,wildflyee.api,java.se
module add --name=com.microsoft --resources=/path/to/sqljdbc42.jar --dependencies=java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,jakarta.xml.bind.api,wildflyee.api,java.seCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the Microsoft SQL Server JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=sqlserver:add(driver-name=sqlserver,driver-module-name=com.microsoft,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=sqlserver:add(driver-name=sqlserver,driver-module-name=com.microsoft,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the Microsoft SQL Server datasource.
data-source add --name=MSSQLDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MSSQLDS --driver-name=sqlserver --connection-url=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;DatabaseName=MyDatabase --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLExceptionSorter
data-source add --name=MSSQLDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MSSQLDS --driver-name=sqlserver --connection-url=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;DatabaseName=MyDatabase --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLExceptionSorterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.10. Example Microsoft SQL server XA datasource
This is an example of a Microsoft SQL Server XA datasource configuration with XA datasource properties, basic security, and validation options.
Example: Microsoft SQL server XA datasource configuration
Example: Microsoft SQL Server JDBC Driver module.xml File
Example Management CLI Commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the Microsoft SQL Server JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.microsoft --resources=/path/to/sqljdbc42.jar --dependencies=java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,jakarta.xml.bind.api,wildflyee.api,java.se
module add --name=com.microsoft --resources=/path/to/sqljdbc42.jar --dependencies=java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,jakarta.xml.bind.api,wildflyee.api,java.seCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the Microsoft SQL Server JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=sqlserver:add(driver-name=sqlserver,driver-module-name=com.microsoft,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=sqlserver:add(driver-name=sqlserver,driver-module-name=com.microsoft,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the Microsoft SQL Server XA datasource.
xa-data-source add --name=MSSQLXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MSSQLXADS --driver-name=sqlserver --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"mssqldb","SelectMethod"=>"cursor"}xa-data-source add --name=MSSQLXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MSSQLXADS --driver-name=sqlserver --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mssql.MSSQLExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"mssqldb","SelectMethod"=>"cursor"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.11. Example IBM DB2 datasource
This is an example of an IBM DB2 datasource configuration with connection information, basic security, and validation options.
Example: IBM DB2 datasource configuration
Example: IBM DB2 JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the IBM DB2 JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.ibm --resources=/path/to/db2jcc4.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.ibm --resources=/path/to/db2jcc4.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the IBM DB2 JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=ibmdb2:add(driver-name=ibmdb2,driver-module-name=com.ibm,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2XADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=ibmdb2:add(driver-name=ibmdb2,driver-module-name=com.ibm,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2XADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the IBM DB2 datasource.
data-source add --name=DB2DS --jndi-name=java:jboss/DB2DS --driver-name=ibmdb2 --connection-url=jdbc:db2://localhost:50000/ibmdb2db --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ExceptionSorter --min-pool-size=0 --max-pool-size=50
data-source add --name=DB2DS --jndi-name=java:jboss/DB2DS --driver-name=ibmdb2 --connection-url=jdbc:db2://localhost:50000/ibmdb2db --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ExceptionSorter --min-pool-size=0 --max-pool-size=50Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.12. Example IBM DB2 XA datasource
This is an example of an IBM DB2 XA datasource configuration with XA datasource properties, basic security, and validation options.
Example: IBM DB2 XA datasource configuration
Example: IBM DB2 JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the IBM DB2 JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.ibm --resources=/path/to/db2jcc4.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.ibm --resources=/path/to/db2jcc4.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the IBM DB2 JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=ibmdb2:add(driver-name=ibmdb2,driver-module-name=com.ibm,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2XADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=ibmdb2:add(driver-name=ibmdb2,driver-module-name=com.ibm,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2XADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the IBM DB2 XA datasource.
xa-data-source add --name=DB2XADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/DB2XADS --driver-name=ibmdb2 --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --recovery-plugin-class-name=org.jboss.jca.core.recovery.ConfigurableRecoveryPlugin --recovery-plugin-properties={"EnableIsValid"=>"false","IsValidOverride"=>"false","EnableClose"=>"false"} --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"ibmdb2db","PortNumber"=>"50000","DriverType"=>"4"}xa-data-source add --name=DB2XADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/DB2XADS --driver-name=ibmdb2 --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.db2.DB2ExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --recovery-plugin-class-name=org.jboss.jca.core.recovery.ConfigurableRecoveryPlugin --recovery-plugin-properties={"EnableIsValid"=>"false","IsValidOverride"=>"false","EnableClose"=>"false"} --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"ibmdb2db","PortNumber"=>"50000","DriverType"=>"4"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.13. Example Sybase datasource
This is an example of a Sybase datasource configuration with connection information, basic security, and validation options.
Example: Sybase datasource configuration
Example: Sybase JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the Sybase JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.sybase --resources=/path/to/jconn4.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.sybase --resources=/path/to/jconn4.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the Sybase JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=sybase:add(driver-name=sybase,driver-module-name=com.sybase,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.sybase.jdbc4.jdbc.SybXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=sybase:add(driver-name=sybase,driver-module-name=com.sybase,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.sybase.jdbc4.jdbc.SybXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the Sybase datasource.
data-source add --name=SybaseDB --jndi-name=java:jboss/SybaseDB --driver-name=sybase --connection-url=jdbc:sybase:Tds:localhost:5000/DATABASE?JCONNECT_VERSION=6 --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseExceptionSorter
data-source add --name=SybaseDB --jndi-name=java:jboss/SybaseDB --driver-name=sybase --connection-url=jdbc:sybase:Tds:localhost:5000/DATABASE?JCONNECT_VERSION=6 --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseExceptionSorterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.14. Example Sybase XA datasource
This is an example of a Sybase XA datasource configuration with XA datasource properties, basic security, and validation options.
Example: Sybase XA datasource configuration
Example: Sybase JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the Sybase JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=com.sybase --resources=/path/to/jconn4.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api
module add --name=com.sybase --resources=/path/to/jconn4.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.apiCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the Sybase JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=sybase:add(driver-name=sybase,driver-module-name=com.sybase,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.sybase.jdbc4.jdbc.SybXADataSource)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=sybase:add(driver-name=sybase,driver-module-name=com.sybase,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=com.sybase.jdbc4.jdbc.SybXADataSource)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the Sybase XA datasource.
xa-data-source add --name=SybaseXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/SybaseXADS --driver-name=sybase --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"mydatabase","PortNumber"=>"4100","NetworkProtocol"=>"Tds"}xa-data-source add --name=SybaseXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/SybaseXADS --driver-name=sybase --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.sybase.SybaseExceptionSorter --same-rm-override=false --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"mydatabase","PortNumber"=>"4100","NetworkProtocol"=>"Tds"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.15. Example MariaDB datasource
This is an example of a MariaDB datasource configuration with connection information, basic security, and validation options.
Example: MariaDB datasource configuration
Example: MariaDB JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the MariaDB JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=org.mariadb --resources=/path/to/mariadb-java-client-3.3.0.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,org.slf4j
module add --name=org.mariadb --resources=/path/to/mariadb-java-client-3.3.0.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,org.slf4jCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the MariaDB JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mariadb:add(driver-name=mariadb,driver-module-name=org.mariadb,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.MySQLDataSource, driver-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mariadb:add(driver-name=mariadb,driver-module-name=org.mariadb,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.MySQLDataSource, driver-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the MariaDB datasource.
data-source add --name=MariaDBDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MariaDBDS --driver-name=mariadb --connection-url=jdbc:mariadb://localhost:3306/jbossdb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorter
data-source add --name=MariaDBDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MariaDBDS --driver-name=mariadb --connection-url=jdbc:mariadb://localhost:3306/jbossdb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.16. Example MariaDB XA datasource
This is an example of a MariaDB XA datasource configuration with XA datasource properties, basic security, and validation options.
Example: MariaDB XA datasource configuration
Example: MariaDB JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the MariaDB JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=org.mariadb --resources=/path/to/mariadb-java-client-3.3.0.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,org.slf4j
module add --name=org.mariadb --resources=/path/to/mariadb-java-client-3.3.0.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,org.slf4jCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the MariaDB JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mariadb:add(driver-name=mariadb,driver-module-name=org.mariadb,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.MySQLDataSource, driver-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mariadb:add(driver-name=mariadb,driver-module-name=org.mariadb,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.MySQLDataSource, driver-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the MariaDB XA datasource.
xa-data-source add --name=MariaDBXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MariaDBXADS --driver-name=mariadb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorter --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"mariadbdb"}xa-data-source add --name=MariaDBXADS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MariaDBXADS --driver-name=mariadb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorter --xa-datasource-properties={"ServerName"=>"localhost","DatabaseName"=>"mariadbdb"}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
11.15.17. Example MariaDB Galera Cluster datasource
This is an example of a MariaDB Galera Cluster datasource configuration with connection information, basic security, and validation options.
MariaDB Galera Cluster does not support XA transactions.
Example: MariaDB Galera Cluster datasource configuration
Example: MariaDB JDBC driver module.xml file
Example management CLI commands
This example configuration can be achieved by using the following management CLI commands.
Add the MariaDB JDBC driver as a core module.
module add --name=org.mariadb --resources=/path/to/mariadb-java-client-3.3.0.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,org.slf4j
module add --name=org.mariadb --resources=/path/to/mariadb-java-client-3.3.0.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api,org.slf4jCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantUsing the
modulemanagement CLI command to add and remove modules is provided as Technology Preview only. This command is not appropriate for use in a managed domain or when connecting to the management CLI remotely. Modules should be added and removed manually in a production environment.Technology Preview features are not supported with Red Hat production service level agreements (SLAs), might not be functionally complete, and Red Hat does not recommend to use them for production. These features provide early access to upcoming product features, enabling customers to test functionality and provide feedback during the development process.
See Technology Preview Features Support Scope on the Red Hat Customer Portal for information about the support scope for Technology Preview features.
Register the MariaDB JDBC driver.
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mariadb:add(driver-name=mariadb,driver-module-name=org.mariadb,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.MySQLDataSource, driver-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver)
/subsystem=datasources/jdbc-driver=mariadb:add(driver-name=mariadb,driver-module-name=org.mariadb,driver-xa-datasource-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.MySQLDataSource, driver-class-name=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the MariaDB Galera Cluster datasource.
data-source add --name=MariaDBGaleraClusterDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MariaDBGaleraClusterDS --driver-name=mariadb --connection-url=jdbc:mariadb://192.168.1.1:3306,192.168.1.2:3306/jbossdb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorter
data-source add --name=MariaDBGaleraClusterDS --jndi-name=java:jboss/MariaDBGaleraClusterDS --driver-name=mariadb --connection-url=jdbc:mariadb://192.168.1.1:3306,192.168.1.2:3306/jbossdb --user-name=admin --password=admin --validate-on-match=true --background-validation=false --valid-connection-checker-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLValidConnectionChecker --exception-sorter-class-name=org.jboss.jca.adapters.jdbc.extensions.mysql.MySQLExceptionSorterCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 12. Configuring the transactions subsystem
12.1. Configuring the transactions subsystem
When you manage an enterprise application that processes financial transactions, order management, or other critical workflows, you need to ensure reliable operations and data consistency. The transactions subsystem in JBoss EAP gives you full control over the Transaction Manager ™, letting you configure timeout values, enable transaction logging, and collect statistics. If your application runs across multiple systems and transaction propagation is required then at least one of JBoss Remoting or JTS needs to be enabled.
JBoss EAP uses the Narayana transaction manager to handle transactions efficiently. It supports industry-standard protocols like Jakarta Transactions, JTS, and Web Services Transactions. Whether you update databases, send messages, or coordinate distributed services, the transactions subsystem ensures consistency, reliability, and resilience.
Please note that this link directs you to the Managing Transactions Guide for JBoss EAP 7.4. We are currently in the process of updating the documentation for Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 8.0. This link will be updated once the new documentation is complete.
Chapter 13. ORB configuration
This chapter guides you through configuring the Object Request Broker (ORB) to support Java Transaction Service (JTS) and ensure secure communications via SSL/TLS in JBoss EAP.
13.1. Understanding Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA)
Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) is a standard that allows applications and services to interoperate across different programming languages and platforms through a component called the Object Request Broker (ORB). JBoss EAP provides an ORB instance, by means of the Open JDK ORB component.
The ORB is used internally for JTS transactions, and is also available for use by your own applications.
The Object Transaction Service (OTS) is a cross-platform service that forms part of CORBA. The OTS specification is maintained by the Object Management Group. JTS is a specification for building a transaction manager, and JTS was designed based on the OTS specification.
13.2. Configuring the ORB for JTS using the management CLI and management console
This section provides steps to configure the Object Request Broker (ORB) for Java Transaction Service (JTS) using both the management CLI and management console in JBoss EAP. Configuring the ORB ensures robust transactional capabilities for distributed environments.
Prerequisites
- You have installed JBoss EAP.
- You have access to the management CLI and the management console with administrative privileges.
You can use this procedure in standalone or domain mode. If you decide to use standalone mode, then please do not use the profile=full prefix and use standalone-full.xml configuration.
Enable security interceptors:
Using the management CLI, execute the following command to set the
securityattribute toidentity:/profile=full/subsystem=iiop-openjdk:write-attribute(name=security,value=identity)
/profile=full/subsystem=iiop-openjdk:write-attribute(name=security,value=identity)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, using the management console:
- Navigate to the Configuration tab.
- Select Subsystems → IIOP (OpenJDK) → View.
- Click Edit, modify the attributes as needed, and click Save.
Enable transactions in the IIOP subsystem:
To enable ORB for JTS, set the
transactionsattribute tofullusing the CLI:/profile=full/subsystem=iiop-openjdk:write-attribute(name=transactions,value=full)
/profile=full/subsystem=iiop-openjdk:write-attribute(name=transactions,value=full)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the management console:
- Navigate to Subsystems → IIOP (OpenJDK) → View.
- Click Edit, modify the attributes as needed, and click Save.
Enable JTS in the Transactions subsystem:
Using the CLI, set the
jtsattribute totrue:/profile=full/subsystem=transactions:write-attribute(name=jts,value=true)
/profile=full/subsystem=transactions:write-attribute(name=jts,value=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the management console:
- Navigate to Subsystems → Transactions → View.
- Click Edit, modify the attributes as needed, and click Save.
Restart the server:
A full server restart is required to activate JTS, as a simple reload is insufficient.
Verification
Verify the configuration using the CLI by reading the attribute settings:
/profile=full/subsystem=iiop-openjdk:read-resource
/profile=full/subsystem=iiop-openjdk:read-resourceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Alternatively, check the updated attributes in the management console after the server restart.
13.3. Configuring IIOP to use SSL/TLS
You can configure the iiop-openjdk subsystem to use SSL/TLS for secure communication between clients and servers. The steps below outline how to configure SSL/TLS for the IIOP subsystem.
Prerequisites
- You have installed JBoss EAP.
- You have access to the management CLI or management console with administrative privileges.
Procedure
Create a
server-ssl-context:/subsystem=elytron/server-ssl-context=<server-ssl-context_name>:add(key-manager=<key-manager_name>, protocols=<list_of_protocols>)
/subsystem=elytron/server-ssl-context=<server-ssl-context_name>:add(key-manager=<key-manager_name>, protocols=<list_of_protocols>)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For a working example of creating a
server-ssl-context, please refer to the latest JBoss EAP security guide: Configuring SSL/TLS in JBoss EAP guide.To use SSL/TLS with the
iiop-openjdksubsystem, you need to define aserver-ssl-context. JBoss EAP uses the configuration provided by theserver-ssl-contextwhen making an SSL/TLS connection as a server. You can find more information aboutserver-ssl-contextattributes in the Configuring SSL/TLS in JBoss EAP guide.Create a
client-ssl-context. For example:/subsystem=elytron/client-ssl-context=exampleCSC:add(key-manager=applicationKM, protocols=["TLSv1.2"])
/subsystem=elytron/client-ssl-context=exampleCSC:add(key-manager=applicationKM, protocols=["TLSv1.2"])Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To use SSL/TLS with the
iiop-openjdksubsystem, you need to define aclient-ssl-context. JBoss EAP uses the configuration provided by theclient-ssl-contextwhen making an SSL/TLS connection as a client. You can find more details on creating aclient-ssl-contextin Using a client-ssl-context in the How to Configure Server Security guide.NotePlease note that this link directs you to the JBoss EAP security guide for JBoss EAP 7.4. We are currently in the process of updating the documentation for Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 8.0. This link will be updated once the new documentation is complete.
Configure the
iiop-openjdksubsystem to use theclient-ssl-contextandserver-ssl-context.Example: Setting
client-ssl-contextandserver-ssl-contextCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the connection to and from the
iiop-openjdksubsystem.You can indicate whether or not SSL/TLS connections are required when connecting to and from the
iiop-openjdksubsystem by adjusting the following attributes:-
To enable support for SSL in the
iiop-openjdksubsystem, setsupport-ssltotrue. Defaults tofalse. -
To require SSL/TLS connections from the
iiop-openjdksubsystem, setclient-requires-ssltotrue. Defaults tofalse. -
To require SSL/TLS connections to the
iiop-openjdksubsystem, setserver-requires-ssltotrue. Defaults tofalse. Note that setting this totruewill block attempts to connect to the non-SSL IIOP socket. -
To adjust the
socket-binding, setssl-socket-bindingto the desired binding. Defaults toiiop-ssl.
Example: Setting SSL/TLS Connections to and from IIOP as Required
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
To enable support for SSL in the
Chapter 14. Jakarta Connectors Management
14.1. About Jakarta connectors
Jakarta Connectors defines a standard architecture for Jakarta EE systems to interact with external heterogeneous Enterprise Information Systems (EIS). Examples of EISs include Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, mainframe transaction processing (TP), databases, and messaging systems. A resource adapter is a component that implements the Jakarta Connectors architecture.
Jakarta Connectors 1.7 provides features for managing:
- Connections
- Transactions
- Security
- Life-cycle
- Work instances
- Transaction inflow
- Message inflow
14.2. About resource adapters
A resource adapter is a deployable Jakarta EE component that provides communication between a Jakarta EE application and an Enterprise Information System (EIS) using the Jakarta Connectors specification. A resource adapter is often provided by EIS vendors to allow easy integration of their products with Jakarta EE applications.
An Enterprise Information System can be any other software system within an organization. Examples include Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, database systems, email servers, and proprietary messaging systems.
A resource adapter is packaged in a Resource Adapter Archive (RAR) file, which can be deployed to JBoss EAP. A RAR file may also be included in an Enterprise Archive (EAR) deployment.
The resource adapter itself is defined within the resource-adapters subsystem, which is provided by the IronJacamar project.
14.3. Configuring the jca Subsystem
The jca subsystem controls the general settings for the Jakarta Connectors container and resource adapter deployments. You can configure the jca subsystem using the management console or the management CLI.
The main jca subsystem elements to configure are:
14.3.1. jca subsystem settings in the management console
You can configure the jca subsystem from the management console by navigating to Configuration → Subsystems → JCA and clicking View. Then, select the appropriate tab:
Configuration
Contains settings for the cached connection manager, archive validation, and bean validation. Modify these settings by opening the appropriate tab and clicking the Edit link.
Bootstrap Context
Contains the list of configured bootstrap contexts. New bootstrap context objects can be added, removed, and configured. Each bootstrap context must be assigned a work manager.
Workmanager
Contains the list of configured work managers. New work managers can be added, removed, and their thread pools configured here. Each work manager can have one short-running thread pool and an optional long-running thread pool.
The thread pool attributes can be configured by clicking Thread Pools on the selected work manager.
14.3.2. jca subsystem settings in the management CLI
You can configure the jca subsystem using the management CLI by following the steps in this procedure.
Procedure
-
Configure the
jcasubsystem using the management CLI:
/subsystem=jca
/subsystem=jcaIn a managed domain, you must precede the command with:
/profile=PROFILE_NAME
/profile=PROFILE_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Attribute names in the tables in the following sections are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-jca_5_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
14.3.3. Archive validation
This determines whether archive validation will be performed on the deployment units. The following table describes the attributes you can set for archive validation.
| Attribute | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Specifies whether archive validation is enabled. |
|
|
| Specifies whether an archive validation error report fails the deployment. |
|
|
| Specifies whether an archive validation warning report fails the deployment. |
If archive validation is not specified, it is considered present, and the enabled attribute defaults to true.
Example error messages during deployment
14.3.4. Bean validation
Bean validation determines whether bean validation is performed. For information about the specification, see the Jakarta Bean Validation specification.
| Attribute | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
| Specifies whether bean validation is enabled. |
If bean validation is not specified, it is considered present, and the enabled attribute defaults to true.
14.3.5. Work managers
Work managers manage work instances within the Jakarta Connectors subsystem. There are two types of work managers:
Default work manager
The default work manager and its thread pools.
Custom work manager
A custom work manager definition and its thread pools.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Specifies the name of the work manager. |
|
| Enables Elytron security for the work manager. |
A work manager also has the following child elements:
| Child Element | Description |
|---|---|
| short-running-threads | Thread pool for standard Work instances. Each work manager has one short-running thread pool. |
| long-running-threads |
Thread pool for Jakarta Connectors 1.7 Work instances that set the |
The following table describes the attributes you can set for work manager thread pools.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| allow-core-timeout |
Boolean setting that determines whether core threads may time out. The default value is |
| core-threads | The core thread pool size. This must be equal to or smaller than the maximum thread pool size. |
| handoff-executor | An executor to delegate tasks to in the event that a task cannot be accepted. If not specified, tasks that cannot be accepted will be silently discarded. |
| keepalive-time | Specifies the amount of time that pool threads should be kept after doing work. |
| max-threads | The maximum thread pool size. |
| name | Specifies the name of the thread pool. |
| queue-length | The maximum queue length. |
| thread-factory | Reference to the thread factory. |
14.3.6. Distributed work managers
A distributed work manager is a work manager instance that is able to reschedule work execution on another work manager instance.
The following example management CLI commands configure a distributed work manager. Note that you must use a configuration that provides high availability capabilities, such as the standalone-ha.xml or standalone-full-ha.xml configuration file for a standalone server.
Example: Configure a distributed work manager
batch /subsystem=jca/distributed-workmanager=myDistWorkMgr:add(name=myDistWorkMgr) /subsystem=jca/distributed-workmanager=myDistWorkMgr/short-running-threads=myDistWorkMgr:add(queue-length=10,max-threads=10) /subsystem=jca/bootstrap-context=myCustomContext:add(name=myCustomContext,workmanager=myDistWorkMgr) run-batch
batch
/subsystem=jca/distributed-workmanager=myDistWorkMgr:add(name=myDistWorkMgr)
/subsystem=jca/distributed-workmanager=myDistWorkMgr/short-running-threads=myDistWorkMgr:add(queue-length=10,max-threads=10)
/subsystem=jca/bootstrap-context=myCustomContext:add(name=myCustomContext,workmanager=myDistWorkMgr)
run-batch
The name of the short-running-threads element must be the same as the name of the distributed-workmanager element.
The following table describes the attributes you can configure for distributed work managers.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| elytron-enabled | Enables Elytron security for the work manager. |
| name | The name of the distributed work manager. |
| policy | The policy decides when to redistribute a work instance. Allowed values are:
|
| policy-options |
List of the policy’s key/value pair options. If you use the /subsystem=jca/distributed-workmanager=myDistWorkMgr:write-attribute(name=policy-options,value={watermark=3})
|
| selector | The selector decides to which nodes in the network to redistribute the work instance. Allowed values are:
|
| selector-options | List of the selector’s key/value pair options. |
A distributed work manager also has the following child elements.
| Child Element | Description |
|---|---|
| long-running-threads |
The thread pool for work instances that set the |
| short-running-threads | The thread pool for standard work instances. Each distributed work manager must have a short-running thread pool. |
14.3.7. Bootstrap Contexts
This is used to define custom bootstrap contexts. The following table describes the attributes you can set for bootstrap contexts.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| name | Specifies the name of the bootstrap context. |
| workmanager | Specifies the name of the work manager to use for this context. |
14.3.8. Cached connection manager
A cached connection manager is used for debugging connections and supporting lazy enlistment of a connection in a transaction, tracking whether they are used and released properly by the application. The following table describes the attributes you can set for the cached connection manager.
| Attribute | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| debug | false | Outputs warning on failure to explicitly close connections. |
| error | false | Throws exception on failure to explicitly close connections. |
| ignore-unknown-connections | false | Specifies that unknown connections will not be cached. |
| install | false | Enable or disable the cached connection manager valve and interceptor. |
14.3.9. Deploying a resource adapter using the management CLI
Use the management CLI to deploy a resource adapter.
Prerequisites
- Access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Deploy the resource adapter to a standalone server:
---- deploy /path/to/resource-adapter.rar ----
---- deploy /path/to/resource-adapter.rar ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Deploy the resource adapter to all server groups in a managed domain:
---- deploy /path/to/resource-adapter.rar --all-server-groups ----
---- deploy /path/to/resource-adapter.rar --all-server-groups ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.3.10. Deploying a resource adapter using the management console
Use the management console to deploy a resource adapter.
Prerequisites
- Access to the management console.
Procedure
- Log in to the management console.
- Navigate to the Deployments tab.
Click the Add (+) button.
- In a managed domain, you will first need to select Content Repository.
- Choose the Upload Deployment option.
- Browse to the resource adapter archive and click Next.
- Verify the upload, then click Finish.
- In a managed domain, deploy the deployment to the appropriate server groups and enable the deployment
14.3.11. Deploying a resource adapter using the deployment scanner
Deploy a resource adapter using the deployment scanner in a standalone server.
Prerequisites
- Access to the file system of the server.
Procedure
-
To deploy a resource adapter manually to a standalone server, copy the resource adapter archive to the server deployments directory, for example,
EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments/. This will be picked up and deployed by the deployment scanner.
This option is not available for managed domains. You must use either the management console or the management CLI to deploy the resource adapter to server groups.
14.4. Configuring a resource adapter
You can configure resource adapters using the management interfaces. The below example shows how to configure a resource adapter using the management CLI. See your resource adapter vendor’s documentation for supported properties and other important information.
14.4.1. Adding the resource adapter configuration
Add the resource adapter configuration using the management CLI.
Prerequisites
- Access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Add the resource adapter configuration:
/subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar:add(archive=eis.rar, transaction-support=XATransaction)
/subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar:add(archive=eis.rar, transaction-support=XATransaction)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.4.2. Configuring the resource adapter settings
Resource adapter settings manage connections between the application server and external systems; configure them to optimize integration and performance.
Prerequisites
- The resource adapter configuration has been added.
- You have access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Configure
config-properties:Add the
serverconfiguration property:---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/config-properties=server:add(value=localhost) -------- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/config-properties=server:add(value=localhost) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the
portconfiguration property:---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/config-properties=port:add(value=9000) -------- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/config-properties=port:add(value=9000) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Configure
admin-objects:Add an admin object:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/admin-objects=aoName:add(class-name=com.acme.eis.ra.EISAdminObjectImpl, jndi-name=java:/eis/AcmeAdminObject) -------- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/admin-objects=aoName:add(class-name=com.acme.eis.ra.EISAdminObjectImpl, jndi-name=java:/eis/AcmeAdminObject) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure an admin object configuration property:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/admin-objects=aoName/config-properties=threshold:add(value=10) -------- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/admin-objects=aoName/config-properties=threshold:add(value=10) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Configure
connection-definitions:Add a connection definition for a managed connection factory:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/connection-definitions=cfName:add(class-name=com.acme.eis.ra.EISManagedConnectionFactory, jndi-name=java:/eis/AcmeConnectionFactory) -------- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/connection-definitions=cfName:add(class-name=com.acme.eis.ra.EISManagedConnectionFactory, jndi-name=java:/eis/AcmeConnectionFactory) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure a managed connection factory configuration property:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/connection-definitions=cfName/config-properties=name:add(value=Acme Inc) -------- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/connection-definitions=cfName/config-properties=name:add(value=Acme Inc) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure whether to record the enlistment trace:
Enable the recording of enlistment traces by setting the
enlistment-traceattribute totrue:---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/connection-definitions=cfName:write-attribute(name=enlistment-trace,value=true) -------- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar/connection-definitions=cfName:write-attribute(name=enlistment-trace,value=true) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningEnabling enlistment tracing makes tracking down errors during transaction enlistment easier, but comes with a performance impact.
14.4.3. Activating the resource adapter
Activate the resource adapter after it has been configured.
Prerequisites
- The resource adapter has been configured.
- Access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Activate the resource adapter:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar:activate ----
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=eis.rar:activate ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
You can also define capacity policies for resource adapters. For more details, see the Capacity Policies section.
14.5. Configuring resource adapters to use the Elytron subsystem
Resource adapters in IronJacamar involve two types of communications between the server and the resource adapter:
- One of the types is when the server opens a resource adapter connection. This can be secured by container-managed sign-on, which requires propagation of a JAAS subject with principal and credentials to the resource adapter when opening the connection. This sign-on can be delegated to Elytron.
- When a resource adapter establishes security information when submitting work to the work manager or delivering messages to endpoints within the same JBoss EAP instance. This mechanism is known as security inflow.
14.5.1. Container-managed sign-On with Elytron
In order to achieve container-managed sign-on with Elytron, the elytron-enabled attribute needs to be set to true. This will result in all connections to the resource adapter to be secured by Elytron.
/subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=<RAR_NAME>/connection-definitions=<FACTORY_NAME>:write-attribute(name=elytron-enabled,value=true)
/subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=<RAR_NAME>/connection-definitions=<FACTORY_NAME>:write-attribute(name=elytron-enabled,value=true)
The elytron-enabled attribute can be configured using the management CLI by setting the elytron-enabled attribute, in the resource-adapters subsystems, to true. By default this attribute is set to false.
The authentication-context attribute defines the name of the Elytron authentication context that will be used for performing sign-on.
An Elytron authentication-context attribute can contain one or more authentication-configuration elements, which in turn contains the credentials you want to use.
If the authentication-context attribute is not set, JBoss EAP will use the current authentication-context, which is the authentication-context used by the caller code that is opening the connection.
Example: Creating an authentication-configuration
/subsystem=elytron/authentication-configuration=exampleAuthConfig:add(authentication-name=sa,credential-reference={clear-text=sa})
/subsystem=elytron/authentication-configuration=exampleAuthConfig:add(authentication-name=sa,credential-reference={clear-text=sa})Example: Creating the authentication-context Using the above Configuration
/subsystem=elytron/authentication-context=exampleAuthContext:add(match-rules=[{authentication-configuration=exampleAuthConfig}])
/subsystem=elytron/authentication-context=exampleAuthContext:add(match-rules=[{authentication-configuration=exampleAuthConfig}])14.5.2. Security Inflow with Elytron
Security inflow enables a resource adapter to establish security information when submitting work to the work manager or delivering messages to endpoints within the same JBoss EAP instance. This allows the work to authenticate itself before execution using Elytron. If authentication succeeds, the submitted work will be executed under the resulting authentication context. If it fails, the work execution will be rejected.
To enable Elytron security inflow, set the wm-elytron-security-domain attribute when configuring the resource adapter’s work manager.
-
When the resource adapter work manager is configured to use the Elytron security domain,
wm-elytron-security-domain, the referenced work manager should have theelytron-enabledattribute set totrue.
/subsystem=jca/workmanager=customWM:add(name=customWM, elytron-enabled=true)
/subsystem=jca/workmanager=customWM:add(name=customWM, elytron-enabled=true)-
If instead of
wm-elytron-security-domainthewm-security-domainattribute is used, the security inflow will be performed by the legacysecuritysubsystem.
In the example configuration of jca subsystem below, we can see the configuration of a resource adapter called ra-with-elytron-security-domain. This resource adapter configures work manager security to use the Elytron security domain’s wm-realm.
The work manager is then referenced using the boostrap context from the resource-adapter subsystem.
Example: Configuration of the Security Domain
The Work class is responsible for providing the credentials for Elytron’s authentication under the specified domain. For that, it must implement jakarta.resource.spi.work.WorkContextProvider.
This interface allows the Work class to use the WorkContext to configure some aspects of the context in which the work will be executed. One of those aspects is the security inflow. For that, the List<WorkContext> getWorkContexts method must provide a jakarta.resource.spi.work.SecurityContext. This context will use jakarta.security.auth.callback.Callback objects as defined by Jakarta Authentication.
Example: Creation of Callbacks Using Context
In the above example, ExampleWork implements the WorkContextProvider interface to provide ExampleSecurityContext. That context will create the callbacks necessary to provide the security information that will be authenticated by Elytron upon work execution.
Additional resources
14.6. Configuring Managed Connection Pools
JBoss EAP provides three implementations of the ManagedConnectionPool interface:
-
org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.mcp.SemaphoreConcurrentLinkedQueueManagedConnectionPool: This is the default connection pool in JBoss EAP 7 and provides the best out-of-the-box performance. -
org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.mcp.SemaphoreArrayListManagedConnectionPool: This was the default connection pool in previous JBoss EAP versions. -
org.jboss.jca.core.connectionmanager.pool.mcp.LeakDumperManagedConnectionPool: This connection pool is used for debugging purposes only and will report any leaks upon shutdown or when the pool is flushed.
Prerequisites
- Access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Set the managed connection pool implementation for a datasource:
---- /subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATA_SOURCE:write-attribute(name=mcp,value=MCP_CLASS) ----
---- /subsystem=datasources/data-source=DATA_SOURCE:write-attribute(name=mcp,value=MCP_CLASS) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the managed connection pool implementation for a resource adapter:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:write-attribute(name=mcp,value=MCP_CLASS) ----
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:write-attribute(name=mcp,value=MCP_CLASS) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the managed connection pool implementation for a messaging server:
---- /subsystem=messaging-activemq/server=SERVER/pooled-connection-factory=CONNECTION_FACTORY:write-attribute(name=managed-connection-pool,value=MCP_CLASS) ----
---- /subsystem=messaging-activemq/server=SERVER/pooled-connection-factory=CONNECTION_FACTORY:write-attribute(name=managed-connection-pool,value=MCP_CLASS) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
14.7. Viewing connection statistics
Read statistics for a defined connection from the /deployment=NAME.rar subtree. This allows you to access statistics for any RAR, even if it is not defined in a standalone.xml or domain.xml configuration.
Prerequisites
- Access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Run the following command to read the connection statistics:
---- /deployment=NAME.rar/subsystem=resource-adapters/statistics=statistics/connection-definitions=java\:\/testMe:read-resource(include-runtime=true) ----
---- /deployment=NAME.rar/subsystem=resource-adapters/statistics=statistics/connection-definitions=java\:\/testMe:read-resource(include-runtime=true) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Be sure to specify the include-runtime=true argument, as all statistics are runtime-only information.
14.8. Flushing resource adapter connections
You can flush resource adapter connections using the following management CLI commands.
In a managed domain, you must precede these commands with /host=HOST_NAME/server=SERVER_NAME/.
Prerequisites
- Access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Flush all connections in the pool:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:flush-all-connection-in-pool ----
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:flush-all-connection-in-pool ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Gracefully flush all connections in the pool:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:flush-gracefully-connection-in-pool ----
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:flush-gracefully-connection-in-pool ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The server will wait until connections become idle before flushing them.
The server will wait until connections become idle before flushing them.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Flush all idle connections in the pool:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:flush-idle-connection-in-pool ----
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:flush-idle-connection-in-pool ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Flush all invalid connections in the pool:
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:flush-invalid-connection-in-pool ----
---- /subsystem=resource-adapters/resource-adapter=RESOURCE_ADAPTER/connection-definitions=CONNECTION_DEFINITION:flush-invalid-connection-in-pool ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The server will flush all connections that it determines to be invalid.
The server will flush all connections that it determines to be invalid.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Theses procedures are not sequential.
Chapter 15. Configuring the Web Server (Undertow) in JBoss EAP
This chapter focuses on configuring the Undertow web server, the default server embedded within JBoss EAP. Here, you will find detailed instructions on enabling SSL/TLS for secure communication, leveraging HTTP/2 for enhanced performance, and fine-tuning server settings to align with your operational requirements.
15.1. Undertow subsystem overview
In JBoss EAP 8.0, the Undertow subsystem serves as the web layer within the application server. It provides the core web server and servlet container functionality, supporting advanced features like the Jakarta Servlet 6.0 specification, websockets, and HTTP upgrade. Undertow can also act as a high-performance reverse proxy with mod_cluster support, contributing to improved scalability, efficiency, and flexibility in handling web traffic.
The undertow subsystem allows you to configure the web server and servlet container settings. It implements the Jakarta Servlet 6.0 Specification as well as websockets. It also supports HTTP upgrade and using high performance non-blocking handlers in servlet deployments. The undertow subsystem also has the ability to act as a high performance reverse proxy which supports mod_cluster.
Within the undertow subsystem, there are five main components to configure:
- Buffer caches
- Server
- Servlet container
- Handlers
- Filters
While JBoss EAP does offer the ability to update the configuration for each of these components, the default configuration is suitable for most use cases and provides reasonable performance settings.
Default undertow subsystem configuration
The undertow subsystem also relies on the io subsystem to provide XNIO workers and buffer pools. The io subsystem is configured separately and provides a default configuration which should give optimal performance in most cases.
15.1.1. Using Elytron with undertow subsystem
As a web application is deployed, the name of the security domain required by that application will be identified. This will either be from within the deployment or, if the deployment does not have a security domain, the default-security-domain as defined in the undertow subsystem will be assumed. By default, the default-security-domain is ApplicationDomain. To ensure proper mapping from the name of the security domain required by the application to the appropriate Elytron configuration, an application-security-domain resource can be added to the undertow subsystem.
Example: Adding a mapping.
/subsystem=undertow/application-security-domain=ApplicationDomain:add(security-domain=ApplicationDomain)
/subsystem=undertow/application-security-domain=ApplicationDomain:add(security-domain=ApplicationDomain)The addition of mapping is successful if the result is:
- If the deployment was already deployed at this point, the application server should be reloaded for the application security domain mapping to take effect.
- In current web service-Elytron integration, the name of the security domain specified to secure a web service endpoint and the Elytron security domain name must be the same.
This simple form is suitable where a deployment is using the standard HTTP mechanism as defined within the Servlet specification like BASIC, CLIENT_CERT, DIGEST, FORM. Here, the authentication will be performed against the ApplicationDomain security domain. This form is also suitable where an application is not using any authentication mechanism and instead is using programmatic authentication or is trying to obtain the SecurityDomain associated with the deployment and use it directly.
Example: Advanced form of the mapping:
/subsystem=undertow/application-security-domain=MyAppSecurity:add(http-authentication-factory=application-http-authentication)
/subsystem=undertow/application-security-domain=MyAppSecurity:add(http-authentication-factory=application-http-authentication)The advanced mapping is successful if the result is:
In this form of the configuration, instead of referencing a security domain, an http-authentication-factory is referenced. This is the factory that will be used to obtain the instances of the authentication mechanisms and is in turn associated with the security domain.
You should reference an http-authentication-factory attribute when using custom HTTP authentication mechanisms or where additional configuration must be defined for mechanisms such as principal transformers, credential factories, and mechanism realms. It is also better to reference an http-authentication-factory attribute when using mechanisms other than the four described in the Servlet specification.
When the advanced form of mapping is used, another configuration option is available, override-deployment-config. The referenced http-authentication-factory can return a complete set of authentication mechanisms. By default, these are filtered to just match the mechanisms requested by the application. If this option is set to true, then the mechanisms offered by the factory will override the mechanisms requested by the application.
The application-security-domain resource also has one additional option enable-jacc. If this is set to true, Java Authorization Contract for Containers will be enabled for any deployments matching this mapping.
15.1.1.1. Runtime information
Where an application-security-domain mapping is in use, it can be useful to double check that deployments did match against it as expected. If the resource is read with include-runtime=true, the deployments that are associated with the mapping will also be shown as:
In this output, the referencing-deployments attribute shows that the deployment simple-webapp.war has been deployed using the mapping.
15.1.2. Configuring buffer caches
This procedure guides you through configuring buffer caches in JBoss EAP, which help cache static resources to improve performance. Different deployments can use different cache sizes to optimize resource management. The total amount of space used can be calculated by multiplying the buffer size by the number of buffers per region by the maximum number of regions. The default size of a buffer cache is 10MB.
JBoss EAP provides a single cache by default.
<subsystem xmlns="{UndertowSubsystemNamespace}" default-server="default-server" default-virtual-host="default-host" default-servlet-container="default" default-security-domain="other">
<buffer-cache name="default"/>
...
</subsystem>
<subsystem xmlns="{UndertowSubsystemNamespace}" default-server="default-server" default-virtual-host="default-host" default-servlet-container="default" default-security-domain="other">
<buffer-cache name="default"/>
...
</subsystem>Prerequisites
- Ensure JBoss EAP is installed and you have administrative access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Update an existing buffer cache:
Modify the buffer size attribute:
/subsystem=undertow/buffer-cache=default/:write-attribute(name=buffer-size,value=2048)
/subsystem=undertow/buffer-cache=default/:write-attribute(name=buffer-size,value=2048)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a new buffer cache:
Add a new buffer cache:
/subsystem=undertow/buffer-cache=new-buffer:add
/subsystem=undertow/buffer-cache=new-buffer:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Delete a buffer cache:
Remove an existing buffer cache:
/subsystem=undertow/buffer-cache=new-buffer:remove
/subsystem=undertow/buffer-cache=new-buffer:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.1.3. Configuring byte buffer Pool
Undertow byte buffer pools are used to allocate pooled NIO ByteBuffer instances. All listeners have a byte buffer pool and you can use different buffer pools and workers for each listener. Byte buffer pools can be shared between different server instances.
These buffers are used for IO operations, and the buffer size has a big impact on application performance. For most servers, the ideal size is usually 16k.
Prerequisites
- Ensure JBoss EAP is installed and you have administrative access to the management CLI.
Procedure
Update an Existing Byte Buffer Pool.
Modify the buffer size attribute:
/subsystem=undertow/byte-buffer-pool=myByteBufferPool:write-attribute(name=buffer-size,value=1024)
/subsystem=undertow/byte-buffer-pool=myByteBufferPool:write-attribute(name=buffer-size,value=1024)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create a New Byte Buffer Pool.
Add a new byte buffer pool:
/subsystem=undertow/byte-buffer-pool=newByteBufferPool:add
/subsystem=undertow/byte-buffer-pool=newByteBufferPool:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Delete a Byte Buffer Pool.
Remove an existing byte buffer pool:
/subsystem=undertow/byte-buffer-pool=newByteBufferPool:remove
/subsystem=undertow/byte-buffer-pool=newByteBufferPool:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
- Verify the changes by checking the buffer pool settings in the management console.
Additional resources
- For detailed attributes for byte buffer pools, see the Byte Buffer Pool Attributes section.
15.1.4. Understanding server configuration in undertow
A server represents an instance of Undertow and consists of several elements:
-
host -
http-listener -
https-listener -
ajp-listener
The host element provides a virtual host configuration, while the three listeners provide connections of that type to the Undertow instance.
The default behavior of the server is to queue requests while the server is starting. You can change this default behavior using the queue-requests-on-start attribute on the host. If this attribute is set to true (the default), then requests that arrive when the server is starting will be held until the server is ready. If this attribute is set to false, then requests that arrive before the server has completely started will be rejected with the default response code.
Regardless of the attribute value, request processing does not start until the server is completely started.
You can configure the queue-requests-on-start attribute using the management console by navigating to Configuration → Subsystems → Web (Undertow) → Server, selecting the server, clicking View, and selecting the Hosts tab. For a managed domain, you must specify which profile to configure.
Multiple servers can be configured, allowing deployments and servers to be completely isolated. This can be useful in certain scenarios such as multi-tenant environments.
JBoss EAP provides a server by default:
15.1.5. Default undertow subsystem configuration
This reference provides the default configuration of the Undertow subsystem.
15.1.6. Configuring a server using the management CLI
This procedure explains how to manage servers in the Undertow subsystem using the management CLI. You can update existing servers, create new ones, or delete servers as needed.
You can also configure a server using the management console by navigating to Configuration → Subsystems → Web (Undertow) → Server.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Update an existing server
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server:write-attribute(name=default-host,value=default-host)
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server:write-attribute(name=default-host,value=default-host)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a new server
/subsystem=undertow/server=new-server:add
/subsystem=undertow/server=new-server:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Delete a server
/subsystem=undertow/server=new-server:remove
/subsystem=undertow/server=new-server:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.1.7. Access logging
You can configure access logging on each host you define.
Two access logging options are available: standard access logging and console access logging.
Note that the additional processing required for access logging can affect system performance.
15.1.7.1. Standard Access logging
Standard access logging writes log entries to a log file.
By default, the log file is stored in the directory standalone/log/access_log.log.
To enable standard access logging, add the access-log setting to the host for which you want to capture access log data. The following CLI command illustrates the configuration on the default host in the default JBoss EAP server:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=access-log:add
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=access-log:addYou must reload the server after enabling standard access logging.
By default, the access log record includes the following data:
- Remote host name
- Remote logical user name (always -)
- Remote user that was authenticated
- The date and time of the request, in Common Log Format
- The first line of the request
- The HTTP status code of the response
- The number of bytes sent, excluding HTTP headers
This set of data is defined as the common pattern. Another pattern, combined, is also available. In addition to the data logged in the common pattern, the combined pattern includes the referer and user agent from the incoming header.
You can change the data logged using the pattern attribute. The following CLI command illustrates updating the pattern attribute to use the combined pattern:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=access-log:write-attribute(name=pattern,value="combined"
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=access-log:write-attribute(name=pattern,value="combined"You must reload the server after updating the pattern attribute.
| Pattern | Description |
|---|---|
| %a | Remote IP address |
| %A | Local IP address |
| %b |
Bytes sent, excluding HTTP headers or |
| %B | Bytes sent, excluding HTTP headers |
| %h | Remote host name |
| %H | Request protocol |
| %l |
Remote logical username from |
| %m | Request method |
| %p | Local port |
| %q |
Query string (excluding the |
| %r | First line of the request |
| %s | HTTP status code of the response |
| %t | Date and time, in Common Log Format format |
| %u | Remote user that was authenticated |
| %U | Requested URL path |
| %v | Local server name |
| %D | Time taken to process the request, in milliseconds |
| %T | Time taken to process the request, in seconds |
| %I | Current Request thread name (can compare later with stack traces) |
| common |
|
| combined |
|
You can also write information from the cookie, the incoming header and response header, or the session. The syntax is modeled after the Apache syntax:
-
%{i,xxx}for incoming headers -
%{o,xxx}for outgoing response headers -
%{c,xxx}for a specific cookie -
%{r,xxx}wherexxxis an attribute in theServletRequest -
%{s,xxx}wherexxxis an attribute in theHttpSession
Additional configuration options are available for this log. For more information see "access-log Attributes" in the appendix.
15.1.7.2. Console access logging
Console access logging writes data to stdout as structured as JSON data.
Each access log record is a single line of data. You can capture this data for processing by log aggregation systems.
To configure console access logging, add the console-access-log setting to the host for which you want to capture access log data. The following CLI command illustrates the configuration on the default host in the default JBoss EAP server:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=console-access-log:add
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=console-access-log:addBy default, the console access log record includes the following data:
| Log data field name | Description |
|---|---|
| eventSource | The source of the event in the request |
| hostName | The JBoss EAP host that processed the request |
| bytesSent | The number of bytes the JBoss EAP server sent in response to the request |
| dateTime | The date and time that the request was processed by the JBoss EAP server |
| remoteHost | The IP address of the machine where the request originated |
| remoteUser | The user name associated with the remote request |
| requestLine | The request submitted |
| responseCode | The HTTP response code returned by the JBoss EAP server |
Default properties are always included in the log output. You can use the attributes attribute to change the labels of the default log data, and in some cases to change the data configuration. You can also use the attributes attribute to add additional log data to the output.
| Log data field name | Description | Format |
|---|---|---|
| authentication-type | The authentication type used to authenticate the user associated with the request. Default label: authenticationType Use the key option to change the label for this property. | authentication-type{} authentication-type={key="authType"} |
| bytes-sent | The number of bytes returned for the request, excluding HTTP headers. Default label: bytesSent Use the key option to change the label for this property. | bytes-sent={} bytes-sent={key="sent-bytes"} |
| date-time | The date and time that the request was received and processed. Default label: dateTime Use the key option to change the label for this property. Use the date-format to define the pattern used to format the date-time record. The pattern must be a Java SimpleDateFormatter pattern. Use the time-zone option to specify the time zone used to format the date and/or time data if the date-format option is defined. This value must be a valid java.util.TimeZone. | date-time={key="<keyname>", date-format="<date-time format>"} date-time={key="@timestamp", date-format="yyyy-MM-dd’T’HH:mm:ssSSS"} |
| host-and-port | The host and port queried by the request. Default label: hostAndPort Use the key option to change the label for this property. | host-and-port{} host-and-port={key="port-host"} |
| local-ip | The IP address of the local connection. Use the key option to change the label for this property. Default label: localIp Use the key option to change the label for this property. | local-ip{} local-ip{key=”localIP”} |
| local-port | The port of the local connection. Default label: localPort Use the key option to change the label for this property. | local-port{} local-port{key=”LocalPort”} |
| local-server-name | The name of the local server that processed the request. Default label: localServerName Use the key option to change the label for this property. | local-server-name {} local-server-name {key=LocalServerName} |
| path-parameter | One or more path or URI parameters included in the request. The names property is a comma-separated list of names used to resolve the exchange values. Use the key-prefix property to make the keys unique. If the key-prefix is specified, the prefix is prepended to the name of each path parameter in the output. | path-parameter{names={store,section}} path-parameter{names={store,section}, key-prefix=”my-”} |
| predicate | The name of the predicate context. The names property is a comma-separated list of names used to resolve the exchange values. Use the key-prefix property to make the keys unique. If the key-prefix is specified, the prefix is prepended to the name of each path parameter in the output. | predicate{names={store,section}} predicate{names={store,section}, key-prefix=”my-”} |
| query-parameter | One or query parameters included in the request. The names property is a comma-separated list of names used to resolve the exchange values. Use the key-prefix property to make the keys unique. If the key-prefix is specified, the prefix is prepended to the name of each path parameter in the output. | query-parameter{names={store,section}} query-parameter{names={store,section}, key-prefix=”my-”} |
| query-string | The query string of the request. Default label: queryString Use the key option to change the label for this property. Use the include-question-mark property to specify whether the query string should include the question mark. By default, the question mark is not included. | query-string{} query-string{key=”QueryString”, include-question-mark=”true”} |
| relative-path | The relative path of the request. Default label: relativePath Use the key option to change the label for this property. | relative-path{} relative-path{key=”RelativePath”} |
| remote-host | The remote host name. Default label: remoteHost Use the key option to change the label for this property. | remote-host{} remote-host{key=”RemoteHost”} |
| remote-ip | The remote IP address. Default label: remoteIp Use the key options to change the label for this property. Use the obfuscated property to obfuscate the IP address in the output log record. The default value is false. | remote-ip{} remote-ip{key=”RemoteIP”, obfuscated=”true”} |
| remote-user | Remote user that was authenticated. Default label: remoteUser Use the key options to change the label for this property. | remote-user{} remote-user{key=”RemoteUser”} |
| request-header | The name of a request header. The key for the structured data is the name of the header; the value is the value of the named header. The names property is a comma-separated list of names used to resolve the exchange values. Use the key-prefix property to make the keys unique. If the key-prefix is specified, the prefix is prepended to the name of the request headers in the log output. | request-header{names={store,section}} request-header{names={store,section}, key-prefix=”my-”} |
| request-line | The request line. Default label: requestLine Use the key option to change the label for this property. | request-line{} request-line{key=”Request-Line”} |
| request-method | The request method. Default label: requestMethod Use the key option to change the label for this property. | request-method{} request-method{key=”RequestMethod”} |
| request-path | The relative path for the request. Default label: requestPath Use the key option to change the label for this property. | request-path{} request-path{key=”RequestPath”} |
| request-protocol | The protocol for the request. Default label: requestProtocol Use the key option to change the label for this property. | request-protocol{} request-protocol{key=”RequestProtocol”} |
| request-scheme | The URI scheme of the request. Default label: requestScheme Use the key option to change the label for this property. | request-scheme{} request-scheme{key=”RequestScheme”} |
| request-url | The original request URI. Includes host name, protocol, and so forth, if specified by the client. Default label: requestUrl Use the key option to change the label for this property. | request-url{} request-url{key=”RequestURL”} |
| resolved-path | The resolved path. Default Label: resolvedPath Use the key option to change the label for this property. | resolved-path{} resolved-path{key=”ResolvedPath”} |
| response-code | The response code. Default label: responseCode Use the key option to change the label for this property. | response-code{} response-code{key=”ResponseCode”} |
| response-header | The name of a response header. The key for the structured data is the name of the header; the value is the value of the named header. The names property is a comma-separated list of names used to resolve the exchange values. Use the key-prefix property to make the keys unique. If the key-prefix is specified, the prefix is prepended to the name of the request headers in the log output. | response-header{names={store,section}} response-header{names={store,section}, key-prefix=”my-”} |
| response-reason-phrase | The text reason for the response code. Default label: responseReasonPhrase Use the key option to change the label for this property. | response-reason-phrase{} response-reason-phrase{key=”ResponseReasonPhrase”} |
| response-time | The time used to process the request. Default label: responseTime Use the key option to change the label for this property. The default time unit is MILLISECONDS. Available time units include: * NANOSECONDS * MICROSECONDS * MILLISECONDS * SECONDS | response-time{} response-time{key=”ResponseTime”, time-unit=SECONDS} |
| secure-exchange | Indicates whether the exchange was secure. Default label: secureExchange Use the key option to change the label for this property. | secure-exchange{} secure-exchange{key=”SecureExchange”} |
| ssl-cipher | The SSL cipher for the request. Default label: sslCipher Use the key option to change the label for this property. | ssl-cipher{} ssl-cipher{key=”SSLCipher”} |
| ssl-client-cert | The SSL client certificate for the request. Default label: sslClientCert Use the key option to change the label for this property. | ssl-client-cert{} ssl-client-cert{key=”SSLClientCert”} |
| ssl-session-id | The SSL session id of the request. Default label: sslSessionId Use the key option to change the label for this property. | ssl-session-id{} stored-response |
| The stored response to the request. Default label: storedResponse Use the key option to change the label for this property. | stored-response{} stored-response{key=”StoredResponse”} | thread-name |
| The thread name of the current thread. Default label: threadName Use the key option to change the label for this property. | thread-name{} thread-name{key=”ThreadName”} | transport-protocol |
You can use the metadata attribute to configure additional arbitrary data to include in the access log record. The value of the metadata attribute is a set of key:value pairs that defines the data to include in the access log record. The value in a pair can be a management model expression. Management model expressions are resolved when the server is started or reloaded. Key-value pairs are comma-separated.
The following CLI command demonstrates an example of a complex console log configuration, including additional log data, customization of log data, and additional metadata:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=console-access-log:add(metadata={"@version"="1", "qualifiedHostName"=${jboss.qualified.host.name:unknown}}, attributes={bytes-sent={}, date-time={key="@timestamp", date-format="yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssSSS"}, remote-host={}, request-line={}, response-header={key-prefix="responseHeader", names=["Content-Type"]}, response-code={}, remote-user={}})
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=console-access-log:add(metadata={"@version"="1", "qualifiedHostName"=${jboss.qualified.host.name:unknown}}, attributes={bytes-sent={}, date-time={key="@timestamp", date-format="yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssSSS"}, remote-host={}, request-line={}, response-header={key-prefix="responseHeader", names=["Content-Type"]}, response-code={}, remote-user={}})The resulting access log record would resemble the following additional JSON data (Note: the example output below is formatted for readability; in an actual record, all data would be output as a single line):
The following command illustrates updates to the log data after activating the console access log:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=console-access-log:write-attribute(name=attributes,value={bytes-sent={}, date-time={key="@timestamp", date-format="yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssSSS"}, remote-host={}, request-line={}, response-header={key-prefix="responseHeader", names=["Content-Type"]}, response-code={}, remote-user={}})
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=console-access-log:write-attribute(name=attributes,value={bytes-sent={}, date-time={key="@timestamp", date-format="yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ssSSS"}, remote-host={}, request-line={}, response-header={key-prefix="responseHeader", names=["Content-Type"]}, response-code={}, remote-user={}})The following command illustrates updates to the custom metadata after activating the console access log:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=console-access-log:write-attribute(name=metadata,value={"@version"="1", "qualifiedHostName"=${jboss.qualified.host.name:unknown}})
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=console-access-log:write-attribute(name=metadata,value={"@version"="1", "qualifiedHostName"=${jboss.qualified.host.name:unknown}})15.2. Configuring a servlet container
A servlet container provides all servlet, JavaServer Pages Jakarta Server Pages, and WebSocket-related configuration, including session-related settings. While most servers will only need a single servlet container, it is possible to configure multiple servlet containers by adding additional servlet-container elements. Having multiple servlet containers enables behavior such as allowing multiple deployments to be deployed to the same context path on different virtual hosts.
Much of the configuration provided by the servlet container can be individually overridden by deployed applications using their web.xml file.
15.2.1. The default undertow subsystem configuration
JBoss EAP provides a servlet container by default. This reference provides the default configuration of the Undertow subsystem, including the servlet container.
15.2.2. Managing servlet containers using the management CLI and management console
This procedure explains how to manage servlet containers in the Undertow subsystem using the management CLI and the management console. You can update existing servlet containers, create new ones, or delete servlet containers as needed.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have access to the management console.
- You have Permissions to modify server configurations.
Managing servlet containers in the Undertow subsystem using the management Console
You can also configure a servlet container using the management console by navigating to Configuration → Subsystems → Web (Undertow) → Servlet Container.
Managing servlet containers in the Undertow subsystem using the management CLI
The following examples show how to configure a servlet container using the management CLI
Procedure
- Connect to the management CLI:
Run the following command to update the servlet container’s attribute:
---- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default:write-attribute(name=ignore-flush,value=true) -------- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default:write-attribute(name=ignore-flush,value=true) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes: +
---- reload -------- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Creating a new servlet container
- Connect to the management CLI:
Run the following command to create a new servlet container:
---- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=new-servlet-container:add -------- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=new-servlet-container:add ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes:
---- reload -------- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Deleting a servlet container
- Connect to the management CLI.
Run the following command to delete the servlet container:
---- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=new-servlet-container:remove -------- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=new-servlet-container:remove ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes:
---- reload -------- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.3. Configuring a servlet extension
Servlet extensions allow you to hook into the servlet deployment process and modify aspects of a servlet deployment. This can be useful in cases where you need to add additional authentication mechanisms to a deployment or use native Undertow handlers as part of a servlet deployment.
To create a custom servlet extension, it is necessary to implement the io.undertow.servlet.ServletExtension interface and then add the name of your implementation class to the META-INF/services/io.undertow.servlet.ServletExtension file in the deployment. You also need to include the compiled class file of the ServletExtension implementation. When Undertow deploys the servlet, it loads all the services from the deployments class loader and then invokes their handleDeployment methods.
An Undertow DeploymentInfo structure, which contains a complete and mutable description of the deployment, is passed to this method. You can modify this structure to change any aspect of the deployment.
The DeploymentInfo structure is the same structure that is used by the embedded API, so in effect a ServletExtension has the same amount of flexibility that you have when using Undertow in embedded mode.
15.4. Configuring Handlers
JBoss EAP allows you to configure two types of handlers:
- File Handlers
- Reverse-Proxy Handlers
File handlers serve static files. Each file handler must be attached to a location in a virtual host. Reverse-proxy handlers allow JBoss EAP to serve as a high-performance reverse proxy.
15.4.1. The default undertow subsystem configuration for configuring Handlers
JBoss EAP provides a file handler by default. This reference provides the default configuration of the Undertow subsystem for Handlers.
15.4.2. Managing file Handlers using the management CLI
This procedure explains how to manage file handlers in the Undertow subsystem using the management CLI. You can update existing file handlers, create new ones, or delete file handlers as needed.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Updating an Existing File Handler
- Connect to the management CLI.
Run the following command to update the file handler’s attribute:
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=welcome-content:write-attribute(name=case-sensitive,value=true) ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=welcome-content:write-attribute(name=case-sensitive,value=true) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes:
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Creating a New File Handler
- Connect to the management CLI.
Run the following command to create a new file handler:
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=new-file-handler:add(path="${jboss.home.dir}/welcome-content") -------- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=new-file-handler:add(path="${jboss.home.dir}/welcome-content") ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow [WARNING] ==== If you set a file handler's `path` directly to a file instead of a directory, any `location` elements that reference that file handler must not end with a forward slash (`/`). Otherwise, the server will return a `404 - Not Found` response. ====
[WARNING] ==== If you set a file handler's `path` directly to a file instead of a directory, any `location` elements that reference that file handler must not end with a forward slash (`/`). Otherwise, the server will return a `404 - Not Found` response. ====Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Deleting a File Handler
- Connect to the management CLI.
Run the following command to delete the file handler:
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=new-file-handler:remove ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=new-file-handler:remove ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes:
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.5. Configuring Filters
A filter enables some aspect of a request to be modified and can use predicates to control when a filter executes. Some common use cases for filters include setting headers or doing GZIP compression.
A filter is functionally equivalent to a global valve used in JBoss EAP 6.
The following types of filters can be defined:
- custom-filter
- error-page
- expression-filter
- gzip
- mod-cluster
- request-limit
- response-header
- rewrite
15.5.1. Managing file Handlers using the management CLI and management console
This procedure explains how to manage filters in the Undertow subsystem using the management CLI and the management console. You can update existing filters, create new ones, or delete filters as needed.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have access to the management console.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Managing file Handlers using the management console
You can configure a filter using the management console by navigating to Configuration → Subsystems → Web (Undertow) → Filters.
Managing file Handlers using the management CLI
The following procedure shows how to configure a filter using the management CLI
Procedure
Updating an existing Filter
- Connect to the management CLI.
Run the following command to update the filter’s attribute:
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/response-header=myHeader:write-attribute(name=header-value,value="JBoss-EAP") ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/response-header=myHeader:write-attribute(name=header-value,value="JBoss-EAP") ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes:
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Creating a new Filter
- Connect to the management CLI.
Run the following command to create a new filter:
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/response-header=new-response-header:add(header-name=new-response-header,header-value="My Value") ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/response-header=new-response-header:add(header-name=new-response-header,header-value="My Value") ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Deleting a Filter
- Connect to the management CLI.
Run the following command to delete the filter:
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/response-header=new-response-header:remove ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/response-header=new-response-header:remove ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes:
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.5.1.1. Configuring the buffer-request Handler
A request from the client or the browser consists of two parts: the header and the body. In a typical situation, the header and the body are sent to JBoss EAP without any delays in between. However, if the header is sent first and then after few seconds, the body is sent, there is a delay sending the complete request. This scenario creates a thread in JBoss EAP to show as waiting to execute the complete request.
The delay caused in sending the header and the body of the request can be corrected using the buffer-request handler. The buffer-request handler attempts to consume the request from a non-blocking IO thread before allocating it to a worker thread. When no buffer-request handler is added, the thread allocation to the worker thread happens directly. However, when the buffer-request handler is added, the handler attempts to read the amount of data that it can buffer in a non-blocking manner using the IO thread before allocating it to the worker thread.
You can use the following management CLI commands to configure the buffer-request handler:
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Run the following command to add the
buffer-requesthandler:---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/expression-filter=buf:add(expression="buffer-request(buffers=1)") ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/expression-filter=buf:add(expression="buffer-request(buffers=1)") ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Attach the handler to your server and host by running:
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/filter-ref=buf:add ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/filter-ref=buf:add ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Calculate the buffer request size:
`Total_size = num_buffers {MultiplicationSign} buffer_size``Total_size = num_buffers {MultiplicationSign} buffer_size`Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Where:
Where:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Total_sizeis the size of data that will be buffered before the request is dispatched to a worker thread. -
num_buffersis the number of buffers, set by thebuffersparameter on the handler (in this example, it’s set to1). buffer_sizeis the size of each buffer, set in theiosubsystem (default is 16KB per request).WarningAvoid configuring very large buffer requests, or else you might run out of memory.
-
Reload the server to apply the changes:
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.5.1.2. Understanding the SameSite attribute
Use the SameSite attribute to define the accessibility of a cookie within the same site. This attribute helps prevent cross-site request forgery attacks because browsers do not send the cookie with cross-site requests.
You can configure the SameSite attribute for cookies with SameSiteCookieHandler in the undertow subsystem. With this configuration, you do not need to change your application code.
15.5.1.3. SameSiteCookieHandler parameters
The following table details the parameters of SameSiteCookieHandler:
| Parameter Name | Presence | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
| Optional |
Adds a |
|
| Optional |
Indicates if the |
|
| Optional |
Accepts a regex pattern for the cookie name. If not specified, the attribute |
|
| Optional |
Verifies if client applications are incompatible with the
If you use this default value and set the
To prevent issues with incompatible clients, this parameter skips setting the |
|
| Mandatory |
Specifies the
To improve security against cross-site request forgery attacks, some browsers set the default |
SameSiteCookieHandler adds the attribute SameSite=<specified-mode> to cookies that match cookie-pattern or to all cookies when cookie-pattern is not specified. The cookie-pattern is matched according to the value set in case-sensitive.
Before configuring the SameSite attribute, consider the following points:
-
Review your application to identify whether the cookies require the
SameSiteattribute and whether those cookies need to be secured. -
Setting the
SameSiteattribute mode toNonefor all cookies can make the application more susceptible to attacks.
15.5.1.4. Configuring SameSiteCookieHandler using an expression Filter
This procedure explains how to configure SameSiteCookieHandler on the server using an expression-filter.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Create a new
expression-filterwith theSameSiteCookieHandler:---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/expression-filter=addSameSiteLax:add(expression="path-prefix('/mypathprefix') -> samesite-cookie(Lax)") -------- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/expression-filter=addSameSiteLax:add(expression="path-prefix('/mypathprefix') -> samesite-cookie(Lax)") ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable the
expression-filterin theundertowweb server:---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/filter-ref=addSameSiteLax:add ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/filter-ref=addSameSiteLax:add ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.5.1.5. Configuring SameSiteCookieHandler using a configuration file
This procedure explains how to configure SameSiteCookieHandler in your application by adding the undertow-handlers.conf file.
Prerequisites
- Access to your application’s source code.
- Permissions to modify application files.
Procedure
-
Add an
undertow-handlers.conffile to your WAR’sWEB-INFdirectory. In the
undertow-handlers.conffile, add the following command with a specificSameSiteCookieHandlerparameter:---- samesite-cookie(mode=<mode>) ----
---- samesite-cookie(mode=<mode>) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace `<mode>` with one of the valid values: `Strict`, `Lax`, or `None`.
Replace `<mode>` with one of the valid values: `Strict`, `Lax`, or `None`.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can also configure other `SameSiteCookieHandler` parameters, such as `cookie-pattern`, `case-sensitive`, `enable-client-checker`, or `add-secure-for-none`.
You can also configure other `SameSiteCookieHandler` parameters, such as `cookie-pattern`, `case-sensitive`, `enable-client-checker`, or `add-secure-for-none`.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Save the file and redeploy your application if necessary.
15.6. Configure the default welcome web application
JBoss EAP includes a default Welcome application, which displays at the root context on port 8080 by default.
There is a default server preconfigured in Undertow that serves up the welcome content.
Default Undertow Subsystem Configuration
The default server, default-server, has a default host, default-host, configured. The default host is configured to handle requests to the server’s root, using the <location> element, with the welcome-content file handler. The welcome-content handler serves up the content in the location specified in the path property.
This default Welcome application can be replaced with your own web application. This can be configured in one of two ways:
You can also disable the welcome content.
15.6.1. Changing the welcome-content file Handler
This procedure explains how to change the welcome-content file handler to point to your own web application.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Modify the existing
welcome-contentfile handler’s path to point to your new content:---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=welcome-content:write-attribute(name=path,value="/path/to/your/content") ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=welcome-content:write-attribute(name=path,value="/path/to/your/content") ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, you can create a new file handler to be used by the server’s root:
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=NEW_FILE_HANDLER:add(path="/path/to/your/content") /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/location=\/:write-attribute(name=handler,value=NEW_FILE_HANDLER) ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/file=NEW_FILE_HANDLER:add(path="/path/to/your/content") /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/location=\/:write-attribute(name=handler,value=NEW_FILE_HANDLER) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server for the changes to take effect:
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.6.2. Changing the default-web-module
This procedure explains how to map a deployed web application to the server’s root by changing the default-web-module.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Map your deployed web application to the server’s root.
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host:write-attribute(name=default-web-module,value=your-application.war) ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host:write-attribute(name=default-web-module,value=your-application.war) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Reload the server for the changes to take effect:
---- reload ----
----
reload
----15.6.3. Disabling the default welcome web application
This procedure explains how to disable the default welcome web application by removing the location entry for the root context.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Remove the
locationentry/for thedefault-host:---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/location=\/:remove ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/location=\/:remove ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server for the changes to take effect:
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.7. Configuring HTTP session timeout
The HTTP session timeout defines the period of inactive time needed to declare an HTTP session invalid. For example, when a user accesses an application deployed to JBoss EAP, an HTTP session is created. If that user then attempts to access the application again after the HTTP session timeout period has elapsed, the original HTTP session will be invalidated, and the user will be forced to create a new HTTP session. This may result in the loss of unpersisted data or require the user to reauthenticate.
The HTTP session timeout is typically configured in an application’s web.xml file. However, a default HTTP session timeout can also be specified within JBoss EAP. The server’s timeout value will apply to all deployed applications unless overridden by an application’s web.xml file.
The server value is specified in the default-session-timeout property within the servlet-container section of the undertow subsystem. The value of default-session-timeout is specified in minutes, and the default is 30.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
- Connect to the management CLI.
Set the
default-session-timeoutvalue.Run the following command to set the `default-session-timeout` value to `60` minutes: ---- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default:write-attribute(name=default-session-timeout, value=60) ----
Run the following command to set the `default-session-timeout` value to `60` minutes: ---- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default:write-attribute(name=default-session-timeout, value=60) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server for the changes to take effect.
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.8. Configuring HTTP-only session management cookies
Session management cookies can be accessed by both HTTP APIs and non-HTTP APIs such as JavaScript. JBoss EAP offers the ability to send the HttpOnly header as part of the Set-Cookie response header to the client, usually a browser. In supported browsers, enabling this header tells the browser to prevent accessing session management cookies through non-HTTP APIs. Restricting session management cookies to only HTTP APIs can help mitigate the threat of session cookie theft via cross-site scripting attacks. To enable this behavior, the http-only attribute should be set to true.
Using the HttpOnly header does not actually prevent cross-site scripting attacks by itself; it merely notifies the browser. The browser must also support HttpOnly for this behavior to take effect.
Using the http-only attribute only applies the restriction to session management cookies and not to other browser cookies.
The http-only attribute is set in two places in the undertow subsystem:
- In the servlet container as a session cookie setting.
- In the host section of the server as a single sign-on property.
15.8.1. Configuring host-only for the Servlet container session cookie
This procedure explains how to configure the http-only property for the servlet container session cookie in the undertow subsystem.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Add the session cookie setting to the servlet container.
Run the following command:
Run the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ---- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=session-cookie:add ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=session-cookie:add ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
http-onlyattribute totrue.Run the following command:
Run the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ---- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=session-cookie:write-attribute(name=http-only,value=true) ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=session-cookie:write-attribute(name=http-only,value=true) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server for the changes to take effect.
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.8.2. Configuring http-only for the host single sign-On
This procedure explains how to configure the http-only property for the host single sign-on in the undertow subsystem.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Add the single sign-on setting to the host.
Run the following command:
Run the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=single-sign-on:add ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=single-sign-on:add ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
http-onlyattribute totrue.Run the following command:
Run the following command:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=single-sign-on:write-attribute(name=http-only,value=true) ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=single-sign-on:write-attribute(name=http-only,value=true) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server for the changes to take effect.
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
15.9. Understanding HTTP/2 in undertow
Undertow allows for the use of the HTTP/2 standard, which reduces latency by compressing headers and multiplexing many streams over the same TCP connection. It also provides the ability for a server to push resources to the client before it has requested them, leading to faster page loads.
Be aware that HTTP/2 only works with clients and browsers that also support the HTTP/2 standard.
Most modern browsers enforce HTTP/2 over a secured TLS connection, known as h2, and may not support HTTP/2 over plain HTTP, known as h2c. It is still possible to configure JBoss EAP to use HTTP/2 with h2c, without using HTTPS and only using plain HTTP with HTTP upgrade. In that case, you can simply enable HTTP/2 in the HTTP listener:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/http-listener=default:write-attribute(name=enable-http2,value=true)
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/http-listener=default:write-attribute(name=enable-http2,value=true)15.9.1. Configuring HTTP/2 in Undertow
This procedure explains how to enable HTTP/2 in Undertow by configuring the HTTPS listener.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Enable HTTP/2 on the HTTPS listener:
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/https-listener=https:write-attribute(name=enable-http2,value=true) ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/https-listener=https:write-attribute(name=enable-http2,value=true) ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes:
---- reload ----
---- reload ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
In order to utilize HTTP/2 with the elytron subsystem, you will need to ensure that the configured ssl-context in the https-listener of the Undertow is configured as modifiable. This can be achieved by setting the wrap attribute of the appropriate server-ssl-context to false. By default, the wrap attribute is set to false. This is required by Undertow to make modifications in the ssl-context about the ALPN. If the provided ssl-context is not writable, ALPN cannot be used and the connection falls back to HTTP/1.1.
15.9.2. ALPN support when using HTTP/2
When using HTTP/2 over a secured TLS connection, a TLS stack that supports the Application-Layer Protocol Negotiation (ALPN) TLS protocol extension is required. Obtaining this stack varies based on the installed JDK.
- As of Java 9, the JDK supports ALPN natively; however, using the ALPN TLS protocol extension support from the OpenSSL provider should also result in better performance when using Java 9 or later.
Instructions for installing OpenSSL to obtain the ALPN TLS protocol extension support are available in Install OpenSSL from JBoss Core Services. The standard system OpenSSL is supported on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, and no additional OpenSSL is required.
Once OpenSSL has been installed, follow the instructions in xref:"configure-jboss-eap-to-use-openssl_configuring-the-web-server-undertow-in-jboss-eap"[Configure JBoss EAP to Use OpenSSL].
15.9.3. Verifying HTTP/2 usage
To verify that Undertow is using HTTP/2, you will need to inspect the headers coming from Undertow. Navigate to your JBoss EAP instance using https, for example https://localhost:8443, and use your browser’s developer tools to inspect the headers. Some browsers, for example Google Chrome, will show HTTP/2 pseudo headers, such as :path, :authority, :method and :scheme, when using HTTP/2. Other browsers, for example Firefox and Safari, will report the status or version of the header as HTTP/2.0.
15.10. Understanding the RequestDumping Handler
The RequestDumping handler, io.undertow.server.handlers.RequestDumpingHandler, logs the details of request and corresponding response objects handled by Undertow within JBoss EAP.
While this handler can be useful for debugging, it may also log sensitive information. Please keep this in mind when enabling this handler.
The RequestDumping handler replaces the RequestDumperValve from JBoss EAP 6.
You can configure a RequestDumping handler either at the server level directly in JBoss EAP or within an individual application.
15.10.1. Configuring a RequestDumping Handler on the server
This procedure explains how to configure a RequestDumping handler at the server level using an expression filter.
Prerequisites
- You have access to the management CLI.
- You have permissions to modify server configurations.
Procedure
Create a new expression filter with the
RequestDumpinghandler:---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/expression-filter=requestDumperExpression:add(expression="dump-request") ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/expression-filter=requestDumperExpression:add(expression="dump-request") ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable the expression filter in the Undertow web server:
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/filter-ref=requestDumperExpression:add ----
---- /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/filter-ref=requestDumperExpression:add ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
All requests and corresponding responses handled by the Undertow web server will be logged when enabling the RequestDumping handler as an expression filter in this manner.
15.10.1.1. Configuring a Handler for specific URLs
In addition to logging all requests, you can also use an expression filter to only log requests and corresponding responses for specific URLs. This can be accomplished using a predicate in your expression such as path, path-prefix, or path-suffix. For example, if you want to log all requests and corresponding responses to /myApplication/test, you can use the expression "path(/myApplication/test) -> dump-request" instead of the expression "dump-request" when creating your expression filter. This will only direct requests with a path exactly matching /myApplication/test to the RequestDumping handler.
15.10.1.2. Configuring a RequestDumping Handler within an application
This procedure explains how to configure a RequestDumping handler within an individual application. This limits the scope of the handler to that specific application.
Procedure
-
Create or edit the
WEB-INF/undertow-handlers.conffile in your application. To log all requests and corresponding responses for this application, add the following line to
undertow-handlers.conf:---- dump-request ----
---- dump-request ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Alternatively, to log requests and responses for specific URLs within the application, use a predicate in your expression.
Replace `/test` with the desired path relative to the application's context root.
Replace `/test` with the desired path relative to the application's context root.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow [source] ---- path(/test) -> dump-request ----
[source] ---- path(/test) -> dump-request ----Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen using predicates such as
path,path-prefix, orpath-suffixin expressions defined in the application’sWEB-INF/undertow-handlers.conf, the value used is relative to the context root of the application.For example, if the application’s context root is
/myApplicationand you use the expressionpath(/test) → dump-request, it will log requests to/myApplication/test.- Redeploy the application if necessary to apply the changes.
15.11. Configuring cookie security
You can use the secure-cookie handler to enhance the security of cookies that are created over a connection between a server and a client. In this case, if the connection over which the cookie is set is marked as secure, the cookie will have its secure attribute set to true.
You can secure the connection by configuring a listener or by using HTTPS. You configure the secure-cookie handler by defining an expression-filter in the undertow subsystem. For more information, see Configuring Filters.
When the secure-cookie handler is in use, cookies that are set over a secure connection will be implicitly set as secure and will never be sent over an unsecure connection.
Chapter 16. Configuring remoting and connections
You can configure the remoting subsystem and manage various connection types within JBoss EAP. This includes setting up endpoints, connectors, and outbound connections to facilitate communication between servers and applications. You can configure HTTP connectors, remote and local outbound connections, and explore additional remoting configuration options, providing you with the tools needed to manage remoting and connections effectively in JBoss EAP.
16.1. Remoting subsystem configuration
The remoting subsystem configures inbound and outbound connections for local and remote services, along with the settings for those connections.
The JBoss EAP remoting subsystem includes several configurable elements:
For most use cases, you might not need to configure the remoting subsystem. However, if your application uses custom connectors, you must configure it. Applications that act as remoting clients, such as Jakarta Enterprise Beans, require separate configuration to connect to a specific connector.
The default remoting subsystem configuration is as follows:
16.1.1. The remoting endpoint
The remoting endpoint uses the XNIO worker declared and configured by the io subsystem. This worker facilitates non-blocking I/O operations, enhancing the performance and scalability of remoting connections.
16.1.2. http-connector configuration element
The http-connector element is a default configuration element that enables external clients to connect to the server by using the HTTP upgrade feature of undertow.
With this configuration, the client first establishes a connection with the server by using the HTTP protocol and then switches to the remote protocol over the same connection. This enables clients by using different protocols to connect over the same port, such as the default port 8080 of undertow, reducing the number of open ports on the server.
Clients that need to connect to the server by using HTTP upgrade must use the remoting remote+http protocol for unencrypted connections or the remoting remote+https protocol for encrypted connections.
16.1.3. Outbound connections
Outbound connections in the remoting subsystem enable your applications to communicate with external resources.
You can specify three different types of outbound connections:
- An outbound connection, specified by a URI
- A local outbound connection, which connects to a local resource such as a socket
- A remote outbound connection, which connects to a remote resource and authenticates by using a security realm
16.2. Configuring the endpoint
You can configure the remoting endpoint in JBoss EAP to establish connections for your applications. JBoss EAP includes a default endpoint configuration that you can update by using management CLI commands.
As a JBoss EAP administrator or developer, you might need to:
- Configure endpoint settings to tailor communication for specialized services or environments. For example, you can adjust authentication and security settings to separate administrative traffic from regular application traffic.
- Update an existing endpoint configuration to meet security or performance requirements. For example, adjusting settings like authentication retries or timeouts can improve security and ensure optimal performance under varying loads.
In JBoss EAP 8.0, the endpoint configuration in the remoting subsystem uses a worker from the io subsystem. This worker manages the thread pool for remoting operations.
The default endpoint configuration provided by JBoss EAP is as follows:
<subsystem xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:remoting:4.0"> <endpoint worker="default"/> ... </subsystem>
<subsystem xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:remoting:4.0">
<endpoint worker="default"/>
...
</subsystem>Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Update the existing endpoint configuration by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting:write-attribute(name=authentication-retries,value=2)
/subsystem=remoting:write-attribute(name=authentication-retries,value=2)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes by using the following command:
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
16.3. Configuring an HTTP connector
You can configure the HTTP connector in JBoss EAP to establish connections by using the HTTP upgrade-based remoting protocol. JBoss EAP provides a default HTTP connector configuration that you can easily update, create, or delete by using management CLI commands.
As a JBoss EAP administrator or developer, you might need to:
- Create a new HTTP connector to establish remote communication using the HTTP upgrade-based remoting protocol. This enables secure and efficient remote access to JBoss EAP services.
- Update an existing HTTP connector to optimize performance, enhance security, or integrate with specific network configurations. Adjusting attributes such as authentication mechanisms or connection timeouts improves reliability and ensures compliance with security policies.
- Delete unnecessary HTTP connectors to simplify configuration and reduce security risks. Deleting unused connectors helps maintain a clean and secure environment by minimizing exposure to unauthorized access.
The default http-connector configuration provided by JBoss EAP is as follows:
By default, this HTTP connector connects to an HTTP listener named default, which is configured in the undertow subsystem.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Create a new HTTP connector by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/http-connector=new-connector:add(connector-ref=new-connector-ref)
/subsystem=remoting/http-connector=new-connector:add(connector-ref=new-connector-ref)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou must use a unique
connector-refthat is not already in use by another connector. Theconnector-refmust point to a new or unused connector in Undertow, or you may choose to use the predefined https connector instead.Update the existing HTTP connector configuration by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/http-connector=new-connector:write-attribute(name=connector-ref,value=new-connector-ref)
/subsystem=remoting/http-connector=new-connector:write-attribute(name=connector-ref,value=new-connector-ref)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes by using the following command:
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If needed, delete an HTTP connector by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/http-connector=new-connector:remove
/subsystem=remoting/http-connector=new-connector:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
16.4. Configuring an outbound connection
You can configure an outbound connection in JBoss EAP to establish a generic remoting outbound connection specified by a URI. This enables your applications to communicate effectively with external services.
You can easily manage these connections by updating, creating, or deleting configurations by using management CLI commands.
As a JBoss EAP administrator or developer, you might need to:
- Create a new outbound connection to establish communication with external services. This enables seamless data exchange and integration with remote systems.
- Update an existing outbound connection to enhance performance, strengthen security, or align with network configurations. Adjusting attributes such as the target URI improves reliability and ensures compatibility with system requirements.
- Delete unnecessary outbound connections to streamline configuration and reduce security risks. Deleting unused connections helps maintain a clean and secure environment by minimizing exposure to unauthorized access.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Create a new outbound connection by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/outbound-connection=new-outbound-connection:add(uri=http://example.com)
/subsystem=remoting/outbound-connection=new-outbound-connection:add(uri=http://example.com)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the existing outbound connection by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/outbound-connection=new-outbound-connection:write-attribute(name=uri,value=http://example.com)
/subsystem=remoting/outbound-connection=new-outbound-connection:write-attribute(name=uri,value=http://example.com)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If needed, delete an outbound connection by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/outbound-connection=new-outbound-connection:remove
/subsystem=remoting/outbound-connection=new-outbound-connection:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes after deleting the outbound connection by using the following command:
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
16.5. Configuring a remote outbound connection
You can specify a remote outbound connection with a protocol, an outbound socket binding, a username, and a security realm. The protocol can be remote, http-remoting, or https-remoting. You can manage these connections easily by updating, creating, or deleting configurations using management CLI commands.
As a JBoss EAP administrator or developer, you might need to:
- Create a new remote outbound connection to enable secure communication with external services. This ensures applications can interact with remote systems using specified protocols and authentication methods.
- Update an existing remote outbound connection to enhance security, improve performance, or integrate with specific network configurations. Adjusting attributes such as outbound socket bindings or authentication settings ensures stability and compliance with security policies.
- Delete unnecessary remote outbound connections to simplify configuration and reduce security risks. Deleting unused connections helps maintain a clean and secure environment by minimizing exposure to unauthorized access.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Create a new remote outbound connection by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/remote-outbound-connection=new-remote-outbound-connection:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=outbound-socket-binding)
/subsystem=remoting/remote-outbound-connection=new-remote-outbound-connection:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=outbound-socket-binding)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteEnsure that the
outbound-socket-bindingis defined in your configuration before executing these commands. For more information, see Outbound socket binding.Update an existing remote outbound connection by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/remote-outbound-connection=new-remote-outbound-connection:write-attribute(name=outbound-socket-binding-ref,value=outbound-socket-binding)
/subsystem=remoting/remote-outbound-connection=new-remote-outbound-connection:write-attribute(name=outbound-socket-binding-ref,value=outbound-socket-binding)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If needed, you can delete a remote outbound connection by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/remote-outbound-connection=new-remote-outbound-connection:remove
/subsystem=remoting/remote-outbound-connection=new-remote-outbound-connection:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
16.6. Configuring a local outbound connection
You can specify a local outbound connection as a remoting outbound connection with a protocol of local, using only an outbound socket binding. You can manage these connections easily by updating, creating, or deleting configurations using management CLI commands.
As a JBoss EAP administrator or developer, you might need to:
- Create a new local outbound connection to enable secure and efficient communication within the same server instance. This helps streamline internal interactions without requiring external networking.
- Update an existing local outbound connection to improve performance, modify socket bindings, or align with specific configurations. Adjusting attributes such as outbound socket bindings ensures stability and compatibility.
- Delete unnecessary local outbound connections to simplify configuration and reduce security risks. Deleting unused connections helps maintain a clean and secure environment by minimizing exposure to unauthorized access.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Create a new local outbound connection by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/local-outbound-connection=new-local-outbound-connection:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=outbound-socket-binding)
/subsystem=remoting/local-outbound-connection=new-local-outbound-connection:add(outbound-socket-binding-ref=outbound-socket-binding)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteEnsure that the
outbound-socket-bindingis defined in your configuration before executing these commands. For more information,Update an existing local outbound connection by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/local-outbound-connection=new-local-outbound-connection:write-attribute(name=outbound-socket-binding-ref,value=outbound-socket-binding)
/subsystem=remoting/local-outbound-connection=new-local-outbound-connection:write-attribute(name=outbound-socket-binding-ref,value=outbound-socket-binding)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If needed, you can delete a local outbound connection by using the following command:
/subsystem=remoting/local-outbound-connection=new-local-outbound-connection:remove
/subsystem=remoting/local-outbound-connection=new-local-outbound-connection:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
16.7. Additional remoting configurations
There are several remoting elements that are configured outside of the remoting subsystem.
As a JBoss EAP administrator or developer, you might need to:
- Configure an IO worker for remoting to improve performance and manage remoting tasks efficiently. Ensure that the worker is defined in the IO subsystem.
- Modify the network interface settings to align remoting with the required public, management, or unsecure interface. Configuring the correct interface ensures proper connectivity.
- Adjust the socket binding for the remoting subsystem to specify the appropriate port and maintain compatibility with network and security policies.
Enable secure transport with STARTTLS to protect remoting communications. Ensure that your configuration verifies secure connections to prevent security risks, such as man-in-the-middle attacks.
- IO worker
Use the following command to set the IO worker for remoting. Ensure that the worker is defined in the IO subsystem before running this command:
/subsystem=remoting:write-attribute(name=worker, value=WORKER_NAME)
/subsystem=remoting:write-attribute(name=worker, value=WORKER_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Network interface
The network interface used by the
remotingsubsystem is thepublicinterface. This interface is also used by other subsystems, so exercise caution when modifying it.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In a managed domain, the
publicinterface is defined per host in itshost.xmlfile.- Socket binding
-
The default socket binding for the
remotingsubsystem binds to port8080. - Secure transport configuration
- Remoting transports use STARTTLS to establish a secure connection, such as HTTPS or Secure Servlet, if the client requests it. The same socket binding, or network port, is used for secured and unsecured connections, so no additional server-side configuration is necessary. The client requests secure or unsecured transport as needed. JBoss EAP components that use remoting, such as Jakarta Enterprise Beans, ORB, and the Jakarta Messaging provider, request secure interfaces by default.
STARTTLS works by activating a secure connection if the client requests it, and otherwise defaults to an unsecured connection. It is inherently susceptible to man-in-the-middle exploits, where an attacker intercepts a client’s request and modifies it to request an unsecured connection. Clients must be written to fail appropriately if they do not receive a secure connection, unless an unsecured connection is an appropriate fall-back.
Chapter 17. Configuring the IO subsystem
You can configure the io subsystem in JBoss EAP to enhance system performance and support application operations. By managing XNIO workers and buffer pools, you can ensure optimal functionality for subsystems like Undertow and Remoting. Properly adjusting these components might enable efficient data handling and responsiveness in your applications
17.1. IO Subsystem configuration
The io subsystem defines the XNIO workers and buffer pools used by other subsystems, such as Undertow and Remoting.
These workers and buffer pools are defined in the io subsystem by using the following CLI commands:
/subsystem=io/worker=* /subsystem=io/buffer-pool=*
/subsystem=io/worker=*
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=*
This configuration represents the default setup for the io subsystem. To view the default configuration of the io subsystem, run the following CLI command:
/subsystem=io/:read-resource(recursive=true)
/subsystem=io/:read-resource(recursive=true)17.2. Configuring a worker
You can configure a worker in JBoss EAP to efficiently manage IO tasks and worker threads. Workers serve as XNIO worker instances, providing an abstraction layer for the Java NIO APIs and supporting SSL.
Workers are responsible for managing IO operations, coordinating tasks, and ensuring that requests for sending and receiving data are processed efficiently. These tasks are handled by a set of threads maintained in an IO thread pool.
By default, JBoss EAP includes a single worker named default. You can define additional workers if required. When creating more than one worker, be aware that each additional worker results in a separate IO thread pool, which can impact resource utilization.
When no thread sizes are specified for a worker, JBoss EAP calculates the default values based on the number of available CPU cores. The configuration options are as follows:
-
io-threads: Specify the number of IO threads to create for the worker. If not specified, the default is calculated ascpuCount * 2. -
task-max-threads: Specify the maximum number of threads for the worker task thread pool. If not specified, the default value is calculated ascpuCount * 16.
You can manage workers through management CLI commands to update, create, or delete configurations.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Update an existing worker by using the following command:
/subsystem=io/worker=default:write-attribute(name=io-threads,value=10)
/subsystem=io/worker=default:write-attribute(name=io-threads,value=10)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes by using the following command:
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a new worker by using the following command:
/subsystem=io/worker=newWorker:add
/subsystem=io/worker=newWorker:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If needed, you can delete a worker by using the following command:
/subsystem=io/worker=newWorker:remove
/subsystem=io/worker=newWorker:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes by using the following command:
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.3. Configuring a buffer pool
You can configure a buffer pool in JBoss EAP to manage pooled NIO buffer instances, which play a crucial role in application performance. You can update existing buffer pools, create new ones, and delete those no longer needed to optimize system efficiency.
IO buffer pools are deprecated but remain the default configuration in the current release. Buffer pools are pooled NIO buffer instances. Changing the buffer size significantly impacts application performance. For most servers, the ideal buffer size is typically 16k. For more information, see Configuring byte buffer Pool section of the Configuration Guide for JBoss EAP. For more information, see Add lightweight global buffer pool API; deprecate heavier API, which describes the deprecation of the earlier buffer pool API and its replacement with the Undertow subsystem buffer pool.
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is running.
Procedure
Update an existing buffer pool by using the following command:
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=default:write-attribute(name=direct-buffers,value=true)
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=default:write-attribute(name=direct-buffers,value=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes by using the following command:
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create a new buffer pool by using the following command:
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=newBuffer:add
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=newBuffer:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If needed, you can delete a buffer pool by using the following command:
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=newBuffer:remove
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=newBuffer:removeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server to apply the changes by using the following command:
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
17.4. IO subsystem performance tuning
You can optimize and monitor the performance of the io subsystem to ensure efficient resource management and responsiveness. Regular monitoring helps identify potential issues before they affect system performance.
17.5. Configuring a Worker
Workers are XNIO worker instances. An XNIO worker instance is an abstraction layer for the Java NIO APIs, which provide functionality such as management of IO and worker threads as well as SSL support. By default, JBoss EAP provides single worker called default, but more can be defined.
Updating an Existing Worker
To update an existing worker:
/subsystem=io/worker=default:write-attribute(name=io-threads,value=10)
/subsystem=io/worker=default:write-attribute(name=io-threads,value=10)reload
reloadCreating a New Worker
To create a new worker:
/subsystem=io/worker=newWorker:add
/subsystem=io/worker=newWorker:addDeleting a Worker
To delete a worker:
/subsystem=io/worker=newWorker:remove
/subsystem=io/worker=newWorker:removereload
reloadFor a full list of the attributes available for configuring workers, please see the IO Subsystem Attributes section.
17.6. Configuring a Buffer Pool
IO buffer pools are deprecated, but they are still set as the default in the current release. Buffer pools are pooled NIO buffer instances. Changing the buffer size has a big impact on application performance. For most servers, the ideal buffer size is usually 16k. For more information about configuring Undertow byte buffer pools, see the Configuring Byte Buffer Pools section of the Configuration Guide for JBoss EAP.
Updating an Existing Buffer Pool
To update an existing buffer pool:
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=default:write-attribute(name=direct-buffers,value=true)
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=default:write-attribute(name=direct-buffers,value=true)reload
reloadCreating a Buffer Pool
To create a new buffer pool:
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=newBuffer:add
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=newBuffer:addDeleting a Buffer Pool
To delete a buffer pool:
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=newBuffer:remove
/subsystem=io/buffer-pool=newBuffer:removereload
reloadFor a full list of the attributes available for configuring buffer pools, please see the IO Subsystem Attributes section.
17.7. Tuning the IO Subsystem
For tips on monitoring and optimizing performance for the io subsystem, see the IO Subsystem Tuning section of the Performance tuning for JBoss EAP.
Chapter 18. Web services configuration in JBoss EAP
JBoss EAP enables you to configure the behavior of deployed web services through the webservices subsystem by using the management console or management CLI. This configuration applies to Jakarta Web Services (JAX-WS) endpoints and allows you to set up published endpoint addresses, handler chains, and runtime statistics collection for web services.
Chapter 19. Jakarta Server Faces configuration
The jsf subsystem enables the installation of multiple Jakarta Server Faces implementations on the same JBoss EAP server instance. You can install a version of Sun Mojarra or Apache MyFaces that implements the Jakarta Server Faces 4.0 specification or later. The feature pack can only be used to install the Apache MyFaces implementation.
Only the Jakarta Server Faces implementation included with JBoss EAP is fully supported.
19.1. Installing a Jakarta Server Faces implementation
JBoss EAP supports provisioning a server with only the necessary features by using the JBoss EAP Installation Manager, which delivers these features as feature packs.
Prerequisites
- You have installed JBoss EAP.
Procedure
Create the
myfaces-manifest.yamlfile with the following content:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the MyFaces manifest by using the following command:
$JBOSS_HOME/bin/jboss-eap-installation-manager.sh channel add \ --channel-name=myfaces \ --manifest=myfaces-manifest.yaml \ --repositories=https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/
$JBOSS_HOME/bin/jboss-eap-installation-manager.sh channel add \ --channel-name=myfaces \ --manifest=myfaces-manifest.yaml \ --repositories=https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Deploy the MyFaces Maven manifest to your local Maven repository by using the following command:
mvn deploy:deploy-file -Dfile=myfaces-manifest.yaml \ -DgroupId=org.apache.myfaces.channel -DartifactId=myfaces \ -Dclassifier=manifest -Dpackaging=yaml -Dversion=4.0.2 \ -Durl=file://$HOME/.m2/repository
mvn deploy:deploy-file -Dfile=myfaces-manifest.yaml \ -DgroupId=org.apache.myfaces.channel -DartifactId=myfaces \ -Dclassifier=manifest -Dpackaging=yaml -Dversion=4.0.2 \ -Durl=file://$HOME/.m2/repositoryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Provision a server using the MyFaces feature pack by using the following command:
$JBOSS_HOME/bin/jboss-eap-installation-manager.sh fp add \ --fpl=org.jboss.eap:eap-myfaces-feature-pack \ --layers=myfaces
$JBOSS_HOME/bin/jboss-eap-installation-manager.sh fp add \ --fpl=org.jboss.eap:eap-myfaces-feature-pack \ --layers=myfacesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Start the server.
Verification
Use the following CLI command to verify that the new Jakarta Server Faces implementation has been installed successfully:
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] /subsystem=jsf:list-active-jsf-impls()
[standalone@localhost:9990 /] /subsystem=jsf:list-active-jsf-impls()Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
19.2. Changing the default Jakarta Server Faces implementation
The multi-Jakarta Server Faces feature includes the default-jsf-impl-slot attribute in the jsf subsystem, which enables you to change the default Jakarta Server Faces implementation.
Prerequisites
- You have the multiple Jakarta Server Faces implementations installed on the server.
Procedure
Use the
write-attributecommand to set the value of thedefault-jsf-impl-slotattribute to one of the active Jakarta Server Faces implementations:/subsystem=jsf:write-attribute(name=default-jsf-impl-slot,value=JSF_IMPLEMENTATION)
/subsystem=jsf:write-attribute(name=default-jsf-impl-slot,value=JSF_IMPLEMENTATION)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Replace
JSF_IMPLEMENTATIONwith the name of the Jakarta Server Faces implementation you want to set as default.Restart the JBoss EAP server for the change to take effect.
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
Identify the available Jakarta Server Faces implementations by using the following command:
/subsystem=jsf:read-attribute(name=default-jsf-impl-slot)
/subsystem=jsf:read-attribute(name=default-jsf-impl-slot)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Expected output
{ "outcome" => "success", "result" => "myfaces" }{ "outcome" => "success", "result" => "myfaces" }Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
19.3. Jakarta Server Faces application configuration for non-default implementation
To configure a Jakarta Server Faces application to use a Jakarta Server Faces implementation other than the default, add the org.jboss.jbossfaces.JSF_CONFIG_NAME context parameter to the web.xml file. This parameter instructs the jsf subsystem to apply the specified Jakarta Server Faces implementation when deploying the application.
For example, if you want to use MyFaces 4.0.0 in your application, include the following context parameter in the web.xml file:
<context-param>
<param-name>org.jboss.jbossfaces.JSF_CONFIG_NAME</param-name>
<param-value>myfaces-4.0.0</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>org.jboss.jbossfaces.JSF_CONFIG_NAME</param-name>
<param-value>myfaces-4.0.0</param-value>
</context-param>If a Jakarta Server Faces application does not include this context parameter, the 'jsf' subsystem will use the default Jakarta Server Faces implementation.
19.4. Disallowing DOCTYPE declarations
You can configure the jsf subsystem to disallow DOCTYPE declarations in Jakarta Server Faces deployments. This setting improves security by preventing the use of external entities.
Prerequisites
-
You have management CLI access to configure the
jsfsubsystem.
Procedure
Disallow
DOCTYPEdeclarations in all Jakarta Server Faces deployments by using the following command:/subsystem=jsf:write-attribute(name=disallow-doctype-decl, value=true)
/subsystem=jsf:write-attribute(name=disallow-doctype-decl, value=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart the JBoss EAP server for the changes to take effect:
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To allow
DOCTYPEdeclarations for a specific Jakarta Server Faces deployment, add thecom.sun.faces.disallowDoctypeDeclcontext parameter to the deployment’s web.xml file with the following configuration:<context-param> <param-name>com.sun.faces.disallowDoctypeDecl</param-name> <param-value>false</param-value> </context-param><context-param> <param-name>com.sun.faces.disallowDoctypeDecl</param-name> <param-value>false</param-value> </context-param>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Chapter 20. Configuring batch applications
JBoss EAP 8.0 supports Jakarta Batch. You can configure an environment for running batch applications and manage batch jobs using the batch-jberet subsystem.
For information on developing batch applications, see Jakarta Batch Application Development in the JBoss EAP Development Guide.
20.1. Configuring batch jobs
You can configure settings for batch jobs using the batch-jberet subsystem, which is based on the JBeret implementation.
The default batch-jberet subsystem configuration defines an in-memory job repository and default thread pool settings.
By default, any batch jobs stopped during a server suspend will be restarted upon server resume. You can set the restart-jobs-on-resume property to false to leave jobs in the STOPPED state instead.
/subsystem=batch-jberet:write-attribute(name=restart-jobs-on-resume,value=false)
/subsystem=batch-jberet:write-attribute(name=restart-jobs-on-resume,value=false)You can also configure the settings for batch job repositories and thread pools.
20.1.1. Configure batch job repositories
This section shows you how to configure in-memory and JDBC job repositories for storing batch job information using the management CLI. You can also configure job repositories using the management console by navigating to Configuration → Subsystems → Batch (JBeret), clicking View, and selecting either In Memory or JDBC from the left-hand menu.
Add an in-memory job repository
You can add a job repository that stores batch job information in memory.
/subsystem=batch-jberet/in-memory-job-repository=REPOSITORY_NAME:add
/subsystem=batch-jberet/in-memory-job-repository=REPOSITORY_NAME:addAdd a JDBC job repository
You can add a job repository that stores batch job information in a database. You must specify the name of the datasource for connecting to the database.
/subsystem=batch-jberet/jdbc-job-repository=REPOSITORY_NAME:add(data-source=DATASOURCE)
/subsystem=batch-jberet/jdbc-job-repository=REPOSITORY_NAME:add(data-source=DATASOURCE)For more information about datasources, see About JBoss EAP Datasources.
Set a default job repository
You can set an in-memory or JDBC job repository as the default job repository for batch applications.
/subsystem=batch-jberet:write-attribute(name=default-job-repository,value=REPOSITORY_NAME)
/subsystem=batch-jberet:write-attribute(name=default-job-repository,value=REPOSITORY_NAME)This will require a server reload.
reload
reload20.1.2. Configure batch thread pools
This section shows you how to configure thread pools and thread factories to be used for batch jobs using the management CLI. You can also configure thread pools and thread factories using the management console by navigating to Configuration → Subsystems → Batch (JBeret), clicking View, and selecting either Thread Factory or Thread Pool from the left-hand menu.
Configure a thread pool
When adding a thread pool, you must specify the max-threads, which should always be greater than 3 as two threads are reserved to ensure partition jobs can execute as expected.
Procedure
Add a thread pool.
/subsystem=batch-jberet/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:add(max-threads=10)
/subsystem=batch-jberet/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:add(max-threads=10)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If desired, set a
keepalive-timevalue./subsystem=batch-jberet/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:write-attribute(name=keepalive-time,value={time=60,unit=SECONDS})/subsystem=batch-jberet/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:write-attribute(name=keepalive-time,value={time=60,unit=SECONDS})Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Use a thread factory
Procedure
Add a thread factory.
/subsystem=batch-jberet/thread-factory=THREAD_FACTORY_NAME:add
/subsystem=batch-jberet/thread-factory=THREAD_FACTORY_NAME:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the desired attributes for the thread factory.
-
group-name- The name of a thread group to create for this thread factory. -
priority- The thread priority of created threads. thread-name-pattern- The template used to create names for threads. The following patterns may be used:-
%%- A percent sign -
%t- The per-factory thread sequence number -
%g- The global thread sequence number -
%f- The factory sequence number -
%i- The thread ID
-
-
Assign the thread factory to a thread pool.
/subsystem=batch-jberet/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:write-attribute(name=thread-factory,value=THREAD_FACTORY_NAME)
/subsystem=batch-jberet/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:write-attribute(name=thread-factory,value=THREAD_FACTORY_NAME)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This will require a server reload.
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Set a default thread pool
You can set a different thread pool as the default thread pool.
/subsystem=batch-jberet:write-attribute(name=default-thread-pool,value=THREAD_POOL_NAME)
/subsystem=batch-jberet:write-attribute(name=default-thread-pool,value=THREAD_POOL_NAME)This will require a server reload.
reload
reloadView thread pool statistics
You can view runtime information about a batch thread pool using the read-resource management CLI operation. You must use the include-runtime=true parameter in order to see this runtime information.
You can also view runtime information for batch thread pools using the management console by navigating to the Batch subsystem from the Runtime tab.
20.2. Managing batch jobs
The batch-jberet subsystem resource for deployments allows you to start, stop, restart, and view execution details for batch jobs. Batch jobs can be managed from the management CLI or the management console.
Manage batch jobs from the management CLI
Restart a batch job
You can restart a job that is in a STOPPED or FAILED state by providing its execution ID and optionally any properties to use when restarting the batch job.
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=batch-jberet:restart-job(execution-id=EXECUTION_ID,properties={PROPERTY=VALUE})
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=batch-jberet:restart-job(execution-id=EXECUTION_ID,properties={PROPERTY=VALUE})The execution ID must be the most recent execution of the job instance.
Start a batch job
You can start a batch job by providing the job XML file and optionally any properties to use when starting the batch job.
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=batch-jberet:start-job(job-xml-name=JOB_XML_NAME,properties={PROPERTY=VALUE})
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=batch-jberet:start-job(job-xml-name=JOB_XML_NAME,properties={PROPERTY=VALUE})Stop a batch job
You can stop a running batch job by providing its execution ID.
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=batch-jberet:stop-job(execution-id=EXECUTION_ID)
/deployment=DEPLOYMENT_NAME/subsystem=batch-jberet:stop-job(execution-id=EXECUTION_ID)View batch job execution details
You can view the details of batch job executions. You must use the include-runtime=true parameter on the read-resource operation in order to see this runtime information.
Manage batch jobs from the management console
To manage batch jobs from the management console, navigate to the Runtime tab, select the server, select Batch (JBeret), and choose the job from the list.
Start a batch job
Start a new execution of a batch job by selecting the job and choosing Start from the drop down.
20.3. Configure security for batch jobs
You can configure the batch-jberet subsystem to run batch jobs with an Elytron security domain. This allows batch jobs to be securely suspended and resumed by the same secured identity. For example, a secured RESTful endpoint is created to initiate batch jobs using the batch-jberet subsystem. If both the RESTful endpoint and batch-jberet subsystem were secured using the same security domain, or the batch-jberet security domain trusted the RESTful endpoint’s security domain, batch jobs initiated in this manner could be securely paused and resumed by the same secured identity.
Use the following management CLI command to update the security-domain attribute to configure security for batch jobs.
/subsystem=batch-jberet:write-attribute(name=security-domain, value=ExampleDomain) reload
/subsystem=batch-jberet:write-attribute(name=security-domain, value=ExampleDomain)
reload
Batch jobs require the org.wildfly.extension.batch.jberet.deployment.BatchPermission permission. It provides start, stop, restart, abandon, and read permissions that align with jakarta.batch.operations.JobOperator. The default-permission-mapper mapper provides the org.wildfly.extension.batch.jberet.deployment.BatchPermission permission.
Chapter 21. Configuring the naming subsystem
21.1. About the naming subsystem
The naming subsystem provides the JNDI implementation for JBoss EAP. You can configure this subsystem to bind entries in global JNDI namespaces. You can also configure it to activate or deactivate the remote JNDI interface.
The following is an example of the naming subsystem XML configuration example with all of the elements and attributes specified.
21.2. Configuring global bindings
The naming subsystem allows you to bind entries into the java:global, java:jboss, or java global JNDI namespaces; however, it is recommended that you use the standard portable java:global namespace.
Global bindings are configured in the <bindings> element of the naming subsystem. Four types of bindings are supported:
Configuring simple bindings
The simple XML configuration element binds primitive or java.net.URL entries.
-
The
nameattribute is mandatory and specifies the target JNDI name for the entry. -
The
valueattribute is mandatory and defines the entry’s value. -
The optional
typeattribute, which defaults tojava.lang.String, specifies the type of the entry’s value. In addition tojava.lang.String, you can specify primitive types and their corresponding object wrapper classes, such asintorjava.lang.Integer, andjava.net.URL.
The following is an example of a management CLI command that creates a simple binding.
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/simple-integer-binding:add(binding-type=simple, type=int, value=100)
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/simple-integer-binding:add(binding-type=simple, type=int, value=100)Resulting XML configuration
Use the following command to remove the binding.
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/simple-integer-binding:remove
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/simple-integer-binding:removeBinding object factories
The object-factory XML configuration element binds jakarta.naming.spi.ObjectFactory entries.
-
The
nameattribute is mandatory and specifies the target JNDI name for the entry. -
The
classattribute is mandatory and defines the object factory’s Java type. -
The
moduleattribute is mandatory and specifies the JBoss Module ID where the object factory Java class can be loaded from. -
The optional
environmentchild element can be used to provide a custom environment to the object factory.
The following is an example of a management CLI command that creates an object factory binding.
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/foo\/bar\/factory:add(binding-type=object-factory, module=org.foo.bar, class=org.foo.bar.ObjectFactory, environment=[p1=v1, p2=v2])
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/foo\/bar\/factory:add(binding-type=object-factory, module=org.foo.bar, class=org.foo.bar.ObjectFactory, environment=[p1=v1, p2=v2])Resulting XML configuration
Use the following command to remove the binding.
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/foo\/bar\/factory:remove
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/foo\/bar\/factory:removeBinding external contexts
Federation of external JNDI contexts, such as LDAP context, are achieved using the external-context XML configuration element.
-
The
nameattribute is mandatory and specifies the target JNDI name for the entry. -
The
classattribute is mandatory and indicates the Java initial naming context type used to create the federated context. Note that such type must have a constructor with a single environment map argument. -
The optional
moduleattribute specifies the JBoss Module ID where any classes required by the external JNDI context can be loaded from. -
The optional
cacheattribute, which defaults tofalse, indicates whether the external context instance should be cached. -
The optional
environmentchild element can be used to provide the custom environment needed to look up the external context.
The following is an example of a management CLI command that creates an external context binding.
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/federation\/ldap\/example:add(binding-type=external-context, cache=true, class=jakarta.naming.directory.InitialDirContext, module=org.jboss.as.naming, environment=[java.naming.factory.initial=com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory, java.naming.provider.url="ldap://ldap.example.com:389", java.naming.security.authentication=simple, java.naming.security.principal="uid=admin,ou=system", java.naming.security.credentials=secret])
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/federation\/ldap\/example:add(binding-type=external-context, cache=true, class=jakarta.naming.directory.InitialDirContext, module=org.jboss.as.naming, environment=[java.naming.factory.initial=com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory, java.naming.provider.url="ldap://ldap.example.com:389", java.naming.security.authentication=simple, java.naming.security.principal="uid=admin,ou=system", java.naming.security.credentials=secret])Resulting XML configuration
Use the following command to remove the binding:
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/federation\/ldap\/example:remove
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/federation\/ldap\/example:remove
Resource look up for JNDI providers that do not properly implement the lookup(Name) method can result in a "jakarta.naming.InvalidNameException: Only support CompoundName names" error.
You might be able to work around this issue by specifying that the external context environment use the lookup(String) method instead by adding the following property; however, this can result in a performance degradation.
<property name="org.jboss.as.naming.lookup.by.string" value="true"/>
<property name="org.jboss.as.naming.lookup.by.string" value="true"/>Binding lookup aliases
The lookup element allows you to bind existing entries into additional names or aliases.
-
The
nameattribute is mandatory and specifies the target JNDI name for the entry. -
The
lookupattribute is mandatory and indicates the source JNDI name.
The following is an example of a management CLI command that binds an existing entry to an alias:
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/new-alias-name:add(binding-type=lookup, lookup=java\:global\/original-name)
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/new-alias-name:add(binding-type=lookup, lookup=java\:global\/original-name)Resulting XML configuration
<lookup name="java:global/new-alias-name" lookup="java:global/original-name" />
<lookup name="java:global/new-alias-name" lookup="java:global/original-name" />Use the following command to remove the binding:
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/c:remove
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/c:remove21.3. Dynamically change JNDI bindings
JBoss EAP 7.1 introduced the ability to dynamically change JNDI bindings without forcing a server reload or restart. This feature can be useful if the network service endpoints are dynamically reconfigured due to version updates, testing requirements, or application feature updates.
To update a JNDI binding, use the rebind operation. The rebind operation takes the same arguments as the add operation. This command works for all binding types except for external-context binding types. External context bindings require additional dependencies, which affect the Modular Service Container (MSC) state, so they cannot be restarted without restarting services.
The following command dynamically changes the JNDI binding that was defined in the Configuring Simple Bindings example.
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/simple-integer-binding:rebind(binding-type=simple, type=int, value=200)
/subsystem=naming/binding=java\:global\/simple-integer-binding:rebind(binding-type=simple, type=int, value=200)
For more information about how to configure global bindings in the naming subsystem, see Configuring Global Bindings.
21.4. Configuring the remote JNDI interface
The remote JNDI interface allows clients to look up entries in remote JBoss EAP instances. The naming subsystem can be configured to deactivate or activate this interface, which is activated by default. The remote JNDI interface is configured using the <remote-naming> element.
Use the following management CLI command to activate or reactivate the remote JNDI interface.
/subsystem=naming/service=remote-naming:add
/subsystem=naming/service=remote-naming:addUse the following management CLI command to deactivate the remote JNDI interface.
/subsystem=naming/service=remote-naming:remove
/subsystem=naming/service=remote-naming:remove
Only entries within the java:jboss/exported context are accessible over remote JNDI.
Chapter 22. Configuring high availability
22.1. Introduction to high availability
JBoss EAP provides the following high availability services to guarantee the availability of deployed Jakarta EE applications.
- Load balancing
- This allows a service to handle a large number of requests by spreading the workload across multiple servers. A client can have timely responses from the service even in the event of a high volume of requests.
- Failover
- This allows a client to have uninterrupted access to a service even in the event of hardware or network failures. If the service fails, another cluster member takes over the client’s requests so that it can continue processing.
Clustering is a term that encompasses all of these capabilities. Members of a cluster can be configured to share workloads, referred to as load balancing, and pick up client processing in the event of a failure of another cluster member, referred to as failover.
It is important to keep in mind that the JBoss EAP operating mode chosen, either standalone server or managed domain, pertains to how you want to manage your servers. High availability services can be configured in JBoss EAP regardless of its operating mode.
JBoss EAP supports high availability at several different levels using various components. Some of those components of the runtime and your applications that can be made highly-available are:
- Instances of the application server
- Web applications, when used in conjunction with the internal JWS, Apache HTTP Server, Microsoft IIS, or Oracle iPlanet Web Server
- Stateful and stateless session Jakarta Enterprise Beans
- Single sign-on (SSO) mechanisms
- HTTP sessions
- Java Message Service services and message-driven beans (MDBs)
- Singleton MSC services
- Singleton deployments
Clustering is made available to JBoss EAP by the jgroups, infinispan, and modcluster subsystems. The ha and full-ha profiles have these systems enabled. In JBoss EAP, these services start up and shut down on demand, but they will only start up if an application configured as distributable is deployed on the servers.
See the JBoss EAP Development Guide for how to mark an application as distributable.
22.2. Cluster communication with JGroups
22.2.1. About JGroups
JGroups is a toolkit for reliable messaging and can be used to create clusters whose nodes can send messages to each other.
The jgroups subsystem provides group communication support for high availability services in JBoss EAP. It allows you to configure named channels and protocol stacks as well as view runtime statistics for channels. The jgroups subsystem is available when using a configuration that provides high availability capabilities, such as the ha or full-ha profile in a managed domain, or the standalone-ha.xml or standalone-full-ha.xml configuration file for a standalone server.
JBoss EAP is preconfigured with two JGroups stacks:
- udp
- The nodes in the cluster use User Datagram Protocol (UDP) multicasting to communicate with each other. This is the default stack.
- tcp
- The nodes in the cluster use Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) to communicate with each other.
TCP has more overhead and is often considered slower than UDP because it handles error checking, packet ordering, and congestion control itself. JGroups handles these features for UDP, whereas TCP guarantees them itself. TCP is a good choice when using JGroups on unreliable or high congestion networks, or when multicast is not available.
You can use the preconfigured stacks or define your own to suit your system’s specific requirements. For additional information on the available protocols and their attributes, see the following sections.
22.2.2. Switch the default JGroups channel to use TCP
By default, cluster nodes communicate using the udp protocol stack configured for the ee JGroups channel.
22.2.2.1. Configuring TCP with multicast
Some networks only allow TCP to be used.
Procedure
Use the following management CLI command to switch the
eechannel to use the preconfiguredtcpstack:/subsystem=jgroups/channel=ee:write-attribute(name=stack,value=tcp)
/subsystem=jgroups/channel=ee:write-attribute(name=stack,value=tcp)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This default
tcpstack uses theMPINGprotocol, which uses IP multicast to discover the initial cluster membership.
22.2.2.2. Configuring TCP without multicast
You can change the default protocol stack to use TCP without multicast when multicast is not preferable or allowed by security policies.
Procedure
To configure TCP-based clustering without multicast, perform the following steps:
To switch the
eechannel to use the pre-configuredtcpstack in the JGroups subsystem, run the following command:<channel name="ee" stack="tcp" cluster="ejb"/>
<channel name="ee" stack="tcp" cluster="ejb"/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the name of the cluster node:
In the standalone configuration mode, perform one of the following steps:
Run the following command:
<server xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:8.0" name="node_1">
<server xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:8.0" name="node_1">Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Specify a unique name to the system property
jboss.node.namewhen starting the instance.
In the domain mode, the cluster servers are listed in the
host-*.xmlfile in the server’s tag. The default configuration specifies the following server names, which you can edit if needed.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Choose one of the following protocols for discovering other cluster members:
-
TCPGOSSIP: This protocol uses an external gossip router service to discover the members of a cluster. This requires configuration and management of additional processes but allows the individual EAP instances to not list each other cluster member. This protocol is advantageous if the cluster members change frequently. For more details, see TCPPING. -
TCPPING: This protocol defines a static cluster membership list and requires each node to list all the potential cluster members. This protocol is preferred when cluster member addresses are known and do not change frequently. For more details, see TCPGOSSIP.
-
22.2.3. Configure TCPPING
This procedure creates a new JGroups stack that uses the TCPPING protocol to define a static cluster membership list. A base script is provided that creates a tcpping stack and sets the default ee channel to use this new stack. The management CLI commands in this script must be customized for your environment and will be processed as a batch.
Procedure
Copy the following script into a text editor and save it to the local file system.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the order of protocols defined is important. You can also insert a protocol at a particular index by passing an
add-indexvalue to theaddcommand. The index is zero-based, so the following management CLI command adds theUNICAST3protocol as the seventh protocol./subsystem=jgroups/stack=tcpping/protocol=UNICAST3:add(add-index=6)
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=tcpping/protocol=UNICAST3:add(add-index=6)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the script for your environment.
-
If you are running in a managed domain, you must specify which profile to update by preceding the
/subsystem=jgroupscommands with/profile=PROFILE_NAME. Adjust the following properties as appropriate for your environment:
-
socket-bindings: A comma-separated list of the host and port combinations that are considered well-known and will be available to look up the initial membership. See Configuring Socket Bindings for more information on defining socket bindings. -
initial_hosts: A comma-separated list of the host and port combinations, using the syntaxHOST[PORT], that are considered well-known and will be available to look up the initial membership, for example,host1[1000],host2[2000]. -
port_range: This property is used to extend theinitial_hostsport range by the specified value. For example, if you set theinitial_hoststohost1[1000],host2[2000], and theport_rangeto1, theinitial_hostssetting expands tohost1[1000],host1[1001],host2[2000],host2[2001]. This property only works with theinitial_hostsproperty.
-
-
If you are running in a managed domain, you must specify which profile to update by preceding the
Run the script by passing the script file to the management CLI.
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --file=/path/to/SCRIPT_NAME
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --file=/path/to/SCRIPT_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The TCPPING stack is now available and TCP is used for network communication.
22.2.3.1. Configuring TCPPING in standalone mode
This procedure helps you to configure the TCP stack and nodes for a clustered application in the standalone mode.
Procedure
Change the default stack from
udptotcpin the JGroups subsystem:<channel name="ee" stack="tcp" cluster="ejb"/>
<channel name="ee" stack="tcp" cluster="ejb"/>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the TCP stack to use the TCPPING protocol in place of the default MPING protocol. In the following code, the
initial_hostsproperty correlates to a listing of all nodes within the cluster and7600denotes the defaultjgroups-tcpport that can vary based on your configuration and environment.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe port number
7600set ininitial_hostsmust be same as the port number defined in thejgroups-tcpsocket-binding definition. If you use the port-offset feature for socket-binding, you need to specify the same value after offset ininitial_hosts.Set the IP address of the private interface, which is used by the JGroups component. The IP address should correlate to one of the IP addresses specified in
initial_hosts:<interface name="private"> <inet-address value="${jboss.bind.address.private:192.168.1.5}"/> </interface><interface name="private"> <inet-address value="${jboss.bind.address.private:192.168.1.5}"/> </interface>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow - Repeat the above steps for configuring other nodes within the cluster. When the nodes are configured, start each node and deploy a clustered application.
Verification
You can check logs to verify whether the nodes are up and running:
INFO [org.infinispan.remoting.transport.jgroups.JGroupsTransport] (thread-2,ee,node_1) ISPN000094: Received new cluster view for channel server: [node_1|1] (2) [node_1, node_2] INFO [org.infinispan.remoting.transport.jgroups.JGroupsTransport] (thread-2,ee,node_1) ISPN000094: Received new cluster view for channel web: [node_1|1] (2) [node_1, node_2]
INFO [org.infinispan.remoting.transport.jgroups.JGroupsTransport] (thread-2,ee,node_1) ISPN000094: Received new cluster view for channel server: [node_1|1] (2) [node_1, node_2] INFO [org.infinispan.remoting.transport.jgroups.JGroupsTransport] (thread-2,ee,node_1) ISPN000094: Received new cluster view for channel web: [node_1|1] (2) [node_1, node_2]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.2.3.2. Configuring TCPPING in domain mode
This procedure helps you to configure the TCP stack and nodes for a clustered application in the domain mode.
Procedure
If the same profile is used for multiple clusters, set the system property value to
initial_hosts:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the IP address of the private interface within the XML configuration of the host controller. The IP address of the private interface should correlate to one of the IP addresses listed in
initial_hosts.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Verification
You can check logs to verify whether the nodes are up and running:
INFO [org.infinispan.remoting.transport.jgroups.JGroupsTransport] (thread-2,ee,node_1) ISPN000094: Received new cluster view for channel server: [node_1|1] (2) [node_1, node_2] INFO [org.infinispan.remoting.transport.jgroups.JGroupsTransport] (thread-2,ee,node_1) ISPN000094: Received new cluster view for channel web: [node_1|1] (2) [node_1, node_2]
INFO [org.infinispan.remoting.transport.jgroups.JGroupsTransport] (thread-2,ee,node_1) ISPN000094: Received new cluster view for channel server: [node_1|1] (2) [node_1, node_2] INFO [org.infinispan.remoting.transport.jgroups.JGroupsTransport] (thread-2,ee,node_1) ISPN000094: Received new cluster view for channel web: [node_1|1] (2) [node_1, node_2]Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.2.4. Configure TCPGOSSIP
This procedure creates a new JGroups stack that uses the TCPGOSSIP protocol to use an external gossip router to discover the members of a cluster. A base script is provided that creates a tcpgossip stack and sets the default ee channel to use this new stack. The management CLI commands in this script must be customized for your environment and will be processed as a batch.
Procedure
Copy the following script into a text editor and save it to the local file system.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Note that the order of protocols defined is important. You can also insert a protocol at a particular index by passing an
add-indexvalue to theaddcommand. The index is zero-based, so the following management CLI command adds theUNICAST3protocol as the seventh protocol./subsystem=jgroups/stack=tcpgossip/protocol=UNICAST3:add(add-index=6)
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=tcpgossip/protocol=UNICAST3:add(add-index=6)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the script for your environment.
-
If you are running in a managed domain, you must specify which profile to update by preceding the
/subsystem=jgroupscommands with/profile=PROFILE_NAME. Adjust the following properties as appropriate for your environment:
-
socket-bindings: A comma-separated list of the host and port combinations that are considered well-known and will be available to look up the initial membership. See Configuring Socket Bindings for more information on defining socket bindings. -
initial_hosts: A comma-separated list of the host and port combinations, using the syntaxHOST[PORT], that are considered well-known and will be available to look up the initial membership, for example,host1[1000],host2[2000]. -
port_range: This property is used to extend theinitial_hostsport range by the specified value. For example, if you set theinitial_hoststohost1[1000],host2[2000], and theport_rangeto1, theinitial_hostssetting expands tohost1[1000],host1[1001],host2[2000],host2[2001]. This property only works with theinitial_hostsproperty. -
reconnect_interval: The interval in milliseconds by which a disconnected stub attempts to reconnect to the gossip router. -
sock_conn_timeout: The maximum time for socket creation. The default is1000milliseconds. -
sock_read_timeout: The maximum time in milliseconds to block on a read. A value of0will block indefinitely.
-
-
If you are running in a managed domain, you must specify which profile to update by preceding the
Run the script by passing the script file to the management CLI.
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --file=/path/to/SCRIPT_NAME
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --file=/path/to/SCRIPT_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The TCPGOSSIP stack is now available and TCP is used for network communication. This stack is configured for use with a gossip router so that JGroups cluster members can find other cluster members.
22.2.5. Configure JDBC_PING
You can use the JDBC_PING protocol to manage and discover membership in a cluster.
JDBC_PING uses a database, specified in a data-source, to list the members of the cluster.
Procedure
- Create a data-source to connect to the database you want to use to manage cluster membership.
Copy the following script into a text editor and save it to the local file system.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe order of the defined protocols is important. You can also insert a protocol at a particular index by passing an
add-indexvalue to theaddcommand. The index is zero-based, so the following management CLI command adds theUNICAST3protocol as the seventh protocol./subsystem=jgroups/stack=JDBC_PING/protocol=UNICAST3:add(add-index=6)
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=JDBC_PING/protocol=UNICAST3:add(add-index=6)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Modify the script for your environment.
-
If you are running in a managed domain, you must specify which profile to update by preceding the
/subsystem=jgroupscommands with/profile=PROFILE_NAME. - Replace 'ExampleDS' with the name of the data-source you defined in Step 1.
-
If you are running in a managed domain, you must specify which profile to update by preceding the
Run the script by passing the script file to the management CLI.
EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --file=/path/to/SCRIPT_NAME
$ EAP_HOME/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --file=/path/to/SCRIPT_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The JDBC_PING stack is now available and TCP is used for network communication.
22.2.6. Binding JGroups to a network interface
By default, JGroups only binds to the private network interface, which points to localhost in the default configuration. For security reasons, JGroups will not bind to the network interface defined by the -b argument specified during JBoss EAP startup, as clustering traffic should not be exposed on a public network interface.
See the Network and Port Configuration chapter in this guide for information about how to configure network interfaces.
For security reasons, JGroups should only be bound to a non-public network interface. For performance reasons, we also recommend that the network interface for JGroups traffic should be part of a dedicated Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN).
22.2.7. Securing a cluster
There are several concerns to address in order to run a cluster securely:
- Preventing unauthorized nodes from joining the cluster. This is addressed by requiring authentication.
- Preventing non-members from communicating with cluster members. This is addressed by encrypting messages.
22.2.7.1. Configuring authentication
JGroups authentication is performed by the AUTH protocol. The purpose is to ensure that only authenticated nodes can join a cluster.
In the applicable server configuration file, add the AUTH protocol with the appropriate property settings. The AUTH protocol should be configured immediately before the pbcast.GMS protocol.
The following examples demonstrate using AUTH with different forms of authorization tokens.
AUTH with a simple token
AUTH with a digest algorithm token
This format can be used with any digest algorithm, for example MD5 or SHA-2. The default digest algorithm in JBoss EAP 8.0 is SHA-256, the strongest digest algorithm required to be supported by the JVM. Many JVMs will additionally implement SHA-512.
AUTH with an X509 token
This example creates a new keystore in the elytron subsystem, and references it in the JGroups AUTH configuration.
Create the keystore:
keytool -genkeypair -alias jgroups_key -keypass my_password -storepass my_password -storetype jks -keystore jgroups.keystore -keyalg RSA
$ keytool -genkeypair -alias jgroups_key -keypass my_password -storepass my_password -storetype jks -keystore jgroups.keystore -keyalg RSACopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the keystore to the
elytronsubsystem using the management CLI:/subsystem=elytron/key-store=jgroups-token-store:add(type=jks,path=/path/to/jgroups.keystore,credential-reference={clear-text=my_password}, required=true)/subsystem=elytron/key-store=jgroups-token-store:add(type=jks,path=/path/to/jgroups.keystore,credential-reference={clear-text=my_password}, required=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the JGroups stack definition, configure
AUTHto use the keystore:Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.2.7.2. Configuring encryption
To encrypt messages, JGroups uses a secret key that is shared by the members of a cluster. The sender encrypts the message using the shared secret key, and the receiver decrypts the message using the same secret key. With symmetric encryption, which is configured using the SYM_ENCRYPT protocol, nodes use a shared keystore to retrieve the secret key. With asymmetric encryption, which is configured using the ASYM_ENCRYPT protocol, nodes retrieve the secret key from the coordinator of the cluster after being authenticated using AUTH.
Using symmetric encryption
In order to use SYM_ENCRYPT, you must set up a keystore that will be referenced in the JGroups configuration for each node.
Create a keystore.
In the following command, replace
VERSIONwith the appropriate JGroups JAR version andPASSWORDwith a keystore password.java -cp EAP_HOME/modules/system/layers/base/org/jgroups/main/jgroups-VERSION.jar org.jgroups.demos.KeyStoreGenerator --alg AES --size 128 --storeName defaultStore.keystore --storepass PASSWORD --alias mykey
$ java -cp EAP_HOME/modules/system/layers/base/org/jgroups/main/jgroups-VERSION.jar org.jgroups.demos.KeyStoreGenerator --alg AES --size 128 --storeName defaultStore.keystore --storepass PASSWORD --alias mykeyCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This will generate a
defaultStore.keystorefile that will be referenced in the JGroups configuration.Once the keystore has been generated it is defined in the
SYM_PROTOCOLusing one of two methods.- Specify the keystore directly in the configuration.
- Reference the keystore using the Elytron subsystem.
Configuring AUTH is optional when using SYM_ENCRYPT.
Using symmetric encryption by directly referencing the keystore
Configure the
SYM_ENCRYPTprotocol in thejgroupssubsystem.In the applicable server configuration file, add the
SYM_ENCRYPTprotocol with the appropriate property settings. This protocol will reference the previously created keystore. TheSYM_ENCRYPTprotocol should be configured immediately before thepbcast.NAKACK2protocol.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Using symmetric encryption with elytron
Using the management CLI, create a keystore in the
elytronsubsystem that references thedefaultStore.keystorecreated in using symmetric encryption./subsystem=elytron/key-store=jgroups-keystore:add(path=/path/to/defaultStore.keystore,credential-reference={clear-text=PASSWORD},type=JCEKS)/subsystem=elytron/key-store=jgroups-keystore:add(path=/path/to/defaultStore.keystore,credential-reference={clear-text=PASSWORD},type=JCEKS)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the
SYM_ENCRYPTprotocol in thejgroupssubsystem with the appropriate property settings. TheSYM_ENCRYPTprotocol should be configured immediately before thepbcast.NAKACK2protocol, as seen in the following configuration.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe above example uses a clear text password; however, a credential store may also be defined to define the password outside of the configuration file. For more information on configuring this store, see the Credential store section in the How to Configure Server Security guide.
Using asymmetric encryption
In order to use ASYM_ENCRYPT the AUTH protocol must be defined. See the Configuring authentication section for instructions on configuring the AUTH protocol in the jgroups subsystem.
The ASYM_ENCRYPT is configured using one of two methods.
- Generate a secret key and reference it directly in the configuration.
- Create a keystore and reference it using the Elytron subsystem.
Using asymmetric encryption by generating a secret key
Configure the
ASYM_ENCRYPTprotocol in thejgroupssubsystem.In the applicable server configuration file, add the
ASYM_ENCRYPTprotocol with the appropriate property settings. TheASYM_ENCRYPTprotocol should be configured immediately before thepbcast.NAKACK2protocol, as seen in the following configuration.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Using asymmetric encryption with elytron
Create a keystore to contain the key pair. The following command creates a keystore with the
mykeyentry.keytool -genkeypair -alias mykey -keyalg RSA -keysize 1024 -keystore defaultKeystore.keystore -dname "CN=localhost" -keypass secret -storepass secret
$ keytool -genkeypair -alias mykey -keyalg RSA -keysize 1024 -keystore defaultKeystore.keystore -dname "CN=localhost" -keypass secret -storepass secretCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Using the management CLI, create a keystore in the
elytronsubsystem that references thedefaultStore.keystore./subsystem=elytron/key-store=jgroups-keystore:add(path=/path/to/defaultStore.keystore,credential-reference={clear-text=PASSWORD},type=JCEKS)/subsystem=elytron/key-store=jgroups-keystore:add(path=/path/to/defaultStore.keystore,credential-reference={clear-text=PASSWORD},type=JCEKS)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the
ASYM_ENCRYPTprotocol in thejgroupssubsystem with the appropriate property settings. TheASYM_ENCRYPTprotocol should be configured immediately before thepbcast.NAKACK2protocol, as seen in the following configuration.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe above example uses a clear text password; however, a credential store may also be defined to define the password outside of the configuration file. For more information on configuring this store, see the Credential store section in the How to Configure Server Security guide.
22.2.8. Configure JGroups thread pools
The jgroups subsystem contains the default, internal, oob, and timer thread pools. These pools can be configured for any JGroups stack and do not affect bean or other pools configured on local nodes. The JGroup thread pools are used to support cluster communication.
The following table lists the attributes you can configure for each thread pool and the default value for each.
| Thread pool name | Description | keepalive-time | max-threads | min-threads | queue-length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| default | This pool is used to handle incoming messages that are not marked as out-of-band. | 60000L | 300 | 20 | 100 |
| internal | This pool is used to handle internal processes needed for EAP maintenance. | 60000L | 4 | 2 | 100 |
| oob | This pool is used to handle incoming out-of-band messages. | 60000L | 300 | 20 | 0 |
| timer | This pool is used to handle time-bound scheduler messages. | 5000L | 4 | 2 | 500 |
Use the following syntax to configure a JGroups thread pool using the management CLI.
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=STACK_TYPE/transport=TRANSPORT_TYPE/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:write-attribute(name=ATTRIBUTE_NAME, value=ATTRIBUTE_VALUE)
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=STACK_TYPE/transport=TRANSPORT_TYPE/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:write-attribute(name=ATTRIBUTE_NAME, value=ATTRIBUTE_VALUE)
The following is an example of the management CLI command to set the max-threads value to 500 in the default thread pool for the udp stack.
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=udp/transport=UDP/thread-pool=default:write-attribute(name="max-threads", value="500")
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=udp/transport=UDP/thread-pool=default:write-attribute(name="max-threads", value="500")22.2.9. Configure JGroups send and receive buffers
Resolving buffer size warnings
By default, JGroups is configured with certain send and receive buffer values; however, your operating system may limit the available buffer sizes and JBoss EAP may not be able to use its configured buffer values. In this situation you will see warnings in the JBoss EAP logs similar to the following:
To resolve this, consult your operating system documentation for instructions on how to increase the buffer size. For Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems, edit /etc/sysctl.conf as the root user to configure maximum values for buffer sizes that will survive system restarts. For example:
Allow a 25MB UDP receive buffer for JGroups Allow a 1MB UDP send buffer for JGroups
# Allow a 25MB UDP receive buffer for JGroups
net.core.rmem_max = 26214400
# Allow a 1MB UDP send buffer for JGroups
net.core.wmem_max = 1048576
After modifying /etc/sysctl.conf, run sysctl -p for the changes to take effect.
Configuring JGroups buffer sizes
You can configure the JGroups buffer sizes that JBoss EAP uses by setting the following transport properties on the UDP and TCP JGroups stacks.
- UDP stack
-
ucast_recv_buf_size -
ucast_send_buf_size -
mcast_recv_buf_size -
mcast_send_buf_size
-
- TCP stack
-
recv_buf_size -
send_buf_size
-
JGroups buffer sizes can be configured using the management console or the management CLI.
Use the following syntax to set a JGroups buffer size property using the management CLI.
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=STACK_NAME/transport=TRANSPORT/property=PROPERTY_NAME:add(value=BUFFER_SIZE)
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=STACK_NAME/transport=TRANSPORT/property=PROPERTY_NAME:add(value=BUFFER_SIZE)
The following is an example management CLI command to set the recv_buf_size property to 20000000 on the tcp stack.
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=tcp/transport=TRANSPORT/property=recv_buf_size:add(value=20000000)
/subsystem=jgroups/stack=tcp/transport=TRANSPORT/property=recv_buf_size:add(value=20000000)JGroups buffer sizes can also be configured using the management console by navigating to the JGroups subsystem from the Configuration tab, clicking View, selecting the Stack tab, choosing the appropriate stack, clicking Transport, and editing the Properties field.
22.2.10. Tuning the JGroups subsystem
For tips on monitoring and optimizing performance for the jgroups subsystem, see the JGroups Subsystem Tuning section of the Performance tuning for JBoss EAP.
22.2.11. JGroups troubleshooting
22.2.11.1. Nodes do not form a cluster
Make sure your machine is set up correctly for IP multicast. There are two test programs that ship with JBoss EAP that can be used to test IP multicast: McastReceiverTest and McastSenderTest.
In a terminal, start McastReceiverTest.
java -cp EAP_HOME/bin/client/jboss-client.jar org.jgroups.tests.McastReceiverTest -mcast_addr 230.11.11.11 -port 5555
$ java -cp EAP_HOME/bin/client/jboss-client.jar org.jgroups.tests.McastReceiverTest -mcast_addr 230.11.11.11 -port 5555
Then in another terminal window, start McastSenderTest.
java -cp EAP_HOME/bin/client/jboss-client.jar org.jgroups.tests.McastSenderTest -mcast_addr 230.11.11.11 -port 5555
$ java -cp EAP_HOME/bin/client/jboss-client.jar org.jgroups.tests.McastSenderTest -mcast_addr 230.11.11.11 -port 5555
If you want to bind to a specific network interface card (NIC), use -bind_addr YOUR_BIND_ADDRESS, where YOUR_BIND_ADDRESS is the IP address of the NIC to which you want to bind. Use this parameter in both the sender and the receiver.
When you type in the McastSenderTest terminal window, you should see the output in the McastReceiverTest window. If you do not, try the following steps.
-
Increase the time-to-live for multicast packets by adding
-ttl VALUEto the sender command. The default used by this test program is32and theVALUEmust be no greater than255. - If the machines have multiple interfaces, verify that you are using the correct interface.
- Contact a system administrator to make sure that multicast will work on the interface you have chosen.
Once you know multicast is working properly on each machine in your cluster, you can repeat the above test to test the network, putting the sender on one machine and the receiver on another.
22.2.11.2. Causes of missing heartbeats in failure detection
Sometimes a cluster member is suspected by failure detection (FD) because a heartbeat acknowledgment has not been received for some time T, which is defined by timeout and max_tries.
For an example cluster of nodes A, B, C, and D, where A pings B, B pings C, C pings D, and D pings A, C can be suspected for any of the following reasons:
-
B or C are running at 100% CPU for more than
Tseconds. So even if C sends a heartbeat acknowledgment to B, B may not be able to process it because it is at 100% CPU usage. - B or C are garbage collecting, which results in the same situation as above.
- A combination of the two cases above.
- The network loses packets. This usually happens when there is a lot of traffic on the network, and the switch starts dropping packets, usually broadcasts first, then IP multicasts, and TCP packets last.
-
B or C are processing a callback. For example, if C received a remote method call over its channel that takes
T+ 1 seconds to process, during this time C will not process any other messages, including heartbeats. Therefore, B will not receive the heartbeat acknowledgment and will suspect C.
22.3. Infinispan
22.3.1. About Infinispan
Infinispan is a Java data grid platform that provides a Jakarta Persistence 2.2-compatible cache interface for managing cached data.
For more information about Infinispan functionality and configuration options see the Infinispan documentation.
The infinispan subsystem provides caching support for JBoss EAP. It allows you to configure and view runtime metrics for named cache containers and caches.
When using a configuration that provides high availability capabilities, such as the ha or full-ha profile in a managed domain, or the standalone-ha.xml or standalone-full-ha.xml configuration file for a standalone server, the infinispan subsystem provides caching, state replication, and state distribution support. In non-high-availability configurations, the infinispan subsystem provides local caching support.
Infinispan is a public module in the JBoss EAP 8.0. You can use the infinispan subsystem for applications to create and use new cache-containers or caches. Also, the usage of the Infinispan APIs is supported by applications.
22.3.2. Cache containers
A cache container is a repository for the caches used by a subsystem. Each cache container defines a default cache to be used.
JBoss EAP 8.0 defines the following default Infinispan cache containers:
-
serverfor singleton caching -
webfor web session clustering -
ejbfor stateful session bean clustering -
hibernatefor entity caching
Example: Default Infinispan Configuration
Note the default cache defined in each cache container. For example, the web cache container defines the dist distributed cache as the default. The dist cache will therefore be used when clustering web sessions.
See Configure cache containers for information on changing the default cache and adding additional caches.
22.3.2.1. Configure cache containers
Cache containers and cache attributes can be configured using the management console or management CLI.
You should avoid changing cache or cache container names, as other components in the configuration may reference them.
22.3.2.1.1. Configure caches using the management console
Once you navigate to the Infinispan subsystem from the Configuration tab in the management console, you can configure caches and cache containers. In a managed domain, make sure to select the appropriate profile to configure.
Add a cache container.
Click the Add (+) button next to the Cache Container heading, choose Add Cache Container, and enter the settings for the new cache container.
Update cache container settings.
Choose the appropriate cache container and click View. Configure the cache container settings as necessary.
Update cache container transport settings.
Choose the appropriate cache container and click View. Select the Transport tab and configure the cache container transport settings as necessary.
Configure caches.
Choose the appropriate cache container and click View. From the appropriate cache tab, for example, Replicated Cache, you can add, update, and remove caches.
22.3.2.1.2. Configure caches using the management CLI
You can configure caches and cache containers using the management CLI. In a managed domain, you must specify the profile to update by preceding these commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Add a cache container.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER:add
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add a replicated cache.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/replicated-cache=CACHE:add(mode=MODE)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/replicated-cache=CACHE:add(mode=MODE)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the default cache for a cache container.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER:write-attribute(name=default-cache,value=CACHE)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER:write-attribute(name=default-cache,value=CACHE)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure batching for a replicated cache.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/replicated-cache=CACHE/component=transaction:write-attribute(name=mode,value=BATCH)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/replicated-cache=CACHE/component=transaction:write-attribute(name=mode,value=BATCH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This results in the following server configuration:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.3.2.1.3. Change the default Jakarta Enterprise Beans cache container
You can use cache containers in the ejb3 subsystem as described below:
-
To support passivation of Jakarta Enterprise Beans session beans, you can use the
ejbcache container defined in theinfinispansubsystem to store the sessions. - For remote Jakarta Enterprise Beans clients connecting to a clustered deployment on a server, you must provide the cluster topology information to these clients, so that they can fail over to other nodes in the cluster if the node they are interacting with fails.
22.3.2.1.4. Inject resources from Infinispan subsystem into Jakarta EE applications
You can inject Infinispan resources, such as a cache, from the Infinispan subsystem into your application using the @Resource annotation. The following example shows the usage of the @Resource annotation to inject a cache into Jakarta EE application:
@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/cache/foo/bar") private org.infinispan.Cache<Integer, Object> cache;
@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/cache/foo/bar")
private org.infinispan.Cache<Integer, Object> cache;
In the above example, foo is the name of the cache container and bar is the name of the cache to inject.
EAP manages the lifecycle of the injected resources, which means your application does not require to manage those resources, such as caches or a cache manager.
When you manually create any resources, your application manages those resources, not EAP.
The following examples show how to inject different resources from the Infinispan subsystem into your application.
Example of injecting a default cache
To inject the default cache of the cache container from the Infinispan subsystem into your application, use the following command:
@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/cache/foo/default")
@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/cache/foo/default")Example of injecting an embedded cache manager
To inject an embedded cache manager to allow your application to create new cache configurations and caches, use the following command:
@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/container/foo") private org.infinispan.manager.EmbeddedCacheManager manager;
@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/container/foo")
private org.infinispan.manager.EmbeddedCacheManager manager;Example of injecting a cache configuration
Any cache configurations defined within the Infinispan subsystem are not always installed or available unless your application explicitly depends on those cache configurations. To inject a cache configuration from the Infinispan subsystem into your application, use the @Resource annotation.
The following example uses the
@Resourceannotation to inject the cache configuration of thefoocontainer:@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/configuration/foo/bar") private org.infinispan.config.Configuration config;
@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/configuration/foo/bar") private org.infinispan.config.Configuration config;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following example uses the
@Resourceannotation to inject the default cache configuration of thefoocontainer:@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/configuration/foo/default") private org.infinispan.config.Configuration config;
@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/configuration/foo/default") private org.infinispan.config.Configuration config;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.3.2.1.5. Eviction feature in Hibernate cache container
The eviction feature for the hibernate cache container removes cache entries from memory. This feature helps reduce the memory load on the subsystem.
The size attribute sets the maximum number of cache entries that will be stored before eviction of cache entries begins.
Example: Eviction Feature
<cache-container name="hibernate" default-cache="local-query" module="org.hibernate.infinispan">
<transport lock-timeout="60000"/>
<local-cache name="local-query">
<object-memory size="1000"/>
<expiration max-idle="100000"/>
<cache-container name="hibernate" default-cache="local-query" module="org.hibernate.infinispan">
<transport lock-timeout="60000"/>
<local-cache name="local-query">
<object-memory size="1000"/>
<expiration max-idle="100000"/>Note that eviction only occurs within the memory. A cache store holds cache entries that are evicted to prevent permanent loss of information. For more information about the eviction feature, see the Eviction and Data Container section in the Infinispan User Guide.
22.3.2.1.6. Expiration feature in Hibernate cache container
The expiration feature for the hibernate cache container is a clustered operation; thus, when using a clustered cache, an expired cache entry is removed from all cluster members. For more information, see the Expiration section in the Infinispan User Guide.
22.3.3. Clustering modes
Clustering can be configured in two different ways in JBoss EAP using Infinispan. The best method for your application will depend on your requirements. There is a trade-off between availability, consistency, reliability and scalability with each mode. Before choosing a clustering mode, you must identify what are the most important features of your network, and balance those requirements.
Cache modes
- Replication
- Replication mode automatically detects and adds new instances on the cluster. Changes made to these instances will be replicated to all nodes on the cluster. Replication mode typically works best in small clusters because of the amount of information that has to be replicated over the network. Infinispan can be configured to use UDP multicast, which alleviates network traffic congestion to a degree.
- Distribution
Distribution mode allows Infinispan to scale the cluster linearly. Distribution mode uses a consistent hash algorithm to determine where in a cluster a new node should be placed. The number of copies, or owners, of information to be kept is configurable. There is a trade-off between the number of copies kept, durability of the data, and performance. The more copies that are kept, the more impact on performance, but the less likely you are to lose data in a server failure. The hash algorithm also works to reduce network traffic by locating entries without multicasting or storing metadata.
You should consider using distribution mode as a caching strategy when the cluster size exceeds 6-8 nodes. With distribution mode, data is distributed to only a subset of nodes within the cluster, as opposed to all nodes.
22.3.3.1. Configure the Cache Mode
You can change the default cache using the management CLI.
This section shows instructions specific to configuring the web session cache, which defaults to distribution mode. The steps and management CLI commands can easily be adjusted to apply to other cache containers.
Change to replication cache mode
The default JBoss EAP 8.0 configuration for the web session cache does not include a repl replication cache. This cache must first be added.
The below management CLI commands are for a standalone server. When running in a managed domain, you must specify which profile to update by preceding the /subsystem=infinispan commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Add the
replreplication cache and set it as the default cache.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server.
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Change to distribution cache mode
The default JBoss EAP 8.0 configuration for the web session cache already includes a dist distribution cache.
The below management CLI commands are for a standalone server. When running in a managed domain, you must specify which profile to update by preceding the /subsystem=infinispan commands with /profile=PROFILE_NAME.
Change the default cache to the
distdistribution cache./subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=web:write-attribute(name=default-cache,value=dist)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=web:write-attribute(name=default-cache,value=dist)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the number of owners for the distribution cache. The following command sets
5owners. The default is2./subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=web/distributed-cache=dist:write-attribute(name=owners,value=5)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=web/distributed-cache=dist:write-attribute(name=owners,value=5)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server.
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.3.3.2. Cache strategy performance
When using a SYNC caching strategy, the cost of replication is easy to measure and directly seen in response times since the request does not complete until the replication completes.
Although it seems that the ASYNC caching strategy should result in lower response times than the SYNC caching strategy, this is only true under the right conditions. The ASYNC caching strategy is more difficult to measure, but it can provide better performance than the SYNC strategy when the duration between requests is long enough for the cache operation to complete. This is because the cost of replication is not immediately seen in response times.
If requests for the same session are made too quickly, the cost of replication for the previous request is shifted to the front of the subsequent request since it must wait for the replication from the previous request to complete. For rapidly fired requests where a subsequent request is sent immediately after a response is received, the ASYNC caching strategy will perform worse than the SYNC caching strategy. Consequently, there is a threshold for the period of time between requests for the same session where the SYNC caching strategy will actually perform better than the ASYNC caching strategy. In real world usage, requests for the same session are not normally received in rapid succession. Instead, there is typically a period of time in the order of a few seconds or more between the requests. In this case, the ASYNC caching strategy is a sensible default and provides the fastest response times.
22.3.4. State transfer
State transfer is both a basic data grid and clustered cache function. Without state transfer, data would be lost as nodes are added to or removed from the cluster.
State transfer adjusts the cache’s internal state in response to a change in the cache membership. This change automatically occurs when a node joins or leaves the cluster, when two or more cluster partitions merge, or after any combination of these events. The initial state transfer for a newly started cache is the most expensive, as the new cache must receive the maximum amount of state, based on the cache’s mode as discussed below.
The timeout attribute can be used to control how long the newly started cache waits to receive its state. If the timeout attribute is a positive number, then the cache will wait to receive all of its initial state before being made available to service requests. If the state transfer does not complete in the specified time, the default being 240000 milliseconds, then the cache will throw an error and cancel the startup. If timeout is set to 0, then the cache is immediately available, and it will receive its initial state during background operations. Until the initial state transfer is complete, any requests for cache entries that the cache has not yet received will need to be fetched from a remote node.
The timeout attribute can be set to 0 with the following command.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=server/CACHE_TYPE=CACHE/component=state-transfer:write-attribute(name=timeout,value=0)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=server/CACHE_TYPE=CACHE/component=state-transfer:write-attribute(name=timeout,value=0)The state transfer behavior is determined by the cache’s mode.
- In replication mode a new node joining the cache receives the entire cache state from the existing nodes. When a node leaves the cluster there is no state transfer.
-
In distribution mode the new node receives only a part of the state from the existing nodes, and the existing nodes remove some of their state in order to keep
ownerscopies of each key in the cache, as determined through consistent hashing. When a node leaves the cluster, a distribution cache needs to make additional copies of the keys that were stored on that node, so that owners of each key continue to exist. - In invalidation mode the initial state transfer is similar to replication mode, the only difference being that the nodes are not guaranteed to have the same state. When a node leaves the cluster there is no state transfer.
A state transfer transfers both in-memory and persistent state by default, but both can be disabled in the configuration. When state transfer is disabled, a ClusterLoader must be configured, otherwise a node will become the owner or backup owner of a key without the data being loaded into its cache. In addition, if state transfer is disabled in distribution mode then a key will occasionally have less than owners copies in the cache.
22.3.5. Configure Infinispan thread pools
The infinispan subsystem contains the async-operations, expiration, listener, persistence, remote-command, state-transfer, and transport thread pools. These pools can be configured for any Infinispan cache container.
The following table lists the attributes you can configure for each thread pool in the infinispan subsystem and the default value for each.
| Thread Pool Name | keepalive-time | max-threads | min-threads | queue-length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| async-operations | 60000L | 25 | 25 | 1000 |
| expiration | 60000L | 1 | N/A | N/A |
| listener | 60000L | 1 | 1 | 100000 |
| persistence | 60000L | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| remote-command | 60000L | 200 | 1 | 0 |
| state-transfer | 60000L | 60 | 1 | 0 |
| transport | 60000L | 25 | 25 | 100000 |
Use the following syntax to configure an Infinispan thread pool using the management CLI.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER_NAME/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:write-attribute(name=ATTRIBUTE_NAME, value=ATTRIBUTE_VALUE)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER_NAME/thread-pool=THREAD_POOL_NAME:write-attribute(name=ATTRIBUTE_NAME, value=ATTRIBUTE_VALUE)
The following is an example of the management CLI command to set the max-threads value to 10 in the persistence thread pool for the server cache container.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=server/thread-pool=persistence:write-attribute(name="max-threads", value="10")
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=server/thread-pool=persistence:write-attribute(name="max-threads", value="10")22.3.6. Infinispan statistics
Runtime statistics about Infinispan caches and cache containers can be enabled for monitoring purposes. Statistics collection is not enabled by default for performance reasons.
Statistics collection can be enabled for each cache container, cache, or both. The statistics option for each cache overrides the option for the cache container. Enabling or disabling statistics collection for a cache container will cause all caches in that container to inherit the setting, unless they explicitly specify their own.
22.3.6.1. Enable Infinispan statistics
Enabling Infinispan statistics may have a negative impact on the performance of the infinispan subsystem. Statistics should be enabled only when required.
You can enable or disable the collection of Infinispan statistics using the management console or the management CLI. From the management console, navigate to the Infinispan subsystem from the Configuration tab, select the appropriate cache or cache container, and edit the Statistics Enabled attribute. Use the below commands to enable statistics using the management CLI.
Enable statistics collection for a cache container. A server reload will be required.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER:write-attribute(name=statistics-enabled,value=true)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER:write-attribute(name=statistics-enabled,value=true)Enable statistics collection for a cache. A server reload will be required.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/CACHE_TYPE=CACHE:write-attribute(name=statistics-enabled,value=true)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/CACHE_TYPE=CACHE:write-attribute(name=statistics-enabled,value=true)
You can use the following command to undefine the statistics-enabled attribute of a cache so that it will inherit the settings of its cache container’s statistics-enabled attribute.
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/CACHE_TYPE=CACHE:undefine-attribute(name=statistics-enabled)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/CACHE_TYPE=CACHE:undefine-attribute(name=statistics-enabled)22.3.7. Infinispan partition handling
An Infinispan cluster is built out of several nodes where data is stored. To prevent data loss if multiple nodes fail, Infinispan copies the same data over multiple nodes. This level of data redundancy is configured using the owners attribute. As long as fewer than the configured number of nodes crash simultaneously, Infinispan will have a copy of the data available.
However, there are potential catastrophic situations that could occur when too many nodes disappear from the cluster:
- Split brain
This splits the cluster in two or more partitions, or sub-clusters, that operate independently. In these circumstances, multiple clients reading and writing from different partitions see different versions of the same cache entry, which for many applications is problematic.
NoteThere are ways to alleviate the possibility for the split brain to happen, such as redundant networks or IP bonding; however, these only reduce the window of time for the problem to occur.
- Multiple nodes crash in sequence
- If multiple nodes, specifically the number of owners, crash in rapid sequence and Infinispan does not have the time to properly rebalance its state between crashes, the result is partial data loss.
The goal is to avoid situations in which incorrect data is returned to the user as a result of either split brain or multiple nodes crashing in rapid sequence.
22.3.7.1. Split brain
In a split brain situation, each network partition will install its own JGroups view, removing the nodes from the other partitions. We do not have a direct way to determine whether the cluster has been split into two or more partitions, since the partitions are unaware of each other. Instead, we assume the cluster has split when one or more nodes disappear from the JGroups cluster without sending an explicit leave message.
With partition handling disabled, each such partition would continue to function as an independent cluster. Each partition may only see a part of the data, and each partition could write conflicting updates in the cache.
With partition handling enabled, if we detect a split, each partition does not start a rebalance immediately, but first checks whether it should enter degraded mode instead:
- If at least one segment has lost all its owners, meaning that at least the number of owners specified has left since the last rebalance ended, the partition enters degraded mode.
- If the partition does not contain a simple majority of the nodes (floor(numNodes/2) + 1) in the latest stable topology, the partition also enters degraded mode.
- Otherwise, the partition keeps functioning normally and starts a rebalance.
The stable topology is updated every time a rebalance operation ends and the coordinator determines that another rebalance is not necessary. These rules ensure that at most, one partition stays in available mode, and the other partitions enter degraded mode.
When a partition is in degraded mode, it only allows access to the keys that are wholly owned:
- Requests (reads and writes) for entries that have all the copies on nodes within this partition are honored.
-
Requests for entries that are partially or totally owned by nodes that have disappeared are rejected with an
AvailabilityException.
This guarantees that partitions cannot write different values for the same key (cache is consistent), and also that one partition can not read keys that have been updated in the other partitions (no stale data).
Two partitions could start up isolated, and as long as they do not merge, they can read and write inconsistent data. In the future, we may allow custom availability strategies (e.g. check that a certain node is part of the cluster, or check that an external machine is accessible) that could handle that situation as well.
22.3.7.2. Configuring partition handling
Partition handling is disabled by default. When you enable partition handling, there are two configurable attributes:
| Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
|
| "DENY_READ_WRITES", "ALLOW_READS", "ALLOW_READ_WRITES" |
|
| "NONE", "PREFERRED_ALWAYS", "PREFERRED_NON_NULL", "REMOVE_ALL" |
Configure when-split to determines the read and write behavior of the cache when a network partition is detected.
Configure merge-policy to determine the conflict resolution policy strategy when merging two of more network partitions.
Example CLI command:
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=web/distributed-cache=dist/component=partition-handling:write-attribute(name=when-split, value=DENY_READ_WRITES)
/subsystem=infinispan/cache-container=web/distributed-cache=dist/component=partition-handling:write-attribute(name=when-split, value=DENY_READ_WRITES)22.3.7.3. Configuring remote cache containers
You must configure a remote cache for every server group in a managed domain. You can enable a collection of metrics for a given remote-cache-container and associated runtime caches with the statistics-enabled attribute.
22.3.7.3.1. Creating a remote cache container
Each server group in a managed domain requires a unique remote cache. The caches can belong to the same data grid. Therefore, users must configure a remote cache for every server group by defining a socket binding for the server group and associating the socket binding with a remote cache container.
Procedure
Define a
socket-binding, repeating the command as necessary for each remote Red Hat Data Grid instance in the cluster./socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=SOCKET_BINDING:add(host=HOSTNAME,port=PORT)
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=SOCKET_BINDING:add(host=HOSTNAME,port=PORT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Define a
remote-cache-containerthat references the newly created socket bindings.batch /subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER:add(default-remote-cluster=data-grid-cluster) /subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/remote-cluster=data-grid-cluster:add(socket-bindings=[SOCKET_BINDING,SOCKET_BINDING_2,...]) run-batch
batch /subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER:add(default-remote-cluster=data-grid-cluster) /subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/remote-cluster=data-grid-cluster:add(socket-bindings=[SOCKET_BINDING,SOCKET_BINDING_2,...]) run-batchCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.3.7.3.2. Enabling statistics for a remote cache container
The statistics-enabled attribute enables a collection of metrics for a given remote-cache-container and associated runtime caches.
-
For a
remote-cache-containercalled "foo", enable statistics using the following operation:
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:write-attribute(name=statistics-enabled, value=true)
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:write-attribute(name=statistics-enabled, value=true)-
For a
remote-cache-container"foo", the following metrics are visible at runtime:
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:read-attribute(name=connections) /subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:read-attribute(name=active-connections) /subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:read-attribute(name=idle-connections)
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:read-attribute(name=connections)
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:read-attribute(name=active-connections)
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:read-attribute(name=idle-connections)-
For descriptions of these metrics, execute a read-resource-description operation for the
remote-cache-container:
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:read-resource-description
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo:read-resource-description- The following metrics are specific to the remote cache used by the selected deployment:
- For descriptions of these metrics, execute a read-resource-description operation for the remote cache:
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo/remote-cache=bar.war:read-resource-description
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo/remote-cache=bar.war:read-resource-description- Some of these metrics are computed values (example, average-*), while others are tallied, such as hits and misses. The tallied metrics can be reset by the following operation:
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo/remote-cache=bar.war:reset-statistics()
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=foo/remote-cache=bar.war:reset-statistics()22.3.8. Externalize HTTP sessions to Red Hat Data Grid
You need a Red Hat Data Grid subscription to use this functionality.
Red Hat Data Grid can be used as an external cache container for application-specific data in JBoss EAP, such as HTTP sessions. This allows scaling of the data layer independent of the application, and enables different JBoss EAP clusters, which may reside in various domains, to access data from the same Red Hat Data Grid cluster. Additionally, other applications can interface with the caches presented by Red Hat Data Grid.
The following example shows how to externalize HTTP sessions. It applies to both standalone instances of JBoss EAP as well as managed domains.
-
Create a
remote-cache-container. For more information, see Configuring remote cache containers. Configure the HotRod store. The HotRod store uses one dedicated remote cache for each cache created by the JBoss EAP server. Typically, one invalidation cache is used on the JBoss EAP server, as shown in the CLI script below.
NoteThe remote caches need to be configured manually on the Red Hat Data Grid servers. The recommended configuration for these caches is a transactional distribution mode cache with pessimistic locking. Cache names must correspond to the deployment file names, such as
test.war.Once the remote cache container has been configured, a
hotrodstore can be configured to replace any existing store. The following CLI script demonstrates a typical use case for offloading sessions in conjunction with the invalidation cache.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The script configures a new invalidation cache. Session data is then maintained in the cache for performance and written to the store for resilience.
A HotRod client can be injected directly into Jakarta EE applications using the
@Resourceannotation. In the example below, the@Resourceannotation looks up the configuration properties in the class path, in thehotrod-client.propertiesfile.@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/remote-container/web-sessions") private org.infinispan.client.hotrod.RemoteCacheContainer client;
@Resource(lookup = "java:jboss/infinispan/remote-container/web-sessions") private org.infinispan.client.hotrod.RemoteCacheContainer client;Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Example:
hotrod-client.propertiesfileCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Securing a remote cache container
It is possible to secure the communication to the remote Red Hat Data Grid instance using SSL. This is accomplished by configuring the remote-cache-container on the JBoss EAP instance and adjusting the hotrod connector on the Red Hat Data Grid instance to use an active security realm.
Create a
client-ssl-contextin JBoss EAP. For additional information on creating aclient-ssl-context, including generating the other elytron components, see Using a client-ssl-context in How to Configure Server Security for JBoss EAP./subsystem=elytron/client-ssl-context=CLIENT_SSL_CONTEXT:add(key-manager=KEY_MANAGER,trust-manager=TRUST_MANAGER)
/subsystem=elytron/client-ssl-context=CLIENT_SSL_CONTEXT:add(key-manager=KEY_MANAGER,trust-manager=TRUST_MANAGER)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure the remote cache container to use the client SSL context.
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/component=security:write-attribute(name=ssl-context,value=CLIENT_SSL_CONTEXT)
/subsystem=infinispan/remote-cache-container=CACHE_CONTAINER/component=security:write-attribute(name=ssl-context,value=CLIENT_SSL_CONTEXT)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Secure the remote Red Hat Data Grid instance, repeating as necessary for each instance.
-
Copy the keystore used in the
client-ssl-contextto the remote Red Hat Data Grid instance. Configure the
ApplicationRealmto use this keystore./core-service=management/security-realm=ApplicationRealm/server-identity=ssl:add(keystore-path="KEYSTORE_NAME",keystore-relative-to="jboss.server.config.dir",keystore-password="KEYSTORE_PASSWORD")
/core-service=management/security-realm=ApplicationRealm/server-identity=ssl:add(keystore-path="KEYSTORE_NAME",keystore-relative-to="jboss.server.config.dir",keystore-password="KEYSTORE_PASSWORD")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Adjust the hotrod connector to point to this security realm.
/subsystem=datagrid-infinispan-endpoint/hotrod-connector=hotrod-connector/encryption=ENCRYPTION:add(require-ssl-client-auth=false,security-realm="ApplicationRealm")
/subsystem=datagrid-infinispan-endpoint/hotrod-connector=hotrod-connector/encryption=ENCRYPTION:add(require-ssl-client-auth=false,security-realm="ApplicationRealm")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the remote Red Hat Data Grid instance.
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
-
Copy the keystore used in the
22.3.9. Externalize HTTP sessions to Red Hat Data Grid using a remote store
You need a Red Hat Data Grid subscription to use this functionality.
The instructions here represent an older way of externalizing sessions. JBoss EAP 7.2 introduced a custom optimized cache store based on the HotRod protocol that integrates with the elytron subsystem. It is recommended to use the new hotrod store, as described in Externalize HTTP sessions to Red Hat Data Grid.
For each distributable application, an entirely new cache must be created. It can be created in an existing cache container, for example, web.
To externalize HTTP sessions:
Define the location of the remote Red Hat Data Grid server by adding the networking information to the
socket-binding-group.Example: Adding remote socket bindings
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=remote-rhdg-server1:add(host=RHDGHostName1, port=11222) /socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=remote-rhdg-server2:add(host=RHDGHostName2, port=11222)
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=remote-rhdg-server1:add(host=RHDGHostName1, port=11222) /socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=remote-rhdg-server2:add(host=RHDGHostName2, port=11222)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Resulting XML
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteYou will need a remote socket binding configured for each Red Hat Data Grid server.
Ensure the remote cache containers are defined in JBoss EAP’s
infinispansubsystem; in the example below thecacheattribute in theremote-storeelement defines the cache name on the remote Red Hat Data Grid server.If you are running in a managed domain, precede these commands with
/profile=PROFILE_NAME.Example: Adding a remote cache container
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Resulting XML
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.4. Configuring JBoss EAP as a front-end load balancer
You can configure JBoss EAP and the undertow subsystem to act as a front-end load balancer to proxy requests to back-end JBoss EAP servers. Since Undertow makes use of asynchronous IO, the IO thread that is responsible for the connection is the only thread that is involved in the request. That same thread is also used for the connection made to the back-end server.
You can use the following protocols:
-
HTTP over plain text (
http), supporting HTTP/1 and HTTP/2 (h2c) -
HTTP over secured connection (
https), supporting HTTP/1 and HTTP/2 (h2) -
AJP (
ajp)
You can either define a static load balancer and specify the back-end hosts in your configuration, or use the mod_cluster front end to dynamically update the hosts.
22.4.1. Configure undertow as a load balancer using mod_cluster
You can use the built-in mod_cluster front-end load balancer to load balance other JBoss EAP instances.
This procedure assumes that you are running in a managed domain and already have the following configured:
A JBoss EAP server that will act as the load balancer.
This server uses the
load-balancerprofile, which is bound to theload-balancer-socketssocket binding group.NoteThe
load-balancerprofile is already preconfigured with the socket binding, mod-cluster Undertow filter, and reference in the default host to the filter in order to use this server as a front-end load balancer. * Two JBoss EAP servers, which will act as the back-end servers. ** These servers are running in a cluster and use thehaprofile, which is bound to theha-socketssocket binding group. * The distributable application to be load balanced deployed to the back-end servers.
Configure the mod_cluster front-end load balancer
The below steps load balance servers in a managed domain, but they can be adjusted to apply to a set of standalone servers. Be sure to update the management CLI command values to suit your environment.
Procedure
Set the mod_cluster advertise security key.
Adding the advertise security key allows the load balancer and servers to authenticate during discovery.
Use the following management CLI command to set the mod_cluster advertise security key.
/profile=ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:write-attribute(name=advertise-security-key, value=mypassword)
/profile=ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:write-attribute(name=advertise-security-key, value=mypassword)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the mod_cluster load balancer’s security key.
Use the following management CLI command to set the security key for the mod_cluster filter.
/profile=load-balancer/subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/mod-cluster=load-balancer:write-attribute(name=security-key,value=mypassword)
/profile=load-balancer/subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/mod-cluster=load-balancer:write-attribute(name=security-key,value=mypassword)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
It is recommended that the management and advertise socket bindings used by mod_cluster only be exposed to the internal network, not a public IP address.
The load balancer JBoss EAP server can now load balance the two back-end JBoss EAP servers.
Multiple mod_cluster configurations
The mod_cluster subsystem supports multiple named proxy configurations which allows to register non-default undertow servers with the reverse proxies. Moreover, this allows single application server node to register with different groups of proxy servers.
The following example adds an ajp-listener, a server, and a host to the undertow server. It also adds a new mod_cluster configuration that registers the host using the advertise mechanism.
22.4.2. Enabling ranked session affinity in your load balancer
You must enable ranked session affinity in your load balancer to have session affinity with multiple, ordered routes in the distributable-web subsystem. For more information about the distributable-web subsystem and the different affinity options, see The distributable-web subsystem for distributable web session configurations in the Development Guide for JBoss EAP.
The default delimiter that separates the node routes is .. If you want a different value, you can configure the delimiter attribute of the affinity resource.
Procedure
Enable ranked session affinity for a load balancer:
/subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/mod-cluster=load-balancer/affinity=ranked:add
/subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/mod-cluster=load-balancer/affinity=ranked:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Optional: Configure the
delimiterattribute of theaffinityresource:/subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/mod-cluster=load-balancer/affinity=ranked:write-attribute(name=delimiter,value=':')
/subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter/mod-cluster=load-balancer/affinity=ranked:write-attribute(name=delimiter,value=':')Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.4.3. Configure undertow as a static load balancer
To configure a static load balancer with Undertow, you need to configure a proxy handler in the undertow subsystem. To configure a proxy handler in Undertow, you need to do the following on your JBoss EAP instance that will serve as your static load balancer:
- Add a reverse proxy handler
- Define the outbound socket bindings for each remote host
- Add each remote host to the reverse proxy handler
- Add the reverse proxy location
The following example shows how to configure a JBoss EAP instance to be a static load balancer. The JBoss EAP instance is located at lb.example.com and will load balance between two additional servers: server1.example.com and server2.example.com. The load balancer will reverse-proxy to the location /app and will use the AJP protocol.
Procedure
To add a reverse proxy handler:
/subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/reverse-proxy=my-handler:add
/subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/reverse-proxy=my-handler:addCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To define the outbound socket bindings for each remote host:
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=remote-host1/:add(host=server1.example.com, port=8009) /socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=remote-host2/:add(host=server2.example.com, port=8009)
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=remote-host1/:add(host=server1.example.com, port=8009) /socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=remote-host2/:add(host=server2.example.com, port=8009)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To add each remote host to the reverse proxy handler:
/subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/reverse-proxy=my-handler/host=host1:add(outbound-socket-binding=remote-host1, scheme=ajp, instance-id=myroute1, path=/test) /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/reverse-proxy=my-handler/host=host2:add(outbound-socket-binding=remote-host2, scheme=ajp, instance-id=myroute2, path=/test)
/subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/reverse-proxy=my-handler/host=host1:add(outbound-socket-binding=remote-host1, scheme=ajp, instance-id=myroute1, path=/test) /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler/reverse-proxy=my-handler/host=host2:add(outbound-socket-binding=remote-host2, scheme=ajp, instance-id=myroute2, path=/test)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To add the reverse proxy location:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/location=\/test:add(handler=my-handler)
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/location=\/test:add(handler=my-handler)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
When accessing lb.example.com:8080/app, you will now see the content proxied from server1.example.com and server2.example.com.
22.5. Using an external web server as a proxy server
JBoss EAP can accept requests from an external web server using the supported HTTP, HTTPS, or AJP protocol, depending on the external web server configuration.
See Overview of HTTP Connectors for details on the supported HTTP connectors for each web server. Once you have decided which web server and HTTP connector to use, see the appropriate section for information on configuring your connector:
- See the mod_cluster, mod_jk, or mod_proxy section for Apache HTTP Server.
- See the ISAPI connector section for Microsoft IIS.
- See the NSAPI connector section for Oracle iPlanet Web Server.
For the most current information about supported configurations for HTTP connectors, see JBoss EAP supported configurations.
You also will need to make sure that JBoss EAP is configured to accept requests from external web servers.
22.5.1. Overview of HTTP connectors
JBoss EAP has the ability to use load-balancing and clustering mechanisms built into external web servers, such as Apache HTTP Server, Microsoft IIS, and Oracle iPlanet as well as through Undertow. JBoss EAP communicates with the web servers using a connector. These connectors are configured within the undertow subsystem of JBoss EAP.
The web servers include software modules which control the way that HTTP requests are routed to JBoss EAP nodes. Each of these modules varies in how it works and how it is configured. The modules are configured to balance work loads across multiple JBoss EAP nodes, to move work loads to alternate servers in case of a failure event, or both.
JBoss EAP supports several different connectors. The one you choose depends on the web server in use and the functionality you need. See the tables below for comparisons of the supported configurations and features of the various HTTP connectors that are compatible with JBoss EAP.
For more information about using JBoss EAP 8.0 as a multi-platform load balancer, see Configure Undertow as a load balancer using mod_cluster.
For the most current information about supported configurations for HTTP connectors, see JBoss EAP supported configurations.
| Connector | Web Server | Supported Operating Systems | Supported Protocols |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red Hat JBoss Core Services Apache HTTP Server, Red Hat JBoss Web Server Apache HTTP Server, JBoss EAP (Undertow) | Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Microsoft Windows Server | HTTP, HTTPS, AJP, WebSocket | |
| Red Hat JBoss Core Services Apache HTTP Server, Red Hat JBoss Web Server Apache HTTP Server | Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Microsoft Windows Server | AJP | |
| Red Hat JBoss Core Services Apache HTTP Server, Red Hat JBoss Web Server Apache HTTP Server | Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Microsoft Windows Server | HTTP, HTTPS, AJP | |
| Microsoft IIS | Microsoft Windows Server | AJP | |
| Oracle iPlanet Web Server | AJP |
| Connector | Supports Sticky Sessions | Adapts to Deployment Status |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes. Detects deployment and undeployment of applications and dynamically decides whether to direct client requests to a server based on whether the application is deployed on that server. | |
| Yes | No. Directs client requests to the container as long as the container is available, regardless of application status. | |
| Yes | No. Directs client requests to the container as long as the container is available, regardless of application status. | |
| Yes | No. Directs client requests to the container as long as the container is available, regardless of application status. | |
| Yes | No. Directs client requests to the container as long as the container is available, regardless of application status. |
22.5.2. Apache HTTP Server
A standalone Apache HTTP Server bundle is now available as a separate download with Red Hat JBoss Core Services. This simplifies installation and configuration, and allows for a more consistent update experience.
22.5.2.1. Installing Apache HTTP Server
For information on installing Apache HTTP Server, see the JBoss Core Services Apache HTTP Server Installation Guide.
22.5.3. Accepting requests from external web servers
JBoss EAP does not require any special configuration to begin accepting requests from a proxy server as long as the correct protocol handler, for example AJP, HTTP, or HTTPS, is configured.
If the proxy server uses mod_jk, mod_proxy, ISAPI, or NSAPI, it sends requests to JBoss EAP and JBoss EAP simply provides a response. With mod_cluster, you must also configure your network to allow JBoss EAP to send information, such as its current load, application lifecycle events, and health status, to the proxy server to help it determine where to route requests. For more information about configuring a mod_cluster proxy server, see The mod_cluster HTTP Connector.
Update JBoss EAP configuration
In the following procedure, substitute the protocols and ports in the examples with the ones you need to configure.
Procedure
Configure the
instance-idattribute of Undertow.The external web server identifies the JBoss EAP instance in its connector configuration using the
instance-id. Use the following management CLI command to set theinstance-idattribute in Undertow./subsystem=undertow:write-attribute(name=instance-id,value=node1)
/subsystem=undertow:write-attribute(name=instance-id,value=node1)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the above example, the external web server identifies the current JBoss EAP instance as
node1.Add the necessary listeners to Undertow.
In order for an external web server to be able to connect to JBoss EAP, Undertow needs a listener. Each protocol needs its own listener, which is tied to a socket binding.
NoteDepending on your desired protocol and port configuration, this step may not be necessary. An HTTP listener is configured in all default JBoss EAP configurations, and an AJP listener is configured if you are using the ha or full-ha profile.
You can check whether the required listeners are already configured by reading the default server configuration:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server:read-resource
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server:read-resourceCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To add a listener to Undertow, it must have a socket binding. The socket binding is added to the socket binding group used by your server or server group. The following management CLI command adds an
ajpsocket binding, bound to port8009, to thestandard-socketssocket binding group./socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/socket-binding=ajp:add(port=8009)
/socket-binding-group=standard-sockets/socket-binding=ajp:add(port=8009)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The following management CLI command adds an
ajplistener to Undertow, using theajpsocket binding./subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/ajp-listener=ajp:add(socket-binding=ajp)
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/ajp-listener=ajp:add(socket-binding=ajp)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
22.6. The mod_cluster HTTP Connector
The mod_cluster connector is an Apache HTTP Server-based load balancer. It uses a communication channel to forward requests from the Apache HTTP Server to one of a set of application server nodes.
The mod_cluster connector has several advantages over other connectors.
- The mod_cluster Management Protocol (MCMP) is an additional connection between the JBoss EAP servers and the Apache HTTP Server with the mod_cluster module enabled. It is used by the JBoss EAP servers to transmit server-side load-balance factors and lifecycle events back to the Apache HTTP Server via a custom set of HTTP methods.
- Dynamic configuration of Apache HTTP Server with mod_cluster allows JBoss EAP servers to join the load-balancing arrangement without manual configuration.
- JBoss EAP performs the load-balancing factor calculations, rather than relying on the Apache HTTP Server with mod_cluster. This makes load-balancing metrics more accurate than other connectors.
- The mod_cluster connector gives fine-grained application lifecycle control. Each JBoss EAP server forwards web application context lifecycle events to the Apache HTTP Server, informing it to start or stop routing requests for a given context. This prevents end users from seeing HTTP errors due to unavailable resources.
- AJP, HTTP or HTTPS transports can be used.
For more details on the specific configuration options of the modcluster subsystem, see the ModCluster Subsystem Attributes.
22.6.1. Configure mod_cluster in Apache HTTP Server
The mod_cluster modules are already included when installing JBoss Core Services Apache HTTP Server or using JWS and are loaded by default.
Apache HTTP Server is no longer distributed with JWS as of version 3.1.0.
See the steps below to configure the mod_cluster module to suit your environment.
Red Hat customers can also use the Load Balancer Configuration Tool on the Red Hat Customer Portal to quickly generate optimal configuration templates for mod_cluster and other connectors. Note that you must be logged in to access this tool.
Configure mod_cluster
Apache HTTP Server already contains a mod_cluster configuration file, mod_cluster.conf, that loads the mod_cluster modules and provides basic configuration. The IP address, port, and other settings in this file, shown below, can be configured to suit your needs.
The Apache HTTP Server server is configured as a load balancer and can work with the modcluster subsystem running on JBoss EAP. You must configure a mod_cluster worker node to make JBoss EAP aware of mod_cluster.
If you want to disable advertising for mod_cluster and configure a static proxy list instead, see Disable Advertisement for mod_cluster. For more information on the available mod_cluster configuration options in Apache HTTP Server, see the Apache HTTP Server mod_cluster Directives
For more details on configuring mod_cluster, see the Configure Load Balancing Using Apache HTTP Server and mod_cluster section of the JWS HTTP Connectors and Load Balancing Guide.
22.6.2. Disable advertising for mod_cluster
By default, the modcluster subsystem’s balancer uses multicast UDP to advertise its availability to the background workers. You can disable advertising and to use a proxy list instead using the following procedure.
The management CLI commands in the following procedure assume that you are using the full-ha profile in a managed domain. If you are using a profile other than full-ha, use the appropriate profile name in the command. If you are running a standalone server, remove the /profile=full-ha completely.
Modify the Apache HTTP Server configuration.
Edit the
httpd.confApache HTTP Server configuration file. Make the following updates to the virtual host that listens for MCPM requests, using theEnableMCPMReceivedirective.Add the directive to disable server advertisement.
Set the
ServerAdvertisedirective toOffto disable server advertisement.ServerAdvertise Off
ServerAdvertise OffCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Disable the advertise frequency.
If your configuration specifies the
AdvertiseFrequencyparameter, comment it out using a#character.AdvertiseFrequency 5
# AdvertiseFrequency 5Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Enable the ability to receive MCPM messages.
Ensure that the
EnableMCPMReceivedirective exists, to allow the web server to receive MCPM messages from the worker nodes.EnableMCPMReceive
EnableMCPMReceiveCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Disable advertising in the JBoss EAP
modclustersubsystem.Use the following management CLI command to disable advertising.
/profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:write-attribute(name=advertise,value=false)
/profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:write-attribute(name=advertise,value=false)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantBe sure to continue to the next step to provide the list of proxies. Advertising will not be disabled if the list of proxies is empty.
Provide a list of proxies in the JBoss EAP
modclustersubsystem.It is necessary to provide a list of proxies because the
modclustersubsystem will not be able to automatically discover proxies if advertising is disabled.First, define the outbound socket bindings in the appropriate socket binding group.
/socket-binding-group=full-ha-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=proxy1:add(host=10.33.144.3,port=6666) /socket-binding-group=full-ha-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=proxy2:add(host=10.33.144.1,port=6666)
/socket-binding-group=full-ha-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=proxy1:add(host=10.33.144.3,port=6666) /socket-binding-group=full-ha-sockets/remote-destination-outbound-socket-binding=proxy2:add(host=10.33.144.1,port=6666)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Next, add the proxies to the mod_cluster configuration.
/profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:list-add(name=proxies,value=proxy1) /profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:list-add(name=proxies,value=proxy2)
/profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:list-add(name=proxies,value=proxy1) /profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:list-add(name=proxies,value=proxy2)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The Apache HTTP Server balancer no longer advertises its presence to worker nodes and UDP multicast is no longer used.
22.6.3. Configure a mod_cluster worker node
A mod_cluster worker node consists of a JBoss EAP server. This server can be a standalone server or part of a server group in a managed domain. A separate process runs within JBoss EAP, which manages all of the worker nodes of the cluster. This is called the primary in a managed domain or the master in a standalone server.
Worker nodes in a managed domain share an identical configuration across a server group. Worker nodes running as standalone servers are configured individually. The configuration steps are otherwise identical.
- A standalone server must be started with the standalone-ha or standalone-full-ha profile.
- A server group in a managed domain must use the ha or full-ha profile, and the ha-sockets or full-ha-sockets socket binding group. JBoss EAP ships with a cluster-enabled server group called other-server-group which meets these requirements.
Configure a worker node
The management CLI commands in this procedure assume that you are using a managed domain with the full-ha profile. If you are running a standalone server, remove the /profile=full-ha portion of the commands.
Procedure
Configure the network interfaces.
By default, the network interfaces all default to
127.0.0.1. Every physical host that hosts either a standalone server or one or more servers in a server group needs its interfaces to be configured to use its public IP address, which the other servers can see.Use the following management CLI commands to modify the external IP addresses for the
management,public, andunsecureinterfaces as appropriate for your environment. Be sure to replaceEXTERNAL_IP_ADDRESSin the command with the actual external IP address of the host./interface=management:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address.management:EXTERNAL_IP_ADDRESS}") /interface=public:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address.public:EXTERNAL_IP_ADDRESS}") /interface=unsecure:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address.unsecure:EXTERNAL_IP_ADDRESS}")/interface=management:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address.management:EXTERNAL_IP_ADDRESS}") /interface=public:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address.public:EXTERNAL_IP_ADDRESS}") /interface=unsecure:write-attribute(name=inet-address,value="${jboss.bind.address.unsecure:EXTERNAL_IP_ADDRESS}")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Reload the server.
reload
reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Configure host names.
Set a unique host name for each host that participates in a managed domain. This name must be unique across secondaries and will be used for the secondary to identify to the cluster, so make a note of the name you use.
Start the JBoss EAP secondary host, using the appropriate
host.xmlconfiguration file.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the following management CLI command to set a unique host name. This example uses
secondary1as the new host name./host=EXISTING_HOST_NAME:write-attribute(name=name,value=secondary1)
/host=EXISTING_HOST_NAME:write-attribute(name=name,value=secondary1)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information on configuring a host name, see Configure the name of a host.
Configure each host to connect to the domain controller.
NoteThis step does not apply for a standalone server.
+ For newly configured hosts that need to join a managed domain, you must remove the local element and add the remote element host attribute that points to the domain controller.
+ .. Start the JBoss EAP secondary host, using the appropriate
host.xmlconfiguration file.+
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xmlCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Use the following management CLI command to configure the domain controller settings.
/host=SECONDARY_HOST_NAME:write-remote-domain-controller(host=DOMAIN_CONTROLLER_IP_ADDRESS,port=${jboss.domain.primary.port:9990},security-realm="ManagementRealm")/host=SECONDARY_HOST_NAME:write-remote-domain-controller(host=DOMAIN_CONTROLLER_IP_ADDRESS,port=${jboss.domain.primary.port:9990},security-realm="ManagementRealm")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This modifies the XML in the host-secondary.xml file as follows:
<domain-controller> <remote host="DOMAIN_CONTROLLER_IP_ADDRESS" port="${jboss.domain.primary.port:9990}" security-realm="ManagementRealm"/> </domain-controller><domain-controller> <remote host="DOMAIN_CONTROLLER_IP_ADDRESS" port="${jboss.domain.primary.port:9990}" security-realm="ManagementRealm"/> </domain-controller>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information, see Host Controller Configuration.
Configure authentication for each secondary host.
Each secondary server needs a username and password created in the domain controller’s primary or standalone’s master ManagementRealm. On the domain controller primary or standalone master, run the
EAP_HOME/bin/add-user.shcommand for each host. Add a management user for each host with the username that matches the host name of the secondary.Be sure to answer
yesto the last question, that asks "Is this new user going to be used for one AS process to connect to another AS process?", so that you are provided with a secret value.Example:
add-user.shScript Output (trimmed)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Copy the Base64-encoded secret value provided from this output,
SECRET_VALUE, which may be used in the next step.For more information, see the Adding a user to the primary domain controller section of the JBoss EAP How To Configure Server Security guide.
Modify the secondary host’s security realm to use the new authentication.
You can specify the password by setting the secret value in the server configuration, getting the password from a credential store or vault, or passing the password as a system property.
Specify the Base64-encoded password value in the server configuration file using the Management CLI.
Use the following management CLI command to specify the secret value. Be sure to replace the
SECRET_VALUEwith the secret value returned from the add-user output from the previous step./host=SECONDARY_HOST_NAME/core-service=management/security-realm=ManagementRealm/server-identity=secret:add(value="SECRET_VALUE")
/host=SECONDARY_HOST_NAME/core-service=management/security-realm=ManagementRealm/server-identity=secret:add(value="SECRET_VALUE")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You will need to reload the server. The
--hostargument is not applicable for a standalone server.reload --host=HOST_NAME
reload --host=HOST_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information, see the Configuring the secondary controllers to use the credential section of the JBoss EAP How To Configure Server Security guide.
Configure the host to get the password from a credential store.
If you have stored the secret value in a credential store, you can use the following command to set the server secret to be a value from a credential store:
/host=SECONDARY_HOST_NAME/core-service=management/security-realm=ManagementRealm/server-identity=secret:add(credential-reference={store=STORE_NAME,alias=ALIAS}/host=SECONDARY_HOST_NAME/core-service=management/security-realm=ManagementRealm/server-identity=secret:add(credential-reference={store=STORE_NAME,alias=ALIAS}Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You will need to reload the server. The
--hostargument is not applicable for a standalone server.reload --host=HOST_NAME
reload --host=HOST_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information, see the Credential store section of the JBoss EAP How To Configure Server Security guide.
Configure the host to get the password from a vault.
Use the
EAP_HOME/bin/vault.shscript to generate a masked password. It will generate a string in the formatVAULT::secret::password::VAULT_SECRET_VALUE, for example:VAULT::secret::password::ODVmYmJjNGMtZDU2ZC00YmNlLWE4ODMtZjQ1NWNmNDU4ZDc1TElORV9CUkVBS3ZhdWx0.
VAULT::secret::password::ODVmYmJjNGMtZDU2ZC00YmNlLWE4ODMtZjQ1NWNmNDU4ZDc1TElORV9CUkVBS3ZhdWx0.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteWhen creating a password in the vault, it must be specified in plain text, not Base64-encoded.
Use the following management CLI command to specify the secret value. Be sure to replace the
VAULT_SECRET_VALUEwith the masked password generated in the previous step./host=primary/core-service=management/security-realm=ManagementRealm/server-identity=secret:add(value="${VAULT::secret::password::VAULT_SECRET_VALUE}")/host=primary/core-service=management/security-realm=ManagementRealm/server-identity=secret:add(value="${VAULT::secret::password::VAULT_SECRET_VALUE}")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You will need to reload the server. The
--hostargument is not applicable for a standalone server.reload --host=HOST_NAME
reload --host=HOST_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For more information, see the Password vault section of the JBoss EAP How To Configure Server Security guide.
Specify the password as a system property.
The following examples use
server.identity.passwordas the system property name for the password.Specify the system property for the password in the server configuration file.
Use the following managemente CLI command to configure the secret identity to use the system property.
/host=SECONDARY_HOST_NAME/core-service=management/security-realm=ManagementRealm/server-identity=secret:add(value="${server.identity.password}")/host=SECONDARY_HOST_NAME/core-service=management/security-realm=ManagementRealm/server-identity=secret:add(value="${server.identity.password}")Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You will need to reload the server. The
--hostargument is not applicable for a standalone server.reload --host=primary
reload --host=primaryCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the password for the system property when starting the server.
You can set the
server.identity.passwordsystem property by passing it as a command line argument or in a properties file.Pass in as a plain text command line argument.
Start the server and pass in the
server.identity.passwordproperty.EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Dserver.identity.password=changeme
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml -Dserver.identity.password=changemeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningThe password must be entered in plain text and will be visible to anyone who issues a
ps -efcommand.Set the property in a properties file.
Create a properties file and add the key/value pair to a properties file, for example:
server.identity.password=changeme
server.identity.password=changemeCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow WarningThe password is in plain text and will be visible to anyone who has access to this properties file.
+ Start the server with the command line arguments.
+
EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml --properties=PATH_TO_PROPERTIES_FILE
$ EAP_HOME/bin/domain.sh --host-config=host-secondary.xml --properties=PATH_TO_PROPERTIES_FILECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Restart the server.
The secondary will now authenticate to the primary using its host name as the username and the encrypted string as its password.
Your standalone server, or servers within a server group of a managed domain, are now configured as mod_cluster worker nodes. If you deploy a clustered application, its sessions are replicated to all cluster nodes for failover, and it can accept requests from an external web server or load balancer. Each node of the cluster discovers the other nodes using automatic discovery, by default.
22.6.4. Configure the mod_cluster fail_on_status Parameter
The fail_on_status parameter lists those HTTP status codes which, when returned by a worker node in a cluster, will mark that node as having failed. The load balancer will then send future requests to another worker node in the cluster. The failed worker node will remain in a NOTOK state until it sends the load balancer a STATUS message.
The fail_on_status parameter must be configured in the httpd configuration file of your load balancer. Multiple HTTP status codes for fail_on_status can be specified as a comma-separated list. The following example specifies the HTTP status codes 203 and 204 for fail_on_status.
Example: Configuring fail_on_status
ProxyPass / balancer://MyBalancer stickysession=JSESSIONID|jsessionid nofailover=on failonstatus=203,204 ProxyPassReverse / balancer://MyBalancer ProxyPreserveHost on
ProxyPass / balancer://MyBalancer stickysession=JSESSIONID|jsessionid nofailover=on failonstatus=203,204
ProxyPassReverse / balancer://MyBalancer
ProxyPreserveHost on22.6.5. Migrate traffic between clusters
After creating a new cluster using JBoss EAP, you can migrate traffic from the previous cluster to the new one as part of an upgrade process. In this task, you will see the strategy that can be used to migrate this traffic with minimal outage or downtime.
- A new cluster setup. We will call this cluster ClusterNEW.
- An old cluster setup that is being made redundant. We will call this cluster ClusterOLD.
Upgrade process for clusters - load-balancing groups
- Set up your new cluster using the steps described in the prerequisites.
In both ClusterNEW and ClusterOLD, ensure that the configuration option
sticky-sessionis set to the default setting oftrue. Enabling this option means that all new requests made to a cluster node in any of the clusters will continue to go to the respective cluster node./profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:write-attribute(name=sticky-session,value=true)
/profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:write-attribute(name=sticky-session,value=true)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Set the
load-balancing-grouptoClusterOLD, assuming that all the cluster nodes in ClusterOLD are members of the ClusterOLD load-balancing group./profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:write-attribute(name=load-balancing-group,value=ClusterOLD)
/profile=full-ha/subsystem=modcluster/proxy=default:write-attribute(name=load-balancing-group,value=ClusterOLD)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Add the nodes in ClusterNEW to the mod_cluster configuration individually using the process described in the Configure a mod_cluster Worker Node section. Additionally, use the aforementioned procedure and set their load-balancing group to ClusterNEW.
At this point, you can see an output similar to the undermentioned shortened example on the mod_cluster-manager console:
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Any old active sessions are within the ClusterOLD group, and any new sessions are created either within the ClusterOLD or CLusterNEW group. Next, we want to disable the whole ClusterOLD group, so that its cluster nodes may be removed without causing any error to currently active client’s sessions.
Click on the Disable Nodes link for LBGroup ClusterOLD on the mod_cluster-manager web console.
From this point on, only requests belonging to already established sessions will be routed to members of the ClusterOLD load-balancing group. Any new client’s sessions will be created in the ClusterNEW group only. As soon as there are no active sessions within ClusterOLD group, we can safely remove its members.
NoteUsing Stop Nodes would command the load balancer to stop routing any requests to this domain immediately. This will force a failover to another load-balancing group which will cause session data loss to clients, provided there is no session replication between ClusterNEW and ClusterOLD.
Default load-balancing group
In case the current ClusterOLD setup does not contain any load-balancing group settings, found from LBGroup: on the mod_cluster-manager console, one can still take advantage of disabling the ClusterOLD nodes. In this case, click on Disable Contexts for each of the ClusterOLD nodes. Contexts of these nodes will be disabled, and once there are no active sessions present they will be ready for removal. New clients' sessions will be created only on nodes with enabled contexts, presumably ClusterNEW members in this example.
Using the management CLI
In addition to using the mod_cluster-manager web console, you can use the JBoss EAP management CLI to stop or disable a particular context.
Stop a context
/host=primary/server=server-one/subsystem=modcluster:stop-context(context=/my-deployed-application-context, virtualhost=default-host, waittime=0)
/host=primary/server=server-one/subsystem=modcluster:stop-context(context=/my-deployed-application-context, virtualhost=default-host, waittime=0)
Stopping a context with waittime set to 0, meaning no timeout, instructs the balancer to stop routing any request to it immediately, which forces failover to another available context.
If you set a timeout value using the waittime argument, no new sessions are created on this context, but existing sessions will continue to be directed to this node until they complete or the specified timeout has elapsed. The waittime argument defaults to 10 seconds.
Disable a context
/host=primary/server=server-one/subsystem=modcluster:disable-context(context=/my-deployed-application-context, virtualhost=default-host)
/host=primary/server=server-one/subsystem=modcluster:disable-context(context=/my-deployed-application-context, virtualhost=default-host)Disabling a context tells the balancer that no new sessions should be created on this context.
22.7. Apache mod_jk HTTP connector
Apache mod_jk is an HTTP connector that is provided for customers who need it for compatibility purposes.
JBoss EAP can accept workloads from an Apache HTTP proxy server. The proxy server accepts client requests from the web front end, and passes the work to participating JBoss EAP servers. If sticky sessions are enabled, the same client request always goes to the same JBoss EAP server, unless the server is unavailable.
mod_jk communicates over the AJP 1.3 protocol. Other protocols can be used with mod_cluster or mod_proxy. See the Overview of HTTP Connectors for more information.
mod_cluster is a more advanced load balancer than mod_jk and is the recommended HTTP connector. mod_cluster provides all of the functionality of mod_jk, plus additional features. Unlike the JBoss EAP mod_cluster HTTP connector, an Apache mod_jk HTTP connector does not know the status of deployments on servers or server groups, and cannot adapt where it sends its work accordingly.
See the Apache mod_jk documentation for more information.
22.7.1. Configure mod_jk in Apache HTTP Server
The mod_jk module, mod_jk.so, is already included when installing JBoss Core Services Apache HTTP Server or using JWS; however, it is not loaded by default.
Apache HTTP Server is no longer distributed with JWS as of version 3.1.0.
Use the following steps to load and configure mod_jk in Apache HTTP Server. Note that these steps assume that you have already navigated to the httpd/ directory for Apache HTTP Server, which will vary depending on your platform. For more information, see the installation instructions for your platform in the JBoss Core Services Apache HTTP Server Installation Guide.
Red Hat customers can also use the Load balancer configuration tool on the Red Hat Customer Portal to quickly generate optimal configuration templates for mod_jk and other connectors. Note that you must be logged in to access this tool.
Procedure
Configure the mod_jk module.
NoteA sample mod_jk configuration file is provided at
conf.d/mod_jk.conf.sample. You can use this sample instead of creating your own file by removing the.sampleextension and modifying its contents as needed.Create a new file called
conf.d/mod_jk.conf. Add the following configuration to the file, making sure to modify the contents to suite your needs.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow NoteThe JkMount directive specifies which URLs Apache HTTP Server must forward to the mod_jk module. Based on the directive’s configuration, mod_jk sends the received URL to the correct workers. To serve static content directly and only use the load balancer for Java applications, the URL path must be
/application/*. To use mod_jk as a load balancer, use the value/*, to forward all URLs to mod_jk.Aside from general mod_jk configuration, this file specifies to load the
mod_jk.somodule, and defines where to find theworkers.propertiesfile.Configure the mod_jk worker nodes.
NoteA sample workers configuration file is provided at
conf.d/workers.properties.sample. You can use this sample instead of creating your own file by removing the.sampleextension and modifying its contents as needed.Create a new file called
conf.d/workers.properties. Add the following configuration to the file, making sure to modify the contents to suite your needs.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow For details on the syntax of the mod_jk
workers.propertiesfile and other advanced configuration options, see mod_jk Worker Properties.Optionally, specify a JKMountFile directive.
In addition to the JKMount directive in the
mod-jk.conf, you can specify a file which contains multiple URL patterns to be forwarded to mod_jk.Create a
uriworkermap.propertiesfile.NoteA sample URI worker map configuration file is provided at
conf.d/uriworkermap.properties.sample. You can use this sample instead of creating your own file by removing the.sampleextension and modifying its contents as needed.Create a new file called
conf.d/uriworkermap.properties. Add a line for each URL pattern to be matched, for example:Simple worker configuration file
# Simple worker configuration file /*=loadbalancerCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Update the configuration to point to
uriworkermap.propertiesfile.Append the following to
conf.d/mod_jk.conf.Use external file for mount points. It will be checked for updates each 60 seconds. The format of the file is: /url=worker /examples/*=loadbalancer
# Use external file for mount points. # It will be checked for updates each 60 seconds. # The format of the file is: /url=worker # /examples/*=loadbalancer JkMountFile conf.d/uriworkermap.propertiesCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
For more information about configuring mod_jk, see the Configuring Apache HTTP Server to load mod_jk section of the JWS HTTP connectors and load balancing guide.
22.7.2. Configure JBoss EAP to communicate with mod_jk
The mod_jk HTTP connector has a single component, the mod_jk.so module loaded by the web server. This module receives client requests and forwards them to the container, in this case JBoss EAP. JBoss EAP must also be configured to accept these requests and send replies back to the web server.
The JBoss EAP undertow subsystem needs to specify a listener in order to accept requests from and send replies back to an external web server. Since mod_jk uses the AJP protocol, an AJP listener must be configured.
If you are using one of the default high availability configurations, ha or full-ha, an AJP listener is already configured.
For instructions, see Accepting requests From external web servers.
22.8. Apache mod_proxy HTTP connector
Apache mod_proxy is an HTTP connector that supports connections over AJP, HTTP, and HTTPS protocols. mod_proxy can be configured in load-balanced or non-load-balanced configurations, and it supports the notion of sticky sessions.
The mod_proxy module requires JBoss EAP to have the HTTP, HTTPS or AJP listener configured in the undertow subsystem, depending on which protocol you plan to use.
mod_cluster is a more advanced load balancer than mod_proxy and is the recommended HTTP connector. mod_cluster provides all of the functionality of mod_proxy, plus additional features. Unlike the JBoss EAP mod_cluster HTTP connector, an Apache mod_proxy HTTP connector does not know the status of deployments on servers or server groups, and cannot adapt where it sends its work accordingly.
See the Apache mod_proxy documentation for more information.
22.8.1. Configure mod_proxy in Apache HTTP Server
The mod_proxy modules are already included when installing JBoss Core Services Apache HTTP Server or using JWS and are loaded by default.
Apache HTTP Server is no longer distributed with JWS as of version 3.1.0.
See the appropriate section below to configure a basic load-balancing or non-load-balancing proxy. These steps assume that you have already navigated to the httpd/ directory for Apache HTTP Server, which will vary depending on your platform. For more information, see the installation instructions for your platform in the JBoss Core Services Apache HTTP Server Installation Guide. These steps also assume that the necessary HTTP listener has already been configured in the JBoss EAP undertow subsystem.
Red Hat customers can also use the Load Balancer Configuration Tool on the Red Hat Customer Portal to quickly generate optimal configuration templates for mod_proxy and other connectors. Note that you must be logged in to access this tool.
Add a non-load-balancing proxy
Add the following configuration to your conf/httpd.conf file, directly beneath any other <VirtualHost> directives you may have. Replace the values with ones appropriate to your setup.
Add a load-balancing proxy
The default Apache HTTP Server configuration has the mod_proxy_balancer.so module disabled, as it is incompatible with mod_cluster. In order to complete this task, you will need to load this module and disable the mod_cluster modules.
To use mod_proxy as a load balancer, and send work to multiple JBoss EAP instances, add the following configuration to your conf/httpd.conf file. The example IP addresses are fictional. Replace them with the appropriate values for your environment.
The examples above all communicate using the HTTP protocol. You can use AJP or HTTPS protocols instead, if you load the appropriate mod_proxy modules. See the Apache mod_proxy documentation for more details.
Enable sticky sessions
A sticky session means that if a client request originally goes to a specific JBoss EAP worker, all future requests will be sent to the same worker, unless it becomes unavailable. This is almost always the recommended behavior.
To enable sticky sessions for mod_proxy, add the stickysession parameter to the ProxyPass statement.
ProxyPass / balancer://mycluster stickysession=JSESSIONID
ProxyPass / balancer://mycluster stickysession=JSESSIONID
You can specify additional parameters to the ProxyPass statement, such as lbmethod and nofailover. See the Apache mod_proxy documentation for more information on the available parameters.
22.8.2. Configure JBoss EAP to communicate with mod_proxy
The JBoss EAP undertow subsystem needs to specify a listener in order to accept requests from and send replies back to an external web server. Depending on the protocol that you will be using, you may need to configure a listener.
An HTTP listener is configured in the JBoss EAP default configuration. If you are using one of the default high availability configurations, ha or full-ha, an AJP listener is also preconfigured.
For instructions, see Accepting requests from external web servers.
22.9. Microsoft ISAPI connector
The Internet Server API (ISAPI) is a set of APIs used to write OLE Server extensions and filters for web servers such as Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS). isapi_redirect.dll is an extension of mod_jk adjusted to IIS. isapi_redirect.dll enables you to configure JBoss EAP instances as worker nodes with IIS as a load balancer.
See JBoss EAP supported configurations for information on the supported configurations of Windows Server and IIS.
22.9.1. Configure Microsoft IIS to use the ISAPI connector
Download the ISAPI connector from the Red Hat Customer Portal:
- Open a browser and log in to the Red Hat Customer Portal JBoss Software Downloads page.
- Select Web Connectors in the Product drop-down menu.
- Select the latest JBoss Core Services version from the Version drop-down menu.
- Find the Red Hat JBoss Core Services ISAPI Connector in the list, and click the Download link.
-
Extract the archive and copy the contents of the
sbindirectory to a location on your server. The instructions below assume that the contents were copied toC:\connectors\.
To configure the IIS Redirector Using the IIS Manager (IIS 7):
-
Open the IIS manager by clicking Start → Run, and typing
inetmgr. - In the tree view pane at the left, expand IIS 7.
- Double-click ISAPI and CGI Registrations to open it in a new window.
- In the Actions pane, click Add. The Add ISAPI or CGI Restriction window opens.
Specify the following values:
-
ISAPI or CGI Path:
C:\connectors\isapi_redirect.dll -
Description:
jboss - Allow extension path to execute: select the check box.
-
ISAPI or CGI Path:
- Click OK to close the Add ISAPI or CGI Restriction window.
Define a JBoss Native virtual directory
- Right-click Default Web Site, and click Add Virtual Directory. The Add Virtual Directory window opens.
Specify the following values to add a virtual directory:
-
Alias:
jboss -
Physical Path:
C:\connectors\
-
Alias:
- Click OK to save the values and close the Add Virtual Directory window.
Define a JBoss Native ISAPI Redirect Filter
- In the tree view pane, expand Sites → Default Web Site.
- Double-click ISAPI Filters. The ISAPI Filters Features view appears.
- In the Actions pane, click Add. The Add ISAPI Filter window appears.
Specify the following values in the Add ISAPI Filter window:
-
Filter name:
jboss -
Executable:
C:\connectors\isapi_redirect.dll
-
Filter name:
- Click OK to save the values and close the Add ISAPI Filters window.
Enable the ISAPI-dll handler
- Double-click the IIS 7 item in the tree view pane. The IIS 7 Home Features View opens.
- Double-click Handler Mappings. The Handler Mappings Features View appears.
- In the Group by combo box, select State. The Handler Mappings are displayed in Enabled and Disabled Groups.
-
Find
ISAPI-dll. If it is in the Disabled group, right-click it and select Edit Feature Permissions. Enable the following permissions:
- Read
- Script
- Execute
- Click OK to save the values, and close the Edit Feature Permissions window.
Microsoft IIS is now configured to use the ISAPI connector.
22.9.2. Configure the ISAPI connector to send client requests to JBoss EAP
This task configures a group of JBoss EAP servers to accept requests from the ISAPI connector. It does not include configuration for load-balancing or high-availability failover.
This configuration is done on the IIS server, and assumes that you already have JBoss EAP configured to accept requests from an external web server. You also need full administrator access to the IIS server and to have configured IIS to use the ISAPI connector.
Create property files and set up redirection
Create a directory to store logs, property files, and lock files.
The rest of this procedure assumes that you are using the directory
C:\connectors\for this purpose. If you use a different directory, modify the instructions accordingly.Create the
isapi_redirect.propertiesfile.Create a new file called
C:\connectors\isapi_redirect.properties. Copy the following contents into the file.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you do not want to use a
rewrite.propertiesfile, comment out the last line by placing a#character at the beginning of the line.Create the
uriworkermap.propertiesfileThe
uriworkermap.propertiesfile contains mappings between deployed application URLs and which worker handles requests to them. The following example file shows the syntax of the file. Place youruriworkermap.propertiesfile intoC:\connectors\.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
workers.propertiesfile.The
workers.propertiesfile contains mapping definitions between worker labels and server instances. This file follows the syntax of the same file used for Apache mod_jk worker properties configuration.The following is an example of a
workers.propertiesfile. The worker names,worker01andworker02, must match theinstance-idconfigured in the JBoss EAPundertowsubsystem.Place this file into the
C:\connectors\directory.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
rewrite.propertiesfile.The
rewrite.propertiesfile contains simple URL rewriting rules for specific applications. The rewritten path is specified using name-value pairs, as shown in the example below. Place this file into theC:\connectors\directory.Images are accessible under abc path
#Simple example # Images are accessible under abc path /app-01/abc/=/app-01/images/Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Restart your IIS server by using the
net stopandnet startcommands.net stop was /Y net start w3svc
C:\> net stop was /Y C:\> net start w3svcCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The IIS server is configured to send client requests to the specific JBoss EAP servers you have configured, on an application-specific basis.
22.9.3. Configure the ISAPI connector to balance client requests across multiple JBoss EAP servers
This configuration balances client requests across the JBoss EAP servers you specify. This configuration is done on the IIS server, and assumes that you already have JBoss EAP configured to accept requests from an external web server. You also need full administrator access to the IIS server and to have configured IIS to use the ISAPI connector.
Balance client requests across multiple servers
Create a directory to store logs, property files, and lock files.
The rest of this procedure assumes that you are using the directory
C:\connectors\for this purpose. If you use a different directory, modify the instructions accordingly.Create the
isapi_redirect.propertiesfile.Create a new file called
C:\connectors\isapi_redirect.properties. Copy the following contents into the file.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow If you do not want to use a
rewrite.propertiesfile, comment out the last line by placing a#character at the beginning of the line.Create the
uriworkermap.propertiesfile.The
uriworkermap.propertiesfile contains mappings between deployed application URLs and which worker handles requests to them. The following example file shows the syntax of the file, with a load-balanced configuration. The wildcard (*) character sends all requests for various URL sub-directories to the load balancer called router. The configuration of the load balancer is covered in the next step.Place your
uriworkermap.propertiesfile intoC:\connectors\.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Create the
workers.propertiesfile.The
workers.propertiesfile contains mapping definitions between worker labels and server instances. This file follows the syntax of the same file used for Apache mod_jk worker properties configuration.The following is an example of a
workers.propertiesfile. The load balancer is configured near the end of the file, to comprise workersworker01andworker02. These worker names must match theinstance-idconfigured in the JBoss EAPundertowsubsystem.Place this file into the
C:\connectors\directory.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Create the
rewrite.propertiesfile.The
rewrite.propertiesfile contains simple URL rewriting rules for specific applications. The rewritten path is specified using name-value pairs, as shown in the example below. Place this file into theC:\connectors\directory.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The IIS server is configured to send client requests to the JBoss EAP servers referenced in the workers.properties file, spreading the load across the servers in a 1:3 ratio. This ratio is derived from the load-balancing factor, lbfactor, assigned to each server.
22.10. Oracle NSAPI connector
The Netscape Server API (NSAPI) is an API provided by Oracle iPlanet Web Server, formerly Netscape Web Server, for implementing extensions to the server. These extensions are known as server plugins. The NSAPI connector is used in nsapi_redirector.so, which is an extension of mod_jk adjusted to Oracle iPlanet Web Server. The NSAPI connector enables you to configure JBoss EAP instances as worker nodes with Oracle iPlanet Web Server as a load balancer.
See the JBoss EAP supported configurations for information on the supported configurations of Oracle iPlanet Web Server.
22.10.1. Configure Oracle iPlanet web server to use the NSAPI connector
Prerequisites
- JBoss EAP is installed and configured on each server that will serve as a worker.
Download the NSAPI connector from the Red Hat Customer Portal:
- Open a browser and log in to the Red Hat Customer Portal JBoss Software Downloads page.
- Select Web Connectors in the Product drop-down menu.
- Select the latest JBoss Core Services version from the Version drop-down menu.
- Find the Red Hat JBoss Core Services NSAPI Connector in the list, ensuring that you select the correct platform and architecture for your system, and click the Download link.
-
Extract the
nsapi_redirector.sofile, which is located in either thelib/or thelib64/directory, into either theIPLANET_CONFIG/lib/or theIPLANET_CONFIG/lib64/directory.
Set up the NSAPI Connector:
In these instructions, IPLANET_CONFIG refers to the Oracle iPlanet configuration directory, which is usually /opt/oracle/webserver7/config/. If your Oracle iPlanet configuration directory is different, modify the instructions accordingly.
Disable servlet mappings.
Open the
IPLANET_CONFIG/default.web.xmlfile and locate the section with the heading Built In Server Mappings. Disable the mappings to the following three servlets, by wrapping them in XML comment characters (<!--and-->).- default
- invoker
jsp
The following example configuration shows the disabled mappings.
Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Save and exit the file.
Configure the iPlanet Web Server to load the NSAPI connector module.
Add the following lines to the end of the
IPLANET_CONFIG/magnus.conffile, modifying file paths to suit your configuration. These lines define the location of thensapi_redirector.somodule, as well as theworkers.propertiesfile, which lists the workers and their properties.Init fn="load-modules" funcs="jk_init,jk_service" shlib="/lib/nsapi_redirector.so" shlib_flags="(global|now)" Init fn="jk_init" worker_file="IPLANET_CONFIG/connectors/workers.properties" log_level="info" log_file="IPLANET_CONFIG/connectors/nsapi.log" shm_file="IPLANET_CONFIG/connectors/tmp/jk_shm"
Init fn="load-modules" funcs="jk_init,jk_service" shlib="/lib/nsapi_redirector.so" shlib_flags="(global|now)" Init fn="jk_init" worker_file="IPLANET_CONFIG/connectors/workers.properties" log_level="info" log_file="IPLANET_CONFIG/connectors/nsapi.log" shm_file="IPLANET_CONFIG/connectors/tmp/jk_shm"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The configuration above is for a 32-bit architecture.
Save and exit the file.
Configure the NSAPI connector.
You can configure the NSAPI connector for a basic configuration, with no load balancing, or a load-balancing configuration. Choose one of the following options, after which your configuration will be complete.
22.10.2. Configure the NSAPI Connector to Send Client Requests to JBoss EAP
This task configures the NSAPI connector to redirect client requests to JBoss EAP servers with no load balancing or failover. The redirection is done on a per-deployment, and therefore per-URL, basis.
You must have already configured the NSAPI connector before continuing with this task.
Set Up the Basic HTTP Connector
Define the URL paths to redirect to the JBoss EAP servers.
NoteIn
IPLANET_CONFIG/obj.conf, spaces are not allowed at the beginning of a line, except when the line is a continuation of the previous line.Edit the
IPLANET_CONFIG/obj.conffile. Locate the section which starts with <Object name="default">, and add each URL pattern to match, in the format shown by the example file below. The string jknsapi refers to the HTTP connector which will be defined in the next step. The example shows the use of wildcards for pattern matching.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Define the worker which serves each path.
Continue editing the
IPLANET_CONFIG/obj.conffile. Add the following directly after the closing tag of the section you have just finished editing: </Object>.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The example above redirects requests to the URL path /status to the worker called worker01, and all URL paths beneath
/nc/to the worker called worker02. The third line indicates that all URLs assigned to the jknsapi object which are not matched by the previous lines are served to worker01.Save and exit the file.
Define the workers and their attributes.
Create a file called
workers.propertiesin theIPLANET_CONFIG/connectors/directory. Paste the following contents into the file, and modify them to suit your environment.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
workers.propertiesfile uses the same syntax as Apache mod_jk.Save and exit the file.
Restart the iPlanet Web Server
Issue the following command to restart the iPlanet Web Server.
IPLANET_CONFIG/../bin/stopserv IPLANET_CONFIG/../bin/startserv
IPLANET_CONFIG/../bin/stopserv IPLANET_CONFIG/../bin/startservCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
iPlanet Web Server now sends client requests to the URLs you have configured to deployments on JBoss EAP.
22.10.3. Configure the NSAPI Connector to Balance Client Requests Across Multiple JBoss EAP Servers
This task configures the NSAPI connector to send client requests to JBoss EAP servers in a load-balancing configuration.
You must have already configured the NSAPI connector before continuing with this task.
Configure the Connector for Load Balancing
Define the URL paths to redirect to the JBoss EAP servers.
NoteIn
IPLANET_CONFIG/obj.conf, spaces are not allowed at the beginning of a line, except when the line is a continuation of the previous line.Edit the
IPLANET_CONFIG/obj.conffile. Locate the section which starts with<Object name="default">, and add each URL pattern to match, in the format shown by the example file below. The stringjknsapirefers to the HTTP connector that will be defined in the next step. The example shows the use of wildcards for pattern matching.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Define the worker that serves each path.
Continue editing the
IPLANET_CONFIG/obj.conffile. Directly after the closing tag for the section you modified in the previous step,</Object>, add the following new section and modify it to your needs:<Object name="jknsapi"> ObjectType fn=force-type type=text/plain Service fn="jk_service" worker="status" path="/jkmanager(/*)" Service fn="jk_service" worker="router" </Object>
<Object name="jknsapi"> ObjectType fn=force-type type=text/plain Service fn="jk_service" worker="status" path="/jkmanager(/*)" Service fn="jk_service" worker="router" </Object>Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow This
jksnapiobject defines the worker nodes used to serve each path that was mapped to thename="jksnapi"mapping in thedefaultobject. Everything except for URLs matching/jkmanager/*is redirected to the worker calledrouter.Define the workers and their attributes.
Create a file called
workers.propertiesinIPLANET_CONFIG/connector/. Paste the following contents into the file, and modify them to suit your environment.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The
workers.propertiesfile uses the same syntax as Apache mod_jk.Save and exit the file.
Restart the iPlanet Web Server 7.0.
IPLANET_CONFIG/../bin/stopserv IPLANET_CONFIG/../bin/startserv
IPLANET_CONFIG/../bin/stopserv IPLANET_CONFIG/../bin/startservCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
The iPlanet Web Server redirects the URL patterns you have configured to your JBoss EAP servers in a load-balancing configuration.
Chapter 23. Optimizing the JBoss EAP server configuration
Once you have installed the JBoss EAP server, and you have created a management user, Red Hat recommends that you optimize your server configuration.
Make sure you review information in the Performance tuning for JBoss EAP guide for information about how to optimize the server configuration to avoid common problems when deploying applications in a production environment. Common optimizations include setting ulimits, enabling garbage collection, creating Java heap dumps, and adjusting the thread pool size.
It is also a good idea to keep your instance of JBoss EAP up to date with the latest bug fixes. For more information, see Updating Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform.
Appendix A. Reference Material
A.1. Server runtime arguments
The application server startup script accepts arguments and switches at runtime. This allows the server to start under alternative configurations to those defined in the standalone.xml, domain.xml, and host.xml configuration files.
Alternative configurations might include starting the server with an alternative socket bindings set or a secondary configuration.
The available parameters list can be accessed by passing the help switch -h or --help at startup.
| Argument or Switch | Operating Mode | Description |
|---|---|---|
| --admin-only | Standalone |
Set the server’s running type to |
| --admin-only | Domain |
Set the host controller’s running type to |
| -b=<value>, -b <value> | Standalone, Domain |
Set system property |
| -b<interface>=<value> | Standalone, Domain |
Set system property |
| --backup | Domain | Keep a copy of the persistent domain configuration even if this host is not the domain controller. |
| -c=<config>, -c <config> | Standalone |
Name of the server configuration file to use. The default is |
| -c=<config>, -c <config> | Domain |
Name of the server configuration file to use. The default is |
| --cached-dc | Domain | If the host is not the domain controller and cannot contact the domain controller at boot, boot using a locally cached copy of the domain configuration. |
| --debug [<port>] | Standalone | Activate debug mode with an optional argument to specify the port. Only works if the launch script supports it. |
| -D<name>[=<value>] | Standalone, Domain | Set a system property. |
| --domain-config=<config> | Domain |
Name of the server configuration file to use. The default is |
| --git-repo | Standalone |
The location of the Git repository that is used to manage and persist server configuration data. This can be |
| --git-branch | Standalone | The branch or tag name in the Git repository to use. This argument should name an existing branch or tag name as it will not be created if it does not exist. If you use a tag name, you put the repository in a detached HEAD state, meaning future commits are not attached to any branches. Tag names are read-only and are normally used when you need to replicate a configuration across several nodes. |
| --git-auth | Standalone |
The URL to an Elytron configuration file that contains the credentials to be used when connecting to a remote Git repository. This argument is required if your remote Git repository requires authentication. Elytron does not support SSH. Therefore, only default SSH authentication is supported using private keys without a password. This argument is not used with a |
| -h, --help | Standalone, Domain | Display the help message and exit. |
| --host-config=<config> | Domain |
Name of the host configuration file to use. The default is |
| --interprocess-hc-address=<address> | Domain | Address on which the host controller should listen for communication from the process controller. |
| --interprocess-hc-port=<port> | Domain | Port on which the host controller should listen for communication from the process controller. |
| --primary-address=<address> | Domain |
Set system property |
| --primary-port=<port> | Domain |
Set system property |
| --read-only-server-config=<config> | Standalone |
Name of the server configuration file to use. This differs from |
| --read-only-domain-config=<config> | Domain |
Name of the domain configuration file to use. This differs from |
| --read-only-host-config=<config> | Domain |
Name of the host configuration file to use. This differs from |
| -P=<url>, -P <url>, --properties=<url> | Standalone, Domain | Load system properties from the given URL. |
| --pc-address=<address> | Domain | Address on which the process controller listens for communication from processes it controls. |
| --pc-port=<port> | Domain | Port on which the process controller listens for communication from processes it controls. |
| -S<name>[=<value>] | Standalone | Set a security property. |
| -secmgr | Standalone, Domain | Runs the server with a security manager installed. |
| --server-config=<config> | Standalone |
Name of the server configuration file to use. The default is |
| --start-mode=<mode> | Standalone |
Set the start mode of the server. This option cannot be used in conjunction with
|
| -u=<value>, -u <value> | Standalone, Domain |
Set system property |
| -v, -V, --version | Standalone, Domain | Display the application server version and exit. |
The configuration files that ship with JBoss EAP are set up to handle the behavior of the switches, for example, -b and -u. If you change your configuration files to no longer use the system property controlled by the switch, then adding it to the launch command will have no effect.
A.2. RPM service configuration files
The RPM installation of JBoss EAP includes two additional configuration files compared to a ZIP or installer installation. These files are used by the service init script to specify the JBoss EAP launch environment.
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 and later, RPM service configuration files are loaded using systemd, so variable expressions are not expanded.
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| /etc/opt/rh/eap8/wildfly/eap8-standalone.conf | Settings specific to standalone JBoss EAP servers on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 and later. |
| /etc/opt/rh/eap8/wildfly/eap8-domain.conf | Settings specific to JBoss EAP running as a managed domain on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 and later. |
A.3. RPM service configuration properties
The following table shows a list of available configuration properties for the JBoss EAP RPM service along with their default values.
If a property has the same name in both the RPM service configuration file, such as /usr/lib/systemd/system/eap8-standalone.service:, and in the JBoss EAP startup configuration file, such as EAP_HOME/bin/standalone.conf, the value that takes precedence is the one in the JBoss EAP startup configuration file. One such property is JAVA_HOME.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| JAVA_HOME | The directory where your Java Runtime Environment is installed.
Default value: |
| JAVAPTH | The path where the Java executable files are installed.
Default value: |
| WILDFLY_CONSOLE_LOG | The file that the CONSOLE log handler will be redirected to.
Default value: |
| WILDFLY_SH | The script used to launch the JBoss EAP server.
Default value: |
| WILDFLY_SERVER_CONFIG | The server configuration file to use.
There is no default for this property. Either |
| WILDFLY_HOST_CONFIG |
For a managed domain, this property allows a user to specify the host configuration file, such as |
| WILDFLY_MODULEPATH | The path of the JBoss EAP module directory.
Default value: |
| WILDFLY_BIND |
Sets the |
| WILDFLY_OPTS | Additional arguments to include on startup. For example: -Dorg.wildfly.openssl.path=PATH_TO_OPENSSL_LIBS |
A.4. Overview of JBoss EAP subsystems
The table below gives a brief description of the JBoss EAP subsystems.
| JBoss EAP subsystem | Description |
|---|---|
| batch-jberet | Configure an environment for running batch applications and manage batch jobs. |
| bean-validation | Configure bean validation for validating Java object data. |
| core-management | Register listeners for server lifecycle events and track configuration changes. |
| datasources | Create and configure datasources and manage JDBC database drivers. |
| deployment-scanner | Configure deployment scanners to monitor particular locations for applications to deploy. |
| ee | Configure common functionality in the Jakarta EE platform, such as defining global modules, enabling descriptor-based property replacement, and configuring default bindings. |
| ejb3 | Configure Jakarta Enterprise Beans, including session and message-driven beans.
More information for the |
| elytron | Configure server and application security.
More information on the |
| iiop-openjdk |
Configure Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) services for JTS transactions and other ORB services, including security. In JBoss EAP 7, this functionality was contained in the |
| infinispan | Configure caching functionality for JBoss EAP high availability services. |
| io | Define workers and buffer pools to be used by other subsystems. |
| jaxrs | Enable the deployment and functionality of Jakarta RESTful Web Services applications. |
| jca | Configure the general settings for the Jakarta Connectors container and resource adapter deployments. |
| jdr | Enable the gathering of diagnostic data to aid in troubleshooting. JBoss EAP subscribers can provide this information to Red Hat when requesting support. |
| jgroups | Configure the protocol stacks and communication mechanisms for how servers in a cluster talk to each other. |
| jmx | Configure remote Jakarta Management access. |
| jpa | Manages the Jakarta Persistence 2.2 container-managed requirements and allows you to deploy persistent unit definitions, annotations, and descriptors.
More information for the |
| jsf | Manage Jakarta Server Faces implementations. |
| jsr77 | Provide Jakarta EE management capabilities defined by the Jakarta Management specification. |
| logging | Configure system and application-level logging through a system of log categories and log handlers. |
| | Configure mail server attributes and custom mail transports to create a mail service that allows applications deployed to JBoss EAP to send mail using that service. |
| messaging-activemq |
Configure Java Message Service destinations, connection factories, and other settings for Artemis, the integrated messaging provider. In JBoss EAP 7, messaging functionality was contained in the
More information for the |
| metrics |
Displays base metrics from the management model and Java Virtual Machine (JVM) MBeans. JBoss EAP no longer includes the |
| health |
Exposes the health checks for the JBoss EAP runtime. JBoss EAP no longer includes the |
| modcluster | Configure the server-side mod_cluster worker node. |
| naming | Bind entries into global JNDI namespaces and configure the remote JNDI interface. |
| pojo | Enable deployment of applications containing JBoss Microcontainer services, as supported by previous versions of JBoss EAP. |
| remoting | discovery |
| The discovery subsystem is currently for internal subsystem use only; it is a private API and is not available for public use. | request-controller |
| Configure settings to suspend and shut down servers gracefully. | resource-adapters |
| Configure and maintain resource adapters for communication between Jakarta EE applications and an Enterprise Information System (EIS) using the Jakarta Connectors specification. | rts |
| Unsupported implementation of REST-AT. | sar |
| Enable deployment of SAR archives containing MBean services, as supported by previous versions of JBoss EAP. | security |
| Legacy method to configure application security settings.
More information on the | security-manager |
| Configure Java security policies to be used by the Java Security Manager.
More information on the | singleton |
| Define singleton policies to configure the behavior of singleton deployments or to create singleton MSC services.
More information on the | transactions |
|
Configure the Transaction Manager (TM) options, such as timeout values, transaction logging, and whether to use Java Transaction Service (JTS). More information on the | undertow |
|
Configure JBoss EAP’s web server and servlet container settings. In JBoss EAP 7, this functionality was contained in the | webservices |
| Configure published endpoint addresses and endpoint handler chains, as well as the host name, ports, and WSDL address for the web services provider.
More information for the | weld |
| Configure Jakarta Contexts and Dependency Injection functionality for JBoss EAP. | xts |
A.5. Add-user utility arguments
The following table describes the arguments available for the add-user.sh or add-user.bat script, which is a utility for adding new users to the properties file for out-of-the-box authentication.
| Command Line Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| -a | Create a user in the application realm. If omitted, the default is to create a user in the management realm. |
| -dc <value> |
The domain configuration directory that will contain the properties files. If it is omitted, the default directory is |
| -sc <value> |
An alternative standalone server configuration directory that will contain the properties files. If omitted, the default directory is |
| -up, --user-properties <value> |
The name of the alternative user properties file. It can be an absolute path or it can be a file name used in conjunction with the |
| -g, --group <value> | A comma-separated list of groups to assign to this user. |
| -gp, --group-properties <value> |
The name of the alternative group properties file. It can be an absolute path or it can be a file name used in conjunction with the |
| -p, --password <value> | The password of the user. |
| -u, --user <value> | The name of the user. User names can only contain the following characters, in any number and in any order:
|
| -r, --realm <value> |
The name of the realm used to secure the management interfaces. If omitted, the default is |
| -s, --silent |
Run the |
| -e, --enable | Enable the user. |
| -d, --disable | Disable the user. |
| -cw, --confirm-warning | Automatically confirm warning in interactive mode. |
| -h, --help |
Display usage information for the |
| -ds, --display-secret | Print the secret value in non-interactive mode. |
A.6. Management audit logging attributes
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-config_5_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| enabled | Whether audit logging is enabled. |
| log-boot | Whether operations should be logged on server boot. |
| log-read-only | Whether operations that do not modify the configuration or any runtime services should be logged. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| compact |
If |
| date-format |
The date format to use as understood by |
| date-separator |
The separator between the date and the rest of the formatted log message. This is ignored if |
| escape-control-characters |
If |
| escape-new-line |
If |
| include-date | Whether or not to include the date in the formatted log record. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| disabled-due-to-failure | Whether this handler has been disabled due to logging failures (read-only). |
| failure-count | The number of logging failures since the handler was initialized (read-only). |
| formatter | The JSON formatter used to format the log messages. |
| max-failure-count | The maximum number of logging failures before disabling this handler. |
| path | The path of the audit log file. |
| relative-to |
The name of another previously named path, or of one of the standard paths provided by the system. If |
| rotate-at-startup | Whether the old log file should be rotated at server startup. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| app-name | The application name to add to the syslog records as defined in section 6.2.5 of RFC-5424. If not specified it will default to the name of the product. |
| disabled-due-to-failure | Whether this handler has been disabled due to logging failures (read-only). |
| facility | The facility to use for syslog logging as defined in section 6.2.1 of RFC-5424 and section 4.1.1 of RFC-3164. |
| failure-count | The number of logging failures since the handler was initialized (read-only). |
| formatter | The JSON formatter used to format the log messages. |
| max-failure-count | The maximum number of logging failures before disabling this handler. |
| max-length |
The maximum length in bytes a log message, including the header, is allowed to be. If undefined, it will default to |
| protocol |
The protocol to use for the syslog handler. Must be one and only one of |
| syslog-format |
The syslog format: |
| truncate |
Whether or not a message, including the header, should truncate the message if the length in bytes is greater than the value of the |
Syslog servers vary in their implementation, so not all settings are applicable to all syslog servers. Testing has been conducted using the rsyslog syslog implementation.
This table lists only the high-level attributes. Each attribute has configuration parameters, and some have child configuration parameters.
A.7. Interface attributes
Attribute names in this table are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-config_5_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Interface element | Description |
|---|---|
| any | Element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be that it meets at least one, but not necessarily all, of the nested set of criteria. |
| any-address |
Empty element indicating that sockets using this interface should be bound to a wildcard address. The IPv6 wildcard address ( |
| inet-address | Either an IP address in IPv6 or IPv4 dotted decimal notation, or a host name that can be resolved to an IP address. |
| link-local-address | Empty element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be whether or not an address associated with it is link-local. |
| loopback | Empty element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be whether or not it is a loopback interface. |
| loopback-address | A loopback address that may not actually be configured on the machine’s loopback interface. Differs from inet-address type in that the given value will be used even if no NIC can be found that has the IP address associated with it. |
| multicast | Empty element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be whether or not it supports multicast. |
| name | The name of the interface. |
| nic | The name of a network interface (e.g. eth0, eth1, lo). |
| nic-match | A regular expression against which the names of the network interfaces available on the machine can be matched to find an acceptable interface. |
| not | Element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be that it does not meet any of the nested set of criteria. |
| point-to-point | Empty element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be whether or not it is a point-to-point interface. |
| public-address | Empty element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be whether or not it has a publicly routable address. |
| site-local-address | Empty element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be whether or not an address associated with it is site-local. |
| subnet-match |
A network IP address and the number of bits in the address' network prefix, written in slash notation, for example, |
| up | Empty element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be whether or not it is currently up. |
| virtual | Empty element indicating that part of the selection criteria for an interface should be whether or not it is a virtual interface. |
A.8. Socket binding attributes
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-config_5_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
The following tables show the attributes that can be configured for each of the three types of socket bindings.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| client-mappings | Specifies the client mappings for this socket binding. A client connecting to this socket should use the destination address specified in the mapping that matches its desired outbound interface. This allows for advanced network topologies that use either network address translation, or have bindings on multiple network interfaces to function. Each mapping should be evaluated in declared order, with the first successful match used to determine the destination. |
| fixed-port | Whether the port value should remain fixed even if numeric offsets are applied to the other sockets in the socket group. |
| interface |
Name of the interface to which the socket should be bound, or, for multicast sockets, the interface on which it should listen. This should be one of the declared interfaces. If not defined, the value of the |
| multicast-address | Multicast address on which the socket should receive multicast traffic. If unspecified, the socket will not be configured to receive multicast. |
| multicast-port |
Port on which the socket should receive multicast traffic. Must be configured if |
| name | The name of the socket. Services needing to access the socket configuration information will find it using this name. This attribute is required. |
| port | Number of the port to which the socket should be bound. Note that this value can be overridden if servers apply a port-offset to increment or decrement all port values. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| fixed-source-port | Whether the port value should remain fixed even if numeric offsets are applied to the other outbound sockets in the socket group. |
| host | The host name or IP address of the remote destination to which this outbound socket will connect. |
| port | The port number of the remote destination to which the outbound socket should connect. |
| source-interface | The name of the interface that will be used for the source address of the outbound socket. |
| source-port | The port number that will be used as the source port of the outbound socket. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| fixed-source-port | Whether the port value should remain fixed even if numeric offsets are applied to the other outbound sockets in the socket group. |
| socket-binding-ref | The name of the local socket binding that will be used to determine the port to which this outbound socket connects. |
| source-interface | The name of the interface that will be used for the source address of the outbound socket. |
| source-port | The port number that will be used as the source port of the outbound socket. |
A.9. Default socket bindings groups
The following tables show the default socket bindings for each socket binding group.
| Socket Binding | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ajp | 8009 | Apache JServ Protocol. Used for HTTP clustering and load balancing. |
| http | 8080 | The default port for deployed web applications. |
| https | 8443 | SSL-encrypted connection between deployed web applications and clients. |
| management-http | 9990 | Used for HTTP communication with the management layer. |
| management-https | 9993 | Used for HTTPS communication with the management layer. |
| txn-recovery-environment | 4712 | The Jakarta Transactions recovery manager. |
| txn-status-manager | 4713 | The Jakarta Transactions / JTS transaction manager. |
| Socket Binding | Port | Multicast Port | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ajp | 8009 | Apache JServ Protocol. Used for HTTP clustering and load balancing. | |
| http | 8080 | The default port for deployed web applications. | |
| https | 8443 | SSL-encrypted connection between deployed web applications and clients. | |
| jgroups-mping | 45700 | Multicast. Used to discover initial membership in a HA cluster. | |
| jgroups-tcp | 7600 | Unicast peer discovery in HA clusters using TCP. | |
| jgroups-udp | 55200 | 45688 | Multicast peer discovery in HA clusters using UDP. |
| management-http | 9990 | Used for HTTP communication with the management layer. | |
| management-https | 9993 | Used for HTTPS communication with the management layer. | |
| modcluster | 23364 | Multicast port for communication between JBoss EAP and the HTTP load balancer. | |
| txn-recovery-environment | 4712 | The Jakarta Transactions recovery manager. | |
| txn-status-manager | 4713 | The Jakarta Transactions / JTS transaction manager. |
| Socket Binding | Port | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ajp | 8009 | Apache JServ Protocol. Used for HTTP clustering and load balancing. |
| http | 8080 | The default port for deployed web applications. |
| https | 8443 | SSL-encrypted connection between deployed web applications and clients. |
| iiop | 3528 | CORBA services for JTS transactions and other ORB-dependent services. |
| iiop-ssl | 3529 | SSL-encrypted CORBA services. |
| management-http | 9990 | Used for HTTP communication with the management layer. |
| management-https | 9993 | Used for HTTPS communication with the management layer. |
| txn-recovery-environment | 4712 | The Jakarta Transactions recovery manager. |
| txn-status-manager | 4713 | The Jakarta Transactions / JTS transaction manager. |
| Name | Port | Multicast Port | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ajp | 8009 | Apache JServ Protocol. Used for HTTP clustering and load balancing. | |
| http | 8080 | The default port for deployed web applications. | |
| https | 8443 | SSL-encrypted connection between deployed web applications and clients. | |
| iiop | 3528 | CORBA services for JTS transactions and other ORB-dependent services. | |
| iiop-ssl | 3529 | SSL-encrypted CORBA services. | |
| jgroups-mping | 45700 | Multicast. Used to discover initial membership in a HA cluster. | |
| jgroups-tcp | 7600 | Unicast peer discovery in HA clusters using TCP. | |
| jgroups-udp | 55200 | 45688 | Multicast peer discovery in HA clusters using UDP. |
| management-http | 9990 | Used for HTTP communication with the management layer. | |
| management-https | 9993 | Used for HTTPS communication with the management layer. | |
| modcluster | 23364 | Multicast port for communication between JBoss EAP and the HTTP load balancer. | |
| txn-recovery-environment | 4712 | The Jakarta Transactions recovery manager. | |
| txn-status-manager | 4713 | The Jakarta Transactions / JTS transaction manager. |
| Name | Port | Multicast Port | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| http | 8080 | The default port for deployed web applications. | |
| https | 8443 | SSL-encrypted connection between deployed web applications and clients. | |
| management-http | 9990 | Used for HTTP communication with the management layer. | |
| management-https | 9993 | Used for HTTPS communication with the management layer. | |
| mcmp-management | 8090 | The port for the Mod-Cluster Management Protocol (MCMP) connection to transmit lifecycle events. | |
| modcluster | 23364 | Multicast port for communication between JBoss EAP and the HTTP load balancer. |
A.10. Module command arguments
The following arguments can be passed to the module add management CLI command:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| --absolute-resources |
Use this argument to specify a list of absolute file system paths to reference from its
See |
| --allow-nonexistent-resources |
Use this argument to create empty directories for resources specified by |
| --dependencies | Use this argument to provide a comma-separated list of module names that this module depends on. |
| --export-dependencies | Use this argument to specify exported dependencies. module add --name=com.mysql --resources=/path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --export-dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api Note The MySQL driver JAR name, mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar, is provided only as an example. For information about the tested MySQL version, see Tested databases. |
| --main-class | Use this argument to specify the fully qualified class name that declares the module’s main method. |
| --module-root-dir |
Use this argument if you have defined an external JBoss EAP module directory to use instead of the default module add --module-root-dir=/path/to/my-external-modules/ --name=com.mysql --resources=/path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api Note The MySQL driver JAR name, mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar, is provided only as an example. For information about the tested MySQL version, see Tested databases. |
| --module-xml |
Use this argument to provide a file system path to a |
| --name | Use this argument to provide the name of the module to add. This argument is required. |
| --properties |
Use this argument to provide a comma-separated list of |
| --resource-delimiter |
Use this argument to set a user-defined file path separator for the list of resources provided to the |
| --resources |
Use this argument to specify the resources for this module by providing a list of file system paths. The files are copied to this module directory and referenced from its
See |
| --slot |
Use this argument to add the module to a slot other than the default module add --name=com.mysql --slot=8.0 --resources=/path/to/mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar --dependencies=wildflyee.api,java.se,java.xml,java.xml.crypto,jdk.xml.dom,jakarta.transaction.api Note The MySQL driver JAR name, mysql-connector-j-8.0.33.jar, is provided only as an example. For information about the tested MySQL version, see Tested databases. |
A.11. Deployment scanner marker files
Marker files are used by the deployment scanner to mark the status of an application within the deployment directory of the JBoss EAP server instance. A marker file has the same name as the deployment, with the file suffix indicating the state of the application’s deployment.
For example, a successful deployment of test-application.war would have a marker file named test-application.war.deployed.
The following table lists the available marker file types and their meanings.
| Filename Suffix | Origin | Description |
|---|---|---|
| .deployed | System-generated | Indicates that the content has been deployed. The content will be undeployed if this file is deleted. |
| .dodeploy | User-generated | Indicates that the content should be deployed or redeployed. |
| .failed | System-generated | Indicates deployment failure. The marker file contains information about the cause of failure. If the marker file is deleted, the content will be eligible for auto-deployment again. |
| .isdeploying | System-generated | Indicates that the deployment is in progress. This marker file will be deleted upon completion. |
| .isundeploying | System-generated |
Triggered by deleting a |
| .pending | System-generated | Indicates that the deployment scanner recognizes the need to deploy content, but an issue is currently preventing auto-deployment (for example, if content is in the process of being copied). This marker serves as a global deployment road-block, meaning that the scanner will not instruct the server to deploy or undeploy any content while this marker file exists. |
| .skipdeploy | User-generated | Disables auto-deploy of an application while present. Useful as a method of temporarily blocking the auto-deployment of exploded content, preventing the risk of incomplete content edits being pushed. Can be used with zipped content, although the scanner detects in-progress changes to zipped content and waits until completion. |
| .undeployed | System-generated | Indicates that the content has been undeployed. Deletion of this marker file has no impact to content redeployment. |
A.12. Deployment scanner attributes
The deployment scanner contains the following configurable attributes.
Attribute names in this table are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/jboss-as-deployment-scanner_2_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| auto-deploy-exploded | false |
Allows the automatic deployment of exploded content without requiring a |
| auto-deploy-xml | true |
Allows the automatic deployment of XML content without requiring a |
| auto-deploy-zipped | true |
Allows the automatic deployment of zipped content without requiring a |
| deployment-timeout | 600 | The time value in seconds for the deployment scanner to allow a deployment attempt before being canceled. |
| path | deployments |
The actual file system path to be scanned. Treated as an absolute path, unless the |
| relative-to | jboss.server.base.dir | Reference to a file system path defined as a path in the server configuration. |
| runtime-failure-causes-rollback | false | Whether a runtime failure of a deployment causes a rollback of the deployment as well as all other (possibly unrelated) deployments as part of the scan operation. |
| scan-enabled | true |
Allows the automatic scanning for applications by |
| scan-interval | 5000 |
The time interval in milliseconds that the repository should be scanned for changes. A value of less than |
A.13. Managed domain JVM configuration attributes
The following Java Virtual Machine (JVM) configuration options can be set for a managed domain at the host, server group, or server level. Note that valid values for some of these attributes are dependent upon your JVM. See your JDK vendor’s documentation for additional information.
Attribute names in this table are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-config_20_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| agent-lib |
Sets the value of the |
| agent-path |
Sets the value of the |
| debug-enabled | Specifies whether to enable debugging. This attribute only applies to JVM configurations at the server level. |
| debug-options | Specifies the JVM options to use when debug is enabled. This attribute only applies to JVM configurations at the server level. |
| env-classpath-ignored |
Specifies whether to ignore the |
| environment-variables | Specifies key/value pair environment variables. |
| heap-size |
Sets the value of the |
| java-agent |
Sets the value of the |
| java-home |
Sets the value of the |
| jvm-options | Specifies any additional JVM options needed. |
| launch-command |
Specifies an operating system level command to prefix before the |
| max-heap-size |
Sets the value of the |
| max-permgen-size | Sets the maximum size of the permanent generation. Deprecated: The JVM no longer provides a separate permanent generation space. |
| module-options |
Sets any options passed to JBoss Modules during the boot of the server. Note that if a |
| permgen-size | Sets the initial permanent generation size. Deprecated: The JVM no longer provides a separate permanent generation space. |
| stack-size |
Sets the value of the |
| type |
Specifies which vendor provided the JVM in use. Available options are |
A.14. Mail subsystem attributes
This reference provides details about the attributes in the mail subsystem for mail sessions and the following mail server types:
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-mail_3_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
A.14.1. Mail session attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Whether to enable Jakarta Mail debugging. |
|
| The default "from" address to use if not set when sending. |
|
| The JNDI name to which the mail session should be bound. |
A.14.2. IMAP mail server attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Credential from a credential store to authenticate on the server. |
|
| Reference to the outbound socket binding for the mail server. |
|
| The password to authenticate on the server. |
|
| Whether the server requires SSL. |
|
| Whether the server requires TLS. |
|
| The username to authenticate on the server. |
A.14.3. POP3 mail server attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Credential from a credential store to authenticate on the server. |
|
| Reference to the outbound socket binding for the mail server. |
|
| The password to authenticate on the server. |
|
| Whether the server requires SSL. |
|
| Whether the server requires TLS. |
|
| The username to authenticate on the server. |
A.14.4. SMTP mail server attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Credential from a credential store to authenticate on the server. |
|
| Reference to the outbound socket binding for the mail server. |
|
| The password to authenticate on the server. |
|
| Whether the server requires SSL. |
|
| Whether the server requires TLS. |
|
| The username to authenticate on the server. |
A.14.5. Custom mail server attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
| Credential from a credential store to authenticate on the server. |
|
| Reference to the outbound socket binding for the mail server. |
|
| The password to authenticate on the server. |
|
| The Jakarta Mail properties for this server. |
|
| Whether the server requires SSL. |
|
| Whether the server requires TLS. |
|
| The username to authenticate on the server. |
A.15. Root Logger Attributes
Attribute names in this table are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/jboss-as-logging_3_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| filter |
Defines a simple filter type. Deprecated in favor of |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that excludes log entries that do not match a pattern: |
| handlers | A list of log handlers that are used by the root logger. |
| level | The lowest level of log message that the root logger records. |
A filter-spec specified for the root logger is not inherited by other handlers. Instead a filter-spec must be specified per handler.
A.16. Log Category Attributes
Attribute names in this table are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/jboss-as-logging_6_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| category | The log category from which log messages will be captured. |
| filter |
Defines a simple filter type. Deprecated in favor of |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that does not match a pattern: |
| handlers | A list of log handlers associated with the logger. |
| level | The lowest level of log message that the log category records. |
| use-parent-handlers |
If set to |
A.17. Log Handler Attributes
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/jboss-as-logging_6_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| autoflush |
If set to |
| enabled |
If set to |
| encoding | The character encoding scheme to be used for the output. |
| filter |
Defines a simple filter type. Deprecated in favor of |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that does not match a pattern: |
| formatter | The log formatter used by this log handler. |
| level | The lowest level of log message the log handler records. |
| name | The name of the log handler. Deprecated since the handler’s address contains the name. |
| named-formatter | The name of the defined formatter to be used on the handler. |
| target | The system output stream where the output of the log handler is sent. This can be one of the following:
|
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| append |
If set to |
| autoflush |
If set to |
| enabled |
If set to |
| encoding | The character encoding scheme to be used for the output. |
| file |
The object that represents the file where the output of this log handler is written to. It has two configuration properties, |
| filter |
Defines a simple filter type. Deprecated in favor of |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that does not match a pattern: |
| formatter | The log formatter used by this log handler. |
| level | The lowest level of log message the log handler records. |
| name | The name of the log handler. Deprecated since the handler’s address contains the name. |
| named-formatter | The name of the defined formatter to be used on the handler. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| append |
If set to |
| autoflush |
If set to |
| enabled |
If set to |
| encoding | The character encoding scheme to be used for the output. |
| file |
Object that represents the file to which the output of this log handler is written. It has two configuration properties, |
| filter |
Defines a simple filter type. Deprecated in favor of |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that does not match a pattern: |
| formatter | The log formatter used by this log handler. |
| level | The lowest level of log message the log handler records. |
| name | The name of the log handler. Deprecated since the handler’s address contains the name. |
| named-formatter | The name of the defined formatter to be used on the handler. |
| suffix |
This string is included in the suffix appended to rotated logs. The format of the |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| append |
If set to |
| autoflush |
If set to |
| enabled |
If set to |
| encoding | The character encoding scheme to be used for the output. |
| file |
Object that represents the file where the output of this log handler is written to. It has two configuration properties, |
| filter |
Defines a simple filter type. Deprecated in favor of |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that does not match a pattern: |
| formatter | The log formatter used by this log handler. |
| level | The lowest level of log message the log handler records. |
| max-backup-index |
The maximum number of rotated logs that are kept. When this number is reached, the oldest log is reused. The default is
If the |
| name | The name of the log handler. Deprecated since the handler’s address contains the name. |
| named-formatter | The name of the defined formatter to be used on the handler. |
| rotate-on-boot |
If set to |
| rotate-size |
The maximum size that the log file can reach before it is rotated. A single character appended to the number indicates the size units: |
| suffix |
This string is included in the suffix appended to rotated logs. The format of the |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| append |
If set to |
| autoflush |
If set to |
| enabled |
If set to |
| encoding | The character encoding scheme to be used for the output. |
| file |
Object that represents the file where the output of this log handler is written to. It has two configuration properties, |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that does not match a pattern: |
| formatter | The log formatter used by this log handler. |
| level | The lowest level of log message the log handler records. |
| max-backup-index |
The maximum number of rotated logs that are kept. When this number is reached, the oldest log is reused. The default is
If the |
| name | The name of the log handler. Deprecated since the handler’s address contains the name. |
| named-formatter | The name of the defined formatter to be used on the handler. |
| rotate-on-boot |
If set to |
| rotate-size |
The maximum size that the log file can reach before it is rotated. A single character appended to the number indicates the size units: |
| suffix |
This string is included in the suffix appended to rotated logs. The format of the |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| app-name |
The app name used when formatting the message in RFC5424 format. By default the app name is |
| enabled |
If set to |
| facility | The facility as defined by RFC-5424 and RFC-3164. |
| hostname | The name of the host from which the messages are being sent. For example, the name of the host the application server is running on. |
| level | The lowest level of log message the log handler records. |
| port | The port on which the syslog server is listening. |
| server-address | The address of the syslog server. |
| syslog-format | Formats the log message according to the RFC specification. |
| named-formatter | Formats the message of the syslog payload. With this attribute, you can customize the message as required. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| autoflush | Whether to automatically flush after each write. |
| block-on-reconnect |
If set to |
| enabled |
If set to |
| encoding | The character encoding used by this handler |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that does not match a pattern: |
| level | The lowest level of log message the log handler records. |
| named-formatter | The name of the defined formatter to be used on the handler. |
| outbound-socket-binding-ref | The reference to the outbound socket binding for the socket connection. |
| protocol |
The protocol the socket should communicate over. Allowed values are |
| ssl-context |
The reference to the defined SSL context. This is only used if |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| class | The logging handler class to be used. |
| enabled |
If set to |
| encoding | The character encoding scheme to be used for the output. |
| filter |
Defines a simple filter type. Deprecated in favor of |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that does not match a pattern: |
| formatter | The log formatter used by this log handler. |
| level | The lowest level of log message the log handler records. |
| module | The module one which the logging handler depends. |
| name | The name of the log handler. Deprecated since the handler’s address contains the name. |
| named-formatter | The name of the defined formatter to be used on the handler. |
| properties | The properties used for the logging handler. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| enabled |
If set to |
| filter |
Defines a simple filter type. Deprecated in favor of |
| filter-spec |
An expression value that defines a filter. The following expression defines a filter that does not match a pattern: |
| level | The lowest level of log message the log handler records. |
| name | The name of the log handler. Deprecated since the handler’s address contains the name. |
| overflow-action |
How this handler responds when its queue length is exceeded. This can be set to |
| queue-length | Maximum number of log messages that will be held by this handler while waiting for sub-handlers to respond. |
| subhandlers | The list of log handlers to which this async handler passes its log messages. |
A.18. Log Formatter Attributes
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| %c | The category of the logging event. |
| %p | The level of the log entry (INFO, DEBUG, etc.). |
| %P | The localized level of the log entry. |
| %d |
The current date/time ( |
| %r | The relative time (milliseconds since the log was initialized). |
| %z |
The time zone, which must be specified before the date ( |
| %k | A log resource key (used for localization of log messages). |
| %m | The log message (including exception trace). |
| %s | The simple log message (no exception trace). |
| %e | The exception stack trace (no extended module information). |
| %E | The exception stack trace (with extended module information). |
| %t | The name of the current thread. |
| %n | A newline character. |
| %C | The class of the code calling the log method (slow). |
| %F | The filename of the class calling the log method (slow). |
| %l | The source location of the code calling the log method (slow). |
| %L | The line number of the code calling the log method (slow). |
| %M | The method of the code calling the log method (slow). |
| %x | The Nested Diagnostic Context. |
| %X | The Message Diagnostic Context. |
| %% |
A literal percent ( |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| date-format |
The date-time format pattern. The pattern must be a valid |
| exception-output-type | Indicates how the cause of the logged message, if one is available, is added to the JSON output. The allowed values are:
|
| key-overrides | Allows the names of the keys for the JSON properties to be overridden. |
| meta-data | Sets the metadata to be used in the JSON formatter. |
| pretty-print | Whether or not pretty printing should be used when formatting. |
| print-details | Whether or not details should be printed. The details include the source class name, source file name, source method name, source module name, source module version and source line number. Note Printing the details can be expensive as the values are retrieved from the caller. |
| record-delimiter | The value to be used to indicate the end of a record. If set to null no delimiter will be used at the end of the record. The default value is a line feed. |
| zone-id | The zone ID for formatting the date and time. The system default is used if left undefined. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| date-format |
The date-time format pattern. The pattern must be a valid |
| exception-output-type | Indicates how the cause of the logged message, if one is available, is added to the XML output. The allowed values are:
|
| key-overrides | Allows the names of the keys for the XML properties to be overridden. |
| meta-data | Sets the meta data to use in the XML format. Properties are added to each log message. |
| namespace-uri |
Sets the namespace URI used for each record if print-namespace attribute is true. Note that if no namespace-uri is defined and there are overridden keys no namespace will be written regardless if the |
| pretty-print | Whether or not pretty printing should be used when formatting. |
| print-details | Whether or not details should be printed. The details include the source class name, source file name, source method name, source module name, source module version and source line number. Note Printing the details can be expensive as the values are retrieved from the caller. |
| record-delimiter | The value to be used to indicate the end of a record. If this is null, no delimiter is used at the end of the record. The default value is a line feed. |
| zone-id | The zone ID for formatting the date and time. The system default is used if left undefined. |
A.19. Datasource connection URLs
| Datasource | Connection URL |
|---|---|
| IBM DB2 | jdbc:db2://SERVER_NAME:PORT/DATABASE_NAME |
| MariaDB | jdbc:mariadb://SERVER_NAME:PORT/DATABASE_NAME |
| MariaDB Galera Cluster | jdbc:mariadb://SERVER_NAME:PORT,SERVER_NAME:PORT/DATABASE_NAME |
| Microsoft SQL Server | jdbc:sqlserver://SERVER_NAME:PORT;DatabaseName=DATABASE_NAME |
| MySQL | jdbc:mysql://SERVER_NAME:PORT/DATABASE_NAME |
| Oracle | jdbc:oracle:thin:@SERVER_NAME:PORT:ORACLE_SID |
| PostgreSQL | jdbc:postgresql://SERVER_NAME:PORT/DATABASE_NAME |
| Sybase | jdbc:sybase:Tds:SERVER_NAME:PORT/DATABASE_NAME |
A.20. Datasource attributes
Attribute names in this table are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-datasources_5_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Datasource type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allocation-retry | Non-XA, XA |
The number of times that allocating a connection should be tried before throwing an exception. The default is |
| allocation-retry-wait-millis | Non-XA, XA |
The amount of time, in milliseconds, to wait between retrying to allocate a connection. The default is |
| allow-multiple-users | Non-XA, XA |
Whether multiple users will access the datasource through the |
| authentication-context | Non-XA, XA |
The Elytron authentication context which defines the |
| background-validation | Non-XA, XA |
Whether connections should be validated on a background thread versus being validated prior to use. Background validation is typically not to be used with |
| background-validation-millis | Non-XA, XA | The frequency, in milliseconds, that background validation will run. |
| blocking-timeout-wait-millis | Non-XA, XA | The maximum time, in milliseconds, to block while waiting for a connection before throwing an exception. Note that this blocks only while waiting for locking a connection, and will never throw an exception if creating a new connection takes an inordinately long time. |
| capacity-decrementer-class | Non-XA, XA | Class defining the policy for decrementing connections in the pool. |
| capacity-decrementer-properties | Non-XA, XA | Properties to be injected in the class defining the policy for decrementing connections in the pool. |
| capacity-incrementer-class | Non-XA, XA | Class defining the policy for incrementing connections in the pool. |
| capacity-incrementer-properties | Non-XA, XA | Properties to be injected in the class defining the policy for incrementing connections in the pool. |
| check-valid-connection-sql | Non-XA, XA | An SQL statement to check validity of a pool connection. This may be called when a managed connection is obtained from the pool. |
| connectable | Non-XA, XA | Enable the use of CMR, which means that a local resource can reliably participate in an XA transaction. |
| connection-listener-class | Non-XA, XA |
Specifies class name extending |
| connection-listener-property | Non-XA, XA |
Properties to be injected into the class specified in the |
| connection-properties | Non-XA Only |
Arbitrary string name/value pair connection properties to pass to the |
| connection-url | Non-XA Only | The JDBC driver connection URL. |
| credential-reference | Non-XA, XA | Credential, from a credential store, to authenticate on datasource. |
| datasource-class | Non-XA Only | The fully-qualified name of the JDBC datasource class. |
| driver-class | Non-XA Only | The fully-qualified name of the JDBC driver class. |
| driver-name | Non-XA, XA | Defines the JDBC driver the datasource should use. It is a symbolic name matching the name of installed driver. If the driver is deployed as JAR, the name is the name of the deployment. |
| elytron-enabled | Non-XA, XA |
Enables Elytron security for handling authentication of connections. The Elytron |
| enabled | Non-XA, XA | Whether the datasource should be enabled. |
| enlistment-trace | Non-XA, XA |
Whether enlistment traces should be recorded. This is |
| exception-sorter-class-name | Non-XA, XA |
An instance of |
| exception-sorter-properties | Non-XA, XA | The exception sorter properties. |
| flush-strategy | Non-XA, XA | Specifies how the pool should be flushed in case of an error. Valid values are:
|
| idle-timeout-minutes | Non-XA, XA |
The maximum time, in minutes, a connection may be idle before being closed. If not specified, the default is |
| initial-pool-size | Non-XA, XA | The initial number of connections a pool should hold. |
| interleaving | XA Only | Whether to enable interleaving for XA connections. |
| jndi-name | Non-XA, XA | The unique JNDI name for the datasource. |
| jta | Non-XA Only | Enable Jakarta Transactions integration. |
| max-pool-size | Non-XA, XA | The maximum number of connections that a pool can hold. |
| mcp | Non-XA, XA |
The |
| min-pool-size | Non-XA, XA | The minimum number of connections that a pool can hold. |
| new-connection-sql | Non-XA, XA | An SQL statement to execute whenever a connection is added to the connection pool. |
| no-recovery | XA Only | Whether the connection pool should be excluded from recovery. |
| no-tx-separate-pool | XA Only |
Whether to create a separate sub-pool for each context. This may be required for some Oracle datasources, which may not allow XA connections to be used both inside and outside of a Jakarta Transactions transaction. Using this option will cause your total pool size to be twice the |
| pad-xid | XA Only | Whether to pad the Xid. |
| password | Non-XA, XA | The password to use when creating a new connection. |
| pool-fair | Non-XA, XA |
Defines if pool should be fair. This setting is part of a |
| pool-prefill | Non-XA, XA | Whether the pool should be prefilled. |
| pool-use-strict-min | Non-XA, XA |
Whether |
| prepared-statements-cache-size | Non-XA, XA | The number of prepared statements per connection in a Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. |
| query-timeout | Non-XA, XA | The timeout for queries, in seconds. The default is no timeout. |
| reauth-plugin-class-name | Non-XA, XA | The fully-qualified class name of the reauthentication plugin implementation to reauthenticate physical connections. |
| reauth-plugin-properties | Non-XA, XA | The properties for the reauthentication plugin. |
| recovery-authentication-context | XA Only |
The Elytron authentication context which defines the |
| recovery-credential-reference | XA Only | Credential, from a credential store, to authenticate on datasource. |
| recovery-elytron-enabled | XA Only |
Enables Elytron security for handling authentication of connections for recovery. The Elytron |
| recovery-password | XA Only | The password to use to connect to the resource for recovery. |
| recovery-plugin-class-name | XA Only | The fully-qualified class name of the recovery plugin implementation. |
| recovery-plugin-properties | XA Only | The properties for the recovery plugin. |
| recovery-security-domain | XA Only | The security domain to use to connect to the resource for recovery. |
| recovery-username | XA Only | The user name to use to connect to the resource for recovery. |
| same-rm-override | XA Only |
Whether the |
| security-domain | Non-XA, XA | The name of a JAAS security-manager which handles authentication. This name correlates to the application-policy/name attribute of the JAAS login configuration. |
| set-tx-query-timeout | Non-XA, XA | Whether to set the query timeout based on the time remaining until transaction timeout. Any configured query timeout will be used if no transaction exists. |
| share-prepared-statements | Non-XA, XA |
Whether JBoss EAP should cache, instead of close or terminate, the underlying physical statement when the wrapper supplied to the application is closed by application code. The default is |
| spy | Non-XA, XA |
Enable spy functionality on the JDBC layer. This logs all JDBC traffic to the datasource. Note that the logging category |
| stale-connection-checker-class-name | Non-XA, XA |
An instance of |
| stale-connection-checker-properties | Non-XA, XA | The stale connection checker properties. |
| statistics-enabled | Non-XA, XA |
Whether runtime statistics are enabled. The default is |
| track-statements | Non-XA, XA | Whether to check for unclosed statements when a connection is returned to a pool and a statement is returned to the prepared statement cache. If false, statements are not tracked. Valid values:
|
| tracking | Non-XA, XA | Whether to track connection handles across transaction boundaries. |
| transaction-isolation | Non-XA, XA |
The
|
| url-delimiter | Non-XA, XA | The delimiter for URLs in connection-url for High Availability (HA) datasources. |
| url-property | XA Only |
The property for the |
| url-selector-strategy-class-name | Non-XA, XA |
A class that implements |
| use-ccm | Non-XA, XA | Enable the cached connection manager. |
| use-fast-fail | Non-XA, XA | If true, fail a connection allocation on the first attempt if the connection is invalid. If false, keep trying until the pool is exhausted. |
| use-java-context | Non-XA, XA | Whether to bind the datasource into global JNDI. |
| use-try-lock | Non-XA, XA |
A timeout value for internal locks. This attempts to obtain the lock for the configured number of seconds, before timing out, rather than failing immediately if the lock is unavailable. Uses |
| user-name | Non-XA, XA | The user name to use when creating a new connection. |
| valid-connection-checker-class-name | Non-XA, XA |
An implementation of |
| valid-connection-checker-properties | Non-XA, XA | The valid connection checker properties. |
| validate-on-match | Non-XA, XA |
Whether connection validation is performed when a connection factory attempts to match a managed connection. This should be used when a client must have a connection validated prior to use. Validate-on-match is typically not to be used with |
| wrap-xa-resource | XA Only |
Whether to wrap the XAResource in an |
| xa-datasource-class | XA Only |
The fully-qualified name of the |
| xa-datasource-properties | XA Only | String name/value pair of XA datasource properties. |
| xa-resource-timeout | XA Only |
If non-zero, this value is passed to the |
| Attribute | Datasource Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| datasource-class-info | Non-XA, XA |
The available properties for the |
A.21. Datasource statistics
This reference provides details about the statistics available for datasources in JBoss EAP. The statistics are divided into the following categories:
A.21.1. Core Pool Statistics
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ActiveCount | The number of active connections. Each of the connections is either in use by an application or available in the pool. |
| AvailableCount | The number of available connections in the pool. |
| AverageBlockingTime | The average time spent blocking on obtaining an exclusive lock on the pool. This value is in milliseconds. |
| AverageCreationTime | The average time spent creating a connection. This value is in milliseconds. |
| AverageGetTime | The average time spent obtaining a connection. This value is in milliseconds. |
| AveragePoolTime | The average time that a connection spent in the pool.This value is in milliseconds. |
| AverageUsageTime | The average time spent using a connection. This value is in milliseconds. |
| BlockingFailureCount | The number of failures trying to obtain a connection. |
| CreatedCount | The number of connections created. |
| DestroyedCount | The number of connections destroyed. |
| IdleCount | The number of connections that are currently idle. |
| InUseCount | The number of connections currently in use. |
| MaxCreationTime | The maximum time it took to create a connection. This value is in milliseconds. |
| MaxGetTime | The maximum time for obtaining a connection. This value is in milliseconds. |
| MaxPoolTime | The maximum time for a connection in the pool. This value is in milliseconds. |
| MaxUsageTime | The maximum time using a connection. This value is in milliseconds. |
| MaxUsedCount | The maximum number of connections used. |
| MaxWaitCount | The maximum number of requests waiting for a connection at the same time. |
| MaxWaitTime | The maximum time spent waiting for an exclusive lock on the pool. This value is in milliseconds. |
| TimedOut | The number of timed out connections. |
| TotalBlockingTime | The total time spent waiting for an exclusive lock on the pool. This value is in milliseconds. |
| TotalCreationTime | The total time spent creating connections. This value is in milliseconds. |
| TotalGetTime | The total time spent obtaining connections. This value is in milliseconds. |
| TotalPoolTime | The total time spent by connections in the pool. This value is in milliseconds. |
| TotalUsageTime | The total time spent using connections. This value is in milliseconds. |
| WaitCount | The number of requests that had to wait to obtain a connection. |
| XACommitAverageTime | The average time for an XAResource commit invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XACommitCount | The number of XAResource commit invocations. |
| XACommitMaxTime | The maximum time for an XAResource commit invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XACommitTotalTime | The total time for all XAResource commit invocations. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAEndAverageTime | The average time for an XAResource end invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAEndCount | The number of XAResource end invocations. |
| XAEndMaxTime | The maximum time for an XAResource end invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAEndTotalTime | The total time for all XAResource end invocations. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAForgetAverageTime | The average time for an XAResource forget invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAForgetCount | The number of XAResource forget invocations. |
| XAForgetMaxTime | The maximum time for an XAResource forget invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAForgetTotalTime | The total time for all XAResource forget invocations. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAPrepareAverageTime | The average time for an XAResource prepare invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAPrepareCount | The number of XAResource prepare invocations. |
| XAPrepareMaxTime | The maximum time for an XAResource prepare invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAPrepareTotalTime | The total time for all XAResource prepare invocations. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XARecoverAverageTime | The average time for an XAResource recover invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XARecoverCount | The number of XAResource recover invocations. |
| XARecoverMaxTime | The maximum time for an XAResource recover invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XARecoverTotalTime | The total time for all XAResource recover invocations. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XARollbackAverageTime | The average time for an XAResource rollback invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XARollbackCount | The number of XAResource rollback invocations. |
| XARollbackMaxTime | The maximum time for an XAResource rollback invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XARollbackTotalTime | The total time for all XAResource rollback invocations. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAStartAverageTime | The average time for an XAResource start invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAStartCount | The number of XAResource start invocations. |
| XAStartMaxTime | The maximum time for an XAResource start invocation. This value is in milliseconds. |
| XAStartTotalTime | The total time for all XAResource start invocations. This value is in milliseconds. |
A.21.2. JDBC Statistics
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PreparedStatementCacheAccessCount | The number of times that the statement cache was accessed. |
| PreparedStatementCacheAddCount | The number of statements added to the statement cache. |
| PreparedStatementCacheCurrentSize | The number of prepared and callable statements currently cached in the statement cache. |
| PreparedStatementCacheDeleteCount | The number of statements discarded from the cache. |
| PreparedStatementCacheHitCount | The number of times that statements from the cache were used. |
| PreparedStatementCacheMissCount | The number of times that a statement request could not be satisfied with a statement from the cache. |
A.22. Transaction manager configuration options
This reference describes the configuration options for transaction management in JBoss EAP.
Attribute names match the management model (for example, when using the management CLI). Note that some attributes might differ in XML representation. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-txn_5_0.xsd for more details.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The default transaction timeout, set to |
|
|
Deprecated in favor of |
|
|
Whether to enable the transaction status manager (TSM) service, used for out-of-process recovery. This option is not supported because running an out-of-process recovery manager contacting the |
|
|
Deprecated in favor of |
|
|
Whether the JDBC action store should drop tables. Defaults to |
|
| An optional prefix for tables used to write transaction logs in the configured JDBC action store. |
|
|
Whether the JDBC communication store should drop tables. Defaults to |
|
| An optional prefix for tables used to write transaction logs in the configured JDBC communication store. |
|
|
Whether the JDBC state store should drop tables. Defaults to |
|
| An optional prefix for tables used to write transaction logs in the configured JDBC state store. |
|
|
JNDI name of the non-XA datasource used. The datasource must be defined in the |
|
|
Whether |
|
|
Whether to use Java Transaction Service (JTS) transactions. Defaults to |
|
|
If a transaction is set to |
|
| A unique identifier for the transaction manager. Required if multiple transaction managers share resources or if JTS-to-JTS communication occurs. If unset, you see a warning at server startup. Must also be unique for Jakarta Transactions if multiple nodes interact with the same resource manager or share an object store. |
|
|
Relative or absolute file system path for the transaction manager object store. If |
|
|
References a global path configuration in the domain model. Defaults to |
|
|
The name of the socket binding if using a socket-based process ID. If |
|
|
For socket-based identifiers, this is the maximum number of socket attempts before failing to find a free port. Defaults to |
|
|
Set to |
|
|
Whether or not the transaction recovery process listens on a network socket. Defaults to |
|
|
Specifies which socket binding is used by the transaction periodic recovery listener if |
|
|
Enables transaction statistics. Defaults to |
|
| Specifies the socket binding for the transaction status manager. Not supported in this context. |
|
|
Deprecated in favor of |
|
|
If |
|
|
Enables Apache ActiveMQ Artemis journaled storage rather than a file-based store. Disabled by default, but can improve I/O performance. Not recommended for JTS transactions if multiple transaction managers are involved. A server restart via the |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Whether to expose all logs. Defaults to |
|
|
Specifies the implementation type of the logging store. Defaults to |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The batch size for this CMR resource. Defaults to |
|
|
Whether to perform immediate cleanup for this CMR resource. Defaults to |
|
| The JNDI name of this CMR resource. |
|
|
The table name for storing XIDs. Defaults to |
A.23. IIOP subsystem attributes
A.23.1. Introduction to the IIOP Subsystem
The IIOP subsystem in JBoss EAP enables interoperability between CORBA-compliant services and Java applications. It manages how secure connections, transactions, and identity propagation are handled for remote invocations, ensuring a unified and flexible environment for distributed computing. By adjusting the attributes detailed below, administrators can fine-tune the IIOP configuration, set security requirements (such as SSL and authentication), and control transaction management behaviors.
Attribute names in this table are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-iiop-openjdk_3_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| add-component-via-interceptor | Indicates whether SSL components should be added by an IOR interceptor. Deprecated. |
| auth-method |
The authentication method. Valid values are |
| authentication-context |
The name of the authentication context used when the security initializer is set to |
| caller-propagation |
Indicates whether the caller identity should be propagated in the SAS context. Valid values are |
| client-requires |
Value that indicates the client SSL required parameters. Valid values are |
| client-requires-ssl | Indicates whether IIOP connections from the server require SSL. |
| client-ssl-context | The name of the SSL context used to create client-side SSL sockets. |
| client-supports |
Value that indicates the client SSL supported parameters. Valid values are |
| confidentiality |
Indicates whether the transport must require confidentiality protection or not. Valid values are |
| detect-misordering |
Indicates whether the transport must require misordering detection or not. Valid values are |
| detect-replay |
Indicates whether the transport must require replay detection or not. Valid values are |
| export-corbaloc |
Indicates whether the root context should be exported as |
| giop-version | The GIOP version to be used. |
| high-water-mark |
TCP connection cache parameter. Each time the number of connections exceeds this value, the ORB tries to reclaim connections. The number of reclaimed connections is specified by the |
| integrity |
Indicates whether the transport must require integrity protection or not. Valid values are |
| number-to-reclaim |
TCP connection cache parameter. Each time the number of connections exceeds the |
| persistent-server-id | Persistent ID of the server. Persistent object references are valid across many activations of the server and they identify it using this property. As a result of that, many activations of the same server should have this property set to the same value, and different server instances running on the same host should have different server IDs. |
| properties | A list of generic key/value properties. |
| realm | The authentication service realm name. |
| required | Indicates whether authentication is required. |
| root-context | The naming service root context. |
| security |
Indicates whether the security interceptors are to be installed. Valid values are |
| security-domain | The name of the security domain that holds the keystores and truststores that will be used to establish SSL connections. |
| server-requires |
Value that indicates the server SSL required parameters. Valid values are |
| server-requires-ssl | Indicates whether IIOP connections to the server require SSL. |
| server-ssl-context | The name of the SSL context used to create server-side SSL sockets. |
| server-supports |
Value that indicates the server SSL supported parameters. Valid values are |
| socket-binding | The name of the socket binding configuration that specifies the ORB port. |
| ssl-socket-binding | The name of the socket binding configuration that specifies the ORB SSL port. |
| support-ssl | Indicates whether SSL is supported. |
| transactions |
Indicates whether the transactions interceptors are to be installed or not. Valid values are |
| trust-in-client |
Indicates if the transport must require trust in client to be established. Valid values are |
| trust-in-target |
Indicates if the transport must require trust in target to be established. Valid values are |
A.24. Resource Adapter Attributes
The following tables describe the resource adapter attributes.
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-resource-adapters_5_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| archive | The resource adapter archive. |
| beanvalidationgroups | The bean validation groups that should be used. |
| bootstrap-context | The unique name of the bootstrap context that should be used. |
| config-properties | Custom defined config properties. |
| module | The module from which the resource adapter will be loaded. |
| statistics-enabled | Whether runtime statistics are enabled or not. |
| transaction-support |
The transaction support level of the resource adapter. Valid values are |
| wm-elytron-security-domain | Defines the name of the Elytron security domain that should be used. |
| wm-security |
Toggle on/off |
| wm-security-default-groups |
A default groups list that should be added to the used |
| wm-security-default-principal |
A default principal name that should be added to the used |
| wm-security-domain | The name of the security domain that should be used. |
| wm-security-mapping-groups | List of groups mappings. |
| wm-security-mapping-required | Defines if a mapping is required for security credentials. |
| wm-security-mapping-users | List of user mappings. |
If your resource adapter is using bootstrap-context along with a work manager that has elytron-enabled set to true, you must use the wm-elytron-security-domain attribute instead of the wm-security-domain attribute for security domain specification.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| class-name | The fully qualified class name of an administration object. |
| enabled | Specifies if the administration object should be enabled. |
| jndi-name | The JNDI name for the administration object. |
| use-java-context | Setting this to false will bind the object into global JNDI. |
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| allocation-retry | Indicates the number of times that allocating a connection should be tried before throwing an exception. |
| allocation-retry-wait-millis | The amount of time, in milliseconds, to wait between retrying to allocate a connection. |
| authentication-context |
The Elytron authentication context which defines the |
| authentication-context-and-application |
Indicates that either application-supplied parameters, such as from |
| background-validation | Specifies that connections should be validated on a background thread versus being validated prior to use. Changing this value requires a server restart. |
| background-validation-millis | The amount of time, in milliseconds, that background validation will run. Changing this value requires a server restart. |
| blocking-timeout-wait-millis | The maximum time, in milliseconds, to block while waiting for a connection before throwing an exception. Note that this blocks only while waiting for locking a connection, and will never throw an exception if creating a new connection takes an inordinately long time. |
| capacity-decrementer-class | Class defining the policy for decrementing connections in the pool. |
| capacity-decrementer-properties | Properties to inject in class defining the policy for decrementing connections in the pool. |
| capacity-incrementer-class | Class defining the policy for incrementing connections in the pool. |
| capacity-incrementer-properties | Properties to inject in class defining the policy for incrementing connections in the pool. |
| class-name | The fully qualified class name of a managed connection factory or admin object. |
| connectable | Enable the use of CMR. This feature means that a local resource can reliably participate in an XA transaction. |
| elytron-enabled |
Enables Elytron security for handling authentication of connections. The Elytron |
| enabled | Specifies if the resource adapter should be enabled. |
| enlistment | Specifies if lazy enlistment should be used if supported by the resource adapter. |
| enlistment-trace |
Specifies if JBoss EAP/IronJacamar should record enlistment traces. This is |
| flush-strategy | Specifies how the pool should be flushed in case of an error. Valid values are:
|
| idle-timeout-minutes |
The maximum time, in minutes, a connection may be idle before being closed. The actual maximum time depends also on the |
| initial-pool-size | The initial number of connections a pool should hold. |
| interleaving | Specifies whether to enable interleaving for XA connections. |
| jndi-name | The JNDI name for the connection factory. |
| max-pool-size | The maximum number of connections for a pool. No more connections will be created in each sub-pool. |
| mcp |
The |
| min-pool-size | The minimum number of connections for a pool. |
| no-recovery | Specifies if the connection pool should be excluded from recovery. |
| no-tx-separate-pool | Oracle does not like XA connections getting used both inside and outside a Jakarta Transactions transaction. To workaround the problem you can create separate sub-pools for the different contexts. |
| pad-xid | Specifies whether the Xid should be padded. |
| pool-fair | Specifies if pool use should be fair. |
| pool-prefill | Specifies if the pool should be prefilled. Changing this value requires a server restart. |
| pool-use-strict-min |
Specifies if the |
| recovery-authentication-context |
The Elytron authentication context used for recovery. If no |
| recovery-credential-reference | Credential, from a credential store, to authenticate on recovery of the connection. |
| recovery-elytron-enabled |
Indicates that an Elytron authentication context will be used for recovery. The default is |
| recovery-password | The password used for recovery. |
| recovery-plugin-class-name | The fully qualified class name of the recovery plugin implementation. |
| recovery-plugin-properties | The properties for the recovery plugin. |
| recovery-security-domain | The security domain used for recovery. |
| recovery-username | The user name used for recovery. |
| same-rm-override |
Unconditionally set whether |
| security-application |
Indicates that application-supplied parameters, such as from |
| security-domain |
The security domain which defines the |
| security-domain-and-application |
Indicates that either application-supplied parameters, such as from |
| sharable | Enable the use of sharable connections, which allows lazy association to be enabled if supported. |
| tracking | Specifies if IronJacamar should track connection handles across transaction boundaries. |
| use-ccm | Enable the use of a cached connection manager. |
| use-fast-fail |
When set to |
| use-java-context |
Setting this to |
| validate-on-match | Specifies if connection validation should be done when a connection factory attempts to match a managed connection. This is typically exclusive to the use of background validation. |
| wrap-xa-resource |
Specifies whether |
| xa-resource-timeout |
The value is passed to |
A.25. Resource Adapter Statistics
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ActiveCount | The number of active connections. Each of the connections is either in use by an application or available in the pool |
| AvailableCount | The number of available connections in the pool. |
| AverageBlockingTime | The average time spent blocking on obtaining an exclusive lock on the pool. The value is in milliseconds. |
| AverageCreationTime | The average time spent creating a connection. The value is in milliseconds. |
| CreatedCount | The number of connections created. |
| DestroyedCount | The number of connections destroyed. |
| InUseCount | The number of connections currently in use. |
| MaxCreationTime | The maximum time it took to create a connection. The value is in milliseconds. |
| MaxUsedCount | The maximum number of connections used. |
| MaxWaitCount | The maximum number of requests waiting for a connection at the same time. |
| MaxWaitTime | The maximum time spent waiting for an exclusive lock on the pool. |
| TimedOut | The number of timed out connections. |
| TotalBlockingTime | The total time spent waiting for an exclusive lock on the pool. The value is in milliseconds. |
| TotalCreationTime | The total time spent creating connections. The value is in milliseconds. |
| WaitCount | The number of requests that had to wait for a connection. |
A.26. Undertow Subsystem Attributes
This reference provides details about the attributes of the various elements of the undertow subsystem in Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform.
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-undertow_4_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| default-security-domain | other | The default security domain used by web deployments. |
| default-server | default-server | The default server to use for deployments. |
| default-servlet-container | default | The default servlet container to use for deployments. |
| default-virtual-host | default-host | The default virtual host to use for deployments. |
| instance-id | ${jboss.node.name} | The cluster instance ID. |
| obfuscate-session-route | true | Whether the instance-id value is obfuscated during server routing. The obfuscated server route does not change across server restarts, unless there is a change in the instance-id value. |
| statistics-enabled | false | Whether statistics are enabled. |
Application Security Domain Attributes
The application security domain attributes has the following structure:
application-security-domain Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| enable-jacc | false | Enable authorization using Java Authorization Contract for Containers. |
| enable-jaspi | true | Enable {JAAS} for the associated deployments. |
| http-authentication-factory | The HTTP authentication factory to be used by deployments that reference the mapped security domain. | |
| integrated-jaspi | true |
Whether |
| override-deployment-config | false | Whether the authentication configuration in the deployment should be overridden by the factory. |
| referencing-deployments | The deployments currently referencing this mapping. | |
| security-domain |
The |
single-sign-on Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| client-ssl-context | Reference to the SSL context used to secure back-channel logout connection. | |
| cookie-name | JSESSIONIDSSO | Name of the cookie. |
| credential-reference | The credential reference to decrypt the private key entry. | |
| domain | The cookie domain that will be used. | |
| http-only | false | Set cookie httpOnly attribute. |
| key-alias | Alias of the private key entry used for signing and verifying back-channel logout connection. | |
| key-store | Reference to keystore containing a private key entry. | |
| path | / | Cookie path. |
| secure | false | Set cookie secure attribute. |
Buffer Cache Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| buffer-size | 1024 | The size of the buffers. Smaller buffers allow space to be utilized more effectively. |
| buffers-per-region | 1024 | The numbers of buffers per region. |
| max-regions | 10 | The maximum number of regions. This controls the maximum amount of memory that can be used for caching. |
Byte Buffer Pool Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| buffer-size | The size, in bytes, of each buffer slice. If not specified, the size is set based on the available RAM of your system:
For performance tuning advice on this attribute, see Configuring Buffer Pools in the JBoss EAP Performance tuning for JBoss EAP. | |
| direct | Boolean value that denotes if this buffer is a direct or heap pool. If not specified, the value is set based on the available RAM of your system:
Note that direct pools also have a corresponding heap pool. | |
| leak-detection-percent | 0 | The percentage of buffers that should be allocated with a leak detector. |
| max-pool-size | The maximum number of buffers to keep in the pool. Buffers will still be allocated above this limit, but will not be retained if the pool is full. | |
| thread-local-cache-size | 12 | The size of the per-thread cache. This is a maximum size, the cache will use smart sizing to only keep buffers on the thread if the thread is actually allocating buffers. |
Servlet Container Attributes
The servlet container component has the following structure:
servlet-container Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allow-non-standard-wrappers | false | Whether request and response wrappers that do not extend the standard wrapper classes can be used. |
| default-buffer-cache | default | The buffer cache to use for caching static resources. |
| default-cookie-version | 0 | The default cookie version to use for cookies created by the application. |
| default-encoding | Default encoding to use for all deployed applications. | |
| default-session-timeout | 30 | The default session timeout in minutes for all applications deployed in the container. |
| directory-listing | If directory listing should be enabled for default servlets. | |
| disable-caching-for-secured-pages | true | Whether to set headers to disable caching for secured paged. Disabling this can cause security problems, as sensitive pages may be cached by an intermediary. |
| disable-file-watch-service | false |
If set to |
| disable-session-id-reuse | false |
If set to |
| eager-filter-initialization | false | Whether to call filter init() on deployment start rather than when first requested. |
| ignore-flush | false | Ignore flushes on the servlet output stream. In most cases these just hurt performance for no good reason. |
| max-sessions | The maximum number of sessions that can be active at one time. | |
| proactive-authentication | true |
Whether proactive authentication should be used. If this is |
| session-id-length | 30 | Longer session ID’s are more secure. This value specifies the length of the generated session ID in bytes. The system encodes the generated session ID as a Base64 string and provides the result to the client as a session ID cookie. As a result of this processing, the server sends to the client a cookie value that is approximately 33% larger than the session ID that it originally generated. For example, a session ID length of 30 results in a cookie value length of 40. |
| stack-trace-on-error | local-only |
If an error page with the stack trace should be generated on error. Values are |
| use-listener-encoding | false | Use encoding defined on listener. |
mime-mapping Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| value | The mime type for this mapping. |
crawler-session-management Attributes
Configures special session handling for crawler bots.
When using the management CLI to manage the crawler-session-management element, it is available under settings in the servlet-container element. For example:
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=crawler-session-management:add /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=crawler-session-management:read-resource
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=crawler-session-management:add
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=crawler-session-management:read-resource| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| session-timeout | The session timeout in seconds for sessions that are owned by crawlers. | |
| user-agents | Regular expression that is used to match the user agent of a crawler. |
jsp Attributes
When using the management CLI to manage the jsp element, it is available under settings in the servlet-container element. For example:
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=jsp:read-resource
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=jsp:read-resource| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| check-interval | 0 | Check interval for Jakarta Server Pages updates using a background thread. This has no effect for most deployments where Jakarta Server Pages change notifications are handled using the file system notification API. This only takes effect if the file watch service is disabled. |
| development | false | Enable development mode which enables reloading Jakarta Server Pages on-the-fly. |
| disabled | false | Enable the Jakarta Server Pages container. |
| display-source-fragment | true | When a runtime error occurs, attempts to display corresponding Jakarta Server Pages source fragment. |
| dump-smap | false | Write SMAP data to a file. |
| error-on-use-bean-invalid-class-attribute | false | Enable errors when using a bad class in useBean. |
| generate-strings-as-char-arrays | false | Generate String constants as char arrays. |
| java-encoding | UTF8 | Specify the encoding used for Java sources. |
| keep-generated | true | Keep the generated servlets. |
| mapped-file | true | Map to the Jakarta Server Pages source. |
| modification-test-interval | 4 | Minimum amount of time between two tests for updates, in seconds. |
| optimize-scriptlets | false | If Jakarta Server Pages scriptlets should be optimized to remove string concatenation. |
| recompile-on-fail | false | Retry failed Jakarta Server Pages compilations on each request. |
| scratch-dir | Specify a different work directory. | |
| smap | true | Enable SMAP. |
| source-vm | 1.8 | Source VM level for compilation. |
| tag-pooling | true | Enable tag pooling. |
| target-vm | 1.8 | Target VM level for compilation. |
| trim-spaces | false | Trim some spaces from the generated servlet. |
| x-powered-by | true | Enable advertising the Jakarta Server Pages engine in x-powered-by. |
persistent-sessions Attributes
When using the management CLI to manage the persistent-sessions element, it is available under settings in the servlet-container element. For example:
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=persistent-sessions:add /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=persistent-sessions:read-resource
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=persistent-sessions:add
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=persistent-sessions:read-resource| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| path | The path to the persistent session data directory. If this is null, sessions will be stored in memory. | |
| relative-to | The directory the path is relative to. |
session-cookie Attributes
When using the management CLI to manage the session-cookie element, it is available under settings in the servlet-container element. For example:
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=session-cookie:add /subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=session-cookie:read-resource
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=session-cookie:add
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=session-cookie:read-resource| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| comment | Cookie comment. | |
| domain | Cookie domain. | |
| http-only | Whether the cookie is http-only. | |
| max-age | Maximum age of the cookie. | |
| name | Name of the cookie. | |
| secure | Whether the cookie is secure. |
websockets Attributes
When using the management CLI to manage the websockets element, it is available under settings in the servlet-container element. For example:
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=websockets:read-resource
/subsystem=undertow/servlet-container=default/setting=websockets:read-resource| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| buffer-pool | default | The buffer pool to use for websocket deployments. |
| deflater-level | 0 | Configures the level of compression of the DEFLATE algorithm. |
| dispatch-to-worker | true |
Whether callbacks should be dispatched to a worker thread. If this is |
| per-message-deflate | false | Enables websocket’s per-message compression extension. |
| worker | default | The worker to use for websocket deployments. |
welcome-file Attributes
Defines a welcome file and has no options.
Filter Attributes
These components can be found at /subsystem=undertow/configuration=filter.
custom-filter Filters
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| class-name | Class name of HttpHandler. | |
| module | Module name where class can be loaded from. | |
| parameters | Filter parameters. |
error-page Filters
The error pages
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| code | Error page code. | |
| path | Error page path. |
expression-filter Filters
A filter parsed from the Undertow expression language.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| expression | The expression that defines the filter. | |
| module | Module to use to load the filter definitions. |
gzip Filters
Defines the gzip filter and has no attributes.
mod-cluster Filters
The mod-cluster filter component has the following structure:
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| advertise-frequency | 10000 | The frequency in milliseconds that mod_cluster advertises itself on the network. |
| advertise-path | / | The path that mod_cluster is registered under. |
| advertise-protocol | http | The protocol that is in use. |
| advertise-socket-binding | The multicast group that is used to advertise. | |
| broken-node-timeout | 60000 | The amount of time that must elapse before a broken node is removed from the table. |
| cached-connections-per-thread | 5 | The number of connections that will be kept alive indefinitely. |
| connection-idle-timeout | 60 |
The amount of time a connection can be idle before it will be closed. Connections will not time out once the pool size is down to the configured minimum, which is configured by |
| connections-per-thread | 10 | The number of connections that will be maintained to back-end servers, per IO thread. |
| enable-http2 | false | Whether the load balancer should attempt to upgrade back-end connections to HTTP/2. If HTTP/2 is not supported, HTTP or HTTPS will be used as normal. |
| failover-strategy | LOAD_BALANCED | The attribute that determines how a failover node is chosen, in the event that the node to which a session has affinity is not available. |
| health-check-interval | 10000 | The frequency of health check pings to back-end nodes. |
| http2-enable-push | true | Whether push should be enabled for HTTP/2 connections. |
| http2-header-table-size | 4096 | The size of the header table used for HPACK compression, in bytes. This amount of memory will be allocated per connection for compression. Larger values use more memory but may give better compression. |
| http2-initial-window-size | 65535 | The flow control window size, in bytes, that controls how quickly the client can send data to the server. |
| http2-max-concurrent-streams | The maximum number of HTTP/2 streams that can be active at any time on a single connection. | |
| http2-max-frame-size | 16384 | The maximum HTTP/2 frame size, in bytes. |
| http2-max-header-list-size | The maximum size, in bytes, of request headers the server is prepared to accept. | |
| management-access-predicate |
A predicate that is applied to incoming requests to determine if they can perform mod cluster management commands. Provides additional security on top of what is provided by limiting management to requests that originate from the | |
| management-socket-binding | The socket binding of the mod_cluster management port. When using mod_cluster two HTTP listeners should be defined, a public one to handle requests, and one bound to the internal network to handle mod cluster commands. This socket binding should correspond to the internal listener, and should not be publicly accessible. | |
| max-ajp-packet-size | 8192 | The maximum size, in bytes, for AJP packets. Increasing this will allow AJP to work for requests and responses that have a large amount of headers. This must be the same between load balancers and backend servers. |
| max-request-time | -1 | The maximum amount of time that a request to a back-end node can take before it is killed. |
| max-retries | 1 | The number of times that you can attempt to retry a request will be made, if the request fails. Note If a request is not considered idempotent, it will only be retried if the proxy can be sure that it was not sent to the backend server. |
| request-queue-size | 10 | The number of requests that can be queued if the connection pool is full before requests are rejected with a 503. |
| security-key | The security key that is used for the mod_cluster group. All members must use the same security key. | |
| security-realm |
The security realm that provides the SSL configuration. Deprecated: Use the | |
| ssl-context |
The reference to the | |
| use-alias | false | Whether an alias check is performed. |
| worker | default | The XNIO worker that is used to send the advertise notifications. |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| max-attempts | The number of attempts to send the request to a back-end server. | |
| sticky-session | If sticky sessions are enabled. | |
| sticky-session-cookie | The session cookie name. | |
| sticky-session-force |
If this is | |
| sticky-session-path | The path of the sticky session cookie. | |
| sticky-session-remove | Remove the session cookie if the request cannot be routed to the correct host. | |
| wait-worker | The number of seconds to wait for an available worker. |
load-balancing-group Attributes
Defines a load balancing group and has no options.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| aliases | The nodes aliases. | |
| cache-connections | The number of connections to keep alive indefinitely. | |
| elected | The elected count. | |
| flush-packets | If received data should be immediately flushed. | |
| load | The current load of this node. | |
| load-balancing-group | The load balancing group this node belongs to. | |
| max-connections | The maximum number of connections per IO thread. | |
| open-connections | The current number of open connections. | |
| ping | The nodes ping. | |
| queue-new-requests | If a request is received and there is no worker immediately available should it be queued. | |
| read | The number of bytes read from the node. | |
| request-queue-size | The size of the request queue. | |
| status | The current status of this node. | |
| timeout | The request timeout. | |
| ttl |
The time connections will stay alive with no requests before being closed, if the number of connections is larger than | |
| uri | The URI that the load balancer uses to connect to the node. | |
| written | The number of bytes transferred to the node. |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| requests | The number of requests against this context. | |
| status | The status of this context. |
request-limit Filters
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| max-concurrent-requests | Maximum number of concurrent requests. | |
| queue-size | Number of requests to queue before they start being rejected. |
response-header Filters
Response header filter allows you to add custom headers.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| header-name | The header name. | |
| header-value | The header value. |
rewrite Filters
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| redirect | false | Whether a redirect will be done instead of a rewrite. |
| target | The expression that defines the target. If you are redirecting to a constant target put single quotes around the value. |
Handler Attributes
These components can be found at /subsystem=undertow/configuration=handler.
file Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cache-buffer-size | 1024 | Size of the buffers. |
| cache-buffers | 1024 | Number of buffers. |
| case-sensitive | true |
Whether to use case-sensitive file handling. Note that setting this to |
| directory-listing | false | Whether to enable directory listing. |
| follow-symlink | false | Whether to enable following symbolic links. |
| path | Path on the file system from where file handler will serve resources. | |
| safe-symlink-paths | Paths that are safe to be targets of symbolic links. |
Using WebDAV for Static Resources
Initially, JBoss EAP used the JBoss Web subsystem, WebDAV could be employed through the WebdavServlet to host static resources and enable additional HTTP methods for accessing and manipulating files. With Undertow serving as the integrated web layer in JBoss EAP 8.0, the subsystem now provides a mechanism to serve static files through a file handler. However, it does not include WebDAV support. If you require WebDAV functionality, consider implementing a custom WebDAV servlet for your JBoss EAP 8.0 environment.
reverse-proxy attributes
The reverse-proxy handler component has the following structure:
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cached-connections-per-thread | 5 | The number of connections that will be kept alive indefinitely. |
| connection-idle-timeout | 60 | The amount of time a connection can be idle before it will be closed. Connections will not time out once the pool size is down to the configured minimum (as configured by cached-connections-per-thread). |
| connections-per-thread | 40 | The number of connections that will be maintained to back-end servers, per IO thread. |
| max-request-time | -1 | The maximum time that a proxy request can be active for, before being killed. Defaults to unlimited. |
| max-retries | 1 | The number of times that an attempt to retry a request will be made, if the request fails. Note If a request is not considered idempotent, it will only be retried if the proxy can be sure that it was not sent to the backend server. |
| problem-server-retry | 30 | Time in seconds to wait before attempting to reconnect to a server that is down. |
| request-queue-size | 10 | The number of requests that can be queued if the connection pool is full before requests are rejected with a 503. |
| session-cookie-names | JSESSIONID | Comma-separated list of session cookie names. Generally this will just be JSESSIONID. |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| enable-http2 | false |
If |
| instance-id | The instance ID, or JVM route, that will be used to enable sticky sessions. | |
| outbound-socket-binding | Outbound socket binding for this host. | |
| path | / | Optional path if host is using non root resource. |
| scheme | http | The kind of scheme that is used. |
| security-realm | The security realm that provides the SSL configuration for the connection to the host. | |
| ssl-context | Reference to the SSLContext to be used by this handler. |
Server Attributes
The server component has the following structure:
server Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| default-host | default-host | The server’s default virtual host. |
| servlet-container | default | The server’s default servlet container. |
ajp-listener Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allow-encoded-slash | false |
If a request comes in with encoded characters, for example |
| allow-equals-in-cookie-value | false | Whether to allow non-escaped equals characters in unquoted cookie values. Unquoted cookie values may not contain equals characters. If present the value ends before the equals sign. The remainder of the cookie value will be dropped. |
| allow-unescaped-characters-in-url | false |
Whether to allow non-escaped characters in a URL. If set to |
| always-set-keep-alive | true | Whether a Connection: keep-alive header will be added to responses, even when it is not strictly required by the specification. |
| buffer-pipelined-data | false | Whether to buffer pipelined requests. |
| buffer-pool | default | The AJP listener’s buffer pool. |
| decode-url | true |
If this is |
| disallowed-methods | ["TRACE"] | A comma-separated list of HTTP methods that are not allowed. |
| enabled | true | If the listener is enabled. Deprecated: Enabled attributes can cause problems in enforcement of configuration consistency. |
| max-ajp-packet-size | 8192 | The maximum supported size of AJP packets. If this is modified it has to be increased on the load balancer and the back-end server. |
| max-buffered-request-size | 16384 | Maximum size of a buffered request, in bytes. Requests are not usually buffered, the most common case is when performing SSL renegotiation for a POST request, and the post data must be fully buffered in order to perform the renegotiation. |
| max-connections |
The maximum number of concurrent connections. If no value is set in the server configuration, the limit for the number of concurrent connections is | |
| max-cookies | 200 | The maximum number of cookies that will be parsed. This is used to protect against hash vulnerabilities. |
| max-header-size | 1048576 | The maximum size in bytes of an HTTP request header. |
| max-headers | 200 | The maximum number of headers that will be parsed. This is used to protect against hash vulnerabilities. |
| max-parameters | 1000 | The maximum number of parameters that will be parsed. This is used to protect against hash vulnerabilities. This applies to both query parameters, and to POST data, but is not cumulative. As a result, you can potentially have max parameters * 2 total parameters. |
| max-post-size | 10485760 | The maximum size of a post that will be accepted |
| no-request-timeout | 60000 | The length of time in milliseconds that the connection can be idle before it is closed by the container. |
| read-timeout |
Configure a read timeout for a socket, in milliseconds. If the given amount of time elapses without a successful read taking place, the socket’s next read will throw a | |
| receive-buffer | The receive buffer size. | |
| record-request-start-time | false | Whether to record the request start time, to allow for request time to be logged. This has a small but measurable performance impact. |
| redirect-socket | If this listener is supporting non-SSL requests, and a request is received for which a matching requires SSL transport, whether to automatically redirect the request to the socket binding port specified here. | |
| request-parse-timeout | The maximum amount of time in milliseconds that can be spent parsing the request. | |
| resolve-peer-address | false | Enables host DNS lookup. |
| scheme | The listener scheme, can be HTTP or HTTPS. By default the scheme will be taken from the incoming AJP request. | |
| secure | false |
If this is |
| send-buffer | The send buffer size. | |
| socket-binding | The AJP listener’s socket binding. | |
| tcp-backlog | Configure a server with the specified backlog. | |
| tcp-keep-alive | Configure a channel to send TCP keep-alive messages in an implementation-dependent manner. | |
| url-charset | UTF-8 | URL charset. |
| worker | default | The listener’s XNIO worker. |
| write-timeout |
Configure a write timeout for a socket, in milliseconds. If the given amount of time elapses without a successful write taking place, the socket’s next write will throw a |
host Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| alias | Comma-separated list of aliases for the host. | |
| default-response-code | 404 | If set, this will be response code sent back in case requested context does not exist on server. |
| default-web-module | ROOT.war | Default web module. |
| disable-console-redirect | false |
If set to |
| queue-requests-on-start | true |
If set to |
filter-ref Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| predicate | Predicates provide a simple way of making a true/false decision based on an exchange. Many handlers have a requirement that they be applied conditionally, and predicates provide a general way to specify a condition. | |
| priority | 1 |
Defines filter order. A lower number instructs the server to be included earlier in the handler chain than others above the same context. Values range from |
location Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| handler | Default handler for this location. |
filter-ref Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| predicate | Predicates provide a simple way of making a true/false decision based on an exchange. Many handlers have a requirement that they be applied conditionally, and predicates provide a general way to specify a condition. | |
| priority | 1 | Defines filter order. It should be set to 1 or more. A higher number instructs the server to be included earlier in the handler chain than others under the same context. |
access-log Attributes
When using the management CLI to manage the access-log element, it is available under settings in the host element. For example:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=access-log:add /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=access-log:read-resource
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=access-log:add
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=access-log:read-resource| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| directory | ${jboss.server.log.dir} | The directory in which to save logs. |
| extended | false | Whether the log uses the extended log file format. |
| pattern | common | The access log pattern. For details about the options available for this attribute, see Provided Undertow Handlers in the JBoss EAP Development Guide. Note
If you set the /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/http-listener=default:write-attribute(name=record-request-start-time,value=true) |
| predicate | Predicate that determines whether the request should be logged. | |
| prefix | access_log. | Prefix for the log file name. |
| relative-to | The directory the path is relative to. | |
| rotate | true | Whether to rotate the access log every day. |
| suffix | log | Suffix for the log file name. |
| use-server-log | false | Whether the log should be written to the server log, rather than a separate file. |
| worker | default | Name of the worker to use for logging. |
console-access-log Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| attributes | {remote-host={},remote-user={},date-time={},request-line={},response-code={},bytes-sent={}} | Specifies log data to include in the console access log output, or customizations to default data. |
| include-host-name | false |
Specifies whether to include the host name in the JSON structured output. If set to |
| metadata | Specifies custom metadata to include in console access log output. | |
| predicate | Predicate that determines whether the request should be logged. | |
| worker | default | Name of the worker to use for logging. |
http-invoker Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| http-authentication-factory | The HTTP authentication factory to use for authentication. | |
| path | wildfly-services | The path that the services are installed under. |
| security-realm | The legacy security realm to use for authentication. |
single-sign-on Attributes
When using the management CLI to manage the single-sign-on element, it is available under settings in the host element. For example:
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=single-sign-on:add /subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=single-sign-on:read-resource
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=single-sign-on:add
/subsystem=undertow/server=default-server/host=default-host/setting=single-sign-on:read-resource
By default, when running the ha profile in JBoss EAP 8.0, each host maintains its own Infinispan cache that stores session and SSO cookie information. This cache is based on the default cache of the web cache container. JBoss EAP also manages the propagation of authentication details among all hosts, ensuring consistent session and single sign-on data across the cluster.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookie-name | JSESSIONIDSSO | Name of the cookie. |
| domain | The cookie domain that will be used. | |
| http-only | false | Set cookie httpOnly attribute. |
| path | / | Cookie path. |
| secure | false | Set cookie secure attribute. |
http-listener Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allow-encoded-slash | false |
If a request comes in with encoded characters, for example |
| allow-equals-in-cookie-value | false | Whether to allow non-escaped equals characters in unquoted cookie values. Unquoted cookie values may not contain equals characters. If present the value ends before the equals sign. The remainder of the cookie value will be dropped. |
| allow-unescaped-characters-in-url | false |
Whether to allow non-escaped characters in a URL. If set to |
| always-set-keep-alive | true | Whether a 'Connection: keep-alive' header will be added to responses, even when it is not strictly required by the specification. |
| buffer-pipelined-data | false | Whether to buffer pipelined requests. |
| buffer-pool | default | The listener’s buffer pool. |
| certificate-forwarding | false |
Whether certificate forwarding should be enabled. If this is enabled then the listener will take the certificate from the |
| decode-url | true | Whether the parser will decode the URL and query parameters using the selected character encoding, defaulting to UTF-8. If this is false they will not be decoded. This will allow a later handler to decode them into whatever charset is desired. |
| disallowed-methods | ["TRACE"] | A comma-separated list of HTTP methods that are not allowed. |
| enable-http2 | false | Whether to enable HTTP/2 support for this listener. |
| enabled | true | Whether the listener is enabled. Deprecated: Enabled attributes can cause problems in enforcement of configuration consistency. |
| http2-enable-push | true | Whether server push is enabled for this connection. |
| http2-header-table-size | 4096 | The size, in bytes, of the header table used for HPACK compression. This amount of memory will be allocated per connection for compression. Larger values use more memory but may give better compression. |
| http2-initial-window-size | 65535 | The flow control window size, in bytes, that controls how quickly the client can send data to the server. |
| http2-max-concurrent-streams | The maximum number of HTTP/2 streams that can be active at any time on a single connection. | |
| http2-max-frame-size | 16384 | The maximum HTTP/2 frame size, in bytes. |
| http2-max-header-list-size | The maximum size of request headers the server is prepared to accept. | |
| max-buffered-request-size | 16384 | Maximum size of a buffered request, in bytesRequests are not usually buffered, the most common case is when performing SSL renegotiation for a POST request, and the post data must be fully buffered in order to perform the renegotiation. |
| max-connections |
The maximum number of concurrent connections. If no value is set in the server configuration, the limit for the number of concurrent connections is | |
| max-cookies | 200 | The maximum number of cookies that will be parsed. This is used to protect against hash vulnerabilities. |
| max-header-size | 1048576 | The maximum size in bytes of an HTTP request header. |
| max-headers | 200 | The maximum number of headers that will be parsed. This is used to protect against hash vulnerabilities. |
| max-parameters | 1000 | The maximum number of parameters that will be parsed. This is used to protect against hash vulnerabilities. This applies to both query parameters, and to POST data, but is not cumulative. As a result, you can potentially have max parameters * 2 total parameters). |
| max-post-size | 10485760 | The maximum size of a post that will be accepted. |
| no-request-timeout | 60000 | The length of time in milliseconds that the connection can be idle before it is closed by the container. |
| proxy-address-forwarding | false | Whether to enable x-forwarded-host and similar headers and set a remote IP address and host name. |
| proxy-protocol | false |
Whether to use the PROXY protocol to transport connection information. If set to |
| read-timeout |
Configure a read timeout for a socket, in milliseconds. If the given amount of time elapses without a successful read taking place, the socket’s next read will throw a | |
| receive-buffer | The receive buffer size. | |
| record-request-start-time | false | Whether to record the request start time, to allow for request time to be logged. This has a small but measurable performance impact. |
| redirect-socket | If this listener is supporting non-SSL requests, and a request is received for which a matching requires SSL transport, whether to automatically redirect the request to the socket binding port specified here. | |
| request-parse-timeout | The maximum amount of time in milliseconds that can be spent parsing the request. | |
| require-host-http11 | false |
It requires all HTTP/1.1 requests to have a |
| resolve-peer-address | false | Enables host DNS lookup. |
| secure | false |
If this is |
| send-buffer | The send buffer size. | |
| socket-binding | The listener’s socket binding | |
| tcp-backlog | Configure a server with the specified backlog. | |
| tcp-keep-alive | Configure a channel to send TCP keep-alive messages in an implementation-dependent manner. | |
| url-charset | UTF-8 | URL charset. |
| worker | default | The listener’s XNIO worker. |
| write-timeout |
Configure a write timeout for a socket, in milliseconds. If the given amount of time elapses without a successful write taking place, the socket’s next write will throw a |
https-listener Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allow-encoded-slash | false |
If a request comes in with encoded characters, for example |
| allow-equals-in-cookie-value | false | Whether to allow non-escaped equals characters in unquoted cookie values. Unquoted cookie values may not contain equals characters. If present the value ends before the equals sign. The remainder of the cookie value will be dropped. |
| allow-unescaped-characters-in-url | false |
Whether to allow non-escaped characters in a URL. If set to |
| always-set-keep-alive | true | Whether a Connection: keep-alive header will be added to responses, even when it is not strictly required by the specification. |
| buffer-pipelined-data | false | Whether to buffer pipelined requests. |
| buffer-pool | default | The listener’s buffer pool. |
| certificate-forwarding | false |
Whether certificate forwarding should be enabled or not. If this is enabled then the listener will take the certificate from the |
| decode-url | true | Whether the parser will decode the URL and query parameters using the selected character encoding, defaulting to UTF-8. If this is false they will not be decoded. This will allow a later handler to decode them into whatever charset is desired. |
| disallowed-methods | ["TRACE"] | A comma-separated list of HTTP methods that are not allowed. |
| enable-http2 | false | Enables HTTP/2 support for this listener. |
| enable-spdy | false | Enables SPDY support for this listener. Deprecated: SPDY has been replaced by HTTP/2. |
| enabled | true | If the listener is enabled. Deprecated: Enabled attributes can cause problems in enforcement of configuration consistency. |
| enabled-cipher-suites | Configures Enabled SSL ciphers. Deprecated: Where an SSLContext is referenced it should be configured with the cipher suites to be supported. | |
| enabled-protocols | Configures SSL protocols. Deprecated: Where an SSLContext is referenced it should be configured with the cipher suites to be supported. | |
| http2-enable-push | true | If server push is enabled for this connection. |
| http2-header-table-size | 4096 | The size, in bytes, of the header table used for HPACK compression. This amount of memory will be allocated per connection for compression. Larger values use more memory but may give better compression. |
| http2-initial-window-size | 65535 | The flow control window size, in bytes, that controls how quickly the client can send data to the server. |
| http2-max-concurrent-streams | The maximum number of HTTP/2 streams that can be active at any time on a single connection. | |
| http2-max-frame-size | 16384 | The maximum HTTP/2 frame size, in bytes. |
| http2-max-header-list-size | The maximum size of request headers the server is prepared to accept. | |
| max-buffered-request-size | 16384 | Maximum size of a buffered request, in bytesRequests are not usually buffered, the most common case is when performing SSL renegotiation for a POST request, and the post data must be fully buffered in order to perform the renegotiation. |
| max-connections |
The maximum number of concurrent connections. If no value is set in the server configuration, the limit for the number of concurrent connections is | |
| max-cookies | 100 | The maximum number of cookies that will be parsed. This is used to protect against hash vulnerabilities. |
| max-header-size | 1048576 | The maximum size in bytes of an HTTP request header. |
| max-headers | 200 | The maximum number of headers that will be parsed. This is used to protect against hash vulnerabilities. |
| max-parameters | 1000 | The maximum number of parameters that will be parsed. This is used to protect against hash vulnerabilities. This applies to both query parameters, and to POST data, but is not cumulative. As a result, you can potentially have max parameters * 2 total parameters. |
| max-post-size | 10485760 | The maximum size of a post that will be accepted. |
| no-request-timeout | 60000 | The length of time in milliseconds that the connection can be idle before it is closed by the container. |
| proxy-address-forwarding | false | Enables handling of x-forwarded-host header, and other x-forwarded-* headers, and uses this header information to set the remote address. This should only be used behind a trusted proxy that sets these headers otherwise a remote user can spoof their IP address. |
| proxy-protocol | false |
Whether to use the PROXY protocol to transport connection information. If set to |
| read-timeout |
Configure a read timeout for a socket, in milliseconds. If the given amount of time elapses without a successful read taking place, the socket’s next read will throw a | |
| receive-buffer | The receive buffer size. | |
| record-request-start-time | false | Whether to record the request start time, to allow for request time to be logged. This has a small but measurable performance impact. |
| request-parse-timeout | The maximum amount of time in milliseconds that can be spent parsing the request. | |
| require-host-http11 | false | Require that all HTTP/1.1 requests have a 'Host' header. If the request does not include this header it will be rejected with a 403. |
| resolve-peer-address | false | Enables host DNS lookup. |
| secure | false |
If this is |
| security-realm |
The listener’s security realm. Deprecated: Use the | |
| send-buffer | The send buffer size. | |
| socket-binding | The listener’s socket binding. | |
| ssl-context | Reference to the SSLContext to be used by this listener. | |
| ssl-session-cache-size | The maximum number of active SSL sessions. Deprecated: This can now be configured on the Elytron security context. | |
| ssl-session-timeout | The timeout for SSL sessions, in seconds. Deprecated: This can now be configured on the Elytron security context. | |
| tcp-backlog | Configure a server with the specified backlog. | |
| tcp-keep-alive | Configure a channel to send TCP keep-alive messages in an implementation-dependent manner. | |
| url-charset | UTF-8 | URL charset. |
| verify-client | NOT_REQUESTED | The desired SSL client authentication mode for SSL channels. Deprecated: Where an SSLContext is referenced it should be configured directly for the required mode of client verification. |
| worker | default | The listener’s XNIO worker. |
| write-timeout |
Configure a write timeout for a socket, in milliseconds. If the given amount of time elapses without a successful write taking place, the socket’s next write will throw a |
A.27. Undertow subsystem statistics
This reference provides details about the attributes of the various elements of the undertow subsystem statistics in Red Hat JBoss Enterprise Application Platform.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| bytes-received | The number of bytes that have been received by this listener. |
| bytes-sent | The number of bytes that have been sent out on this listener. |
| error-count | The number of 500 responses that have been sent by this listener. |
| max-processing-time | The maximum processing time taken by a request on this listener. |
| processing-time | The total processing time of all requests handed by this listener. |
| request-count | The number of requests this listener has served. |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| bytes-received | The number of bytes that have been received by this listener. |
| bytes-sent | The number of bytes that have been sent out on this listener. |
| error-count | The number of 500 responses that have been sent by this listener. |
| max-processing-time | The maximum processing time taken by a request on this listener. |
| processing-time | The total processing time of all requests handed by this listener. |
| request-count | The number of requests this listener has served. |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| bytes-received | The number of bytes that have been received by this listener. |
| bytes-sent | The number of bytes that have been sent out on this listener. |
| error-count | The number of 500 responses that have been sent by this listener. |
| max-processing-time | The maximum processing time taken by a request on this listener. |
| processing-time | The total processing time of all requests handed by this listener. |
| request-count | The number of requests this listener has served. |
A.28. Default Behavior of HTTP Methods
Compared to the web subsystem in previous JBoss EAP releases, the undertow subsystem in JBoss EAP 8.0 has different default behaviors for HTTP methods. The following table outlines the default behaviors in JBoss EAP 8.0.
| HTTP Method | Jakarta Server Pages | Static HTML | Static HTML by File Handler |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For servlets, the default behavior depends on their implementation, except for the TRACE method, which has a default behavior of NOT_ALLOWED.
A.29. Remoting Subsystem Attributes
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-remoting_4_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| worker-read-threads | 1 | The number of read threads to create for the remoting worker. |
| worker-task-core-threads | 4 | The number of core threads for the remoting worker task thread pool. |
| worker-task-keepalive | 60 | The number of milliseconds to keep non-core remoting worker task threads alive. |
| worker-task-limit | 16384 | The maximum number of remoting worker tasks to allow before rejecting. |
| worker-task-max-threads | 16 | The maximum number of threads for the remoting worker task thread pool. |
| worker-write-threads | 1 | The number of write threads to create for the remoting worker. |
The above attributes of the remoting element are deprecated. These attributes should now be configured using the io subsystem.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| auth-realm | The authentication realm to use if no authentication CallbackHandler is specified. | |
| authentication-retries | 3 | Specify the number of times a client is allowed to retry authentication before closing the connection. |
| authorize-id | The SASL authorization ID. Used as authentication user name to use if no authentication CallbackHandler is specified and the selected SASL mechanism demands a user name. | |
| buffer-region-size | The size of allocated buffer regions. | |
| heartbeat-interval | 2147483647 | The interval to use for connection heartbeat, in milliseconds. If the connection is idle in the outbound direction for this amount of time, a ping message will be sent, which will trigger a corresponding reply message. |
| max-inbound-channels | 40 | The maximum number of concurrent inbound messages on a channel. |
| max-inbound-message-size | 9223372036854775807 | The maximum inbound message size to be allowed. Messages exceeding this size will cause an exception to be thrown on the reading side as well as the writing side. |
| max-inbound-messages | 80 | The maximum number of inbound channels to support for a connection. |
| max-outbound-channels | 40 | The maximum number of concurrent outbound messages on a channel. |
| max-outbound-message-size | 9223372036854775807 | The maximum outbound message size to send. No messages larger than this well be transmitted; attempting to do so will cause an exception on the writing side. |
| max-outbound-messages | 65535 | The maximum number of outbound channels to support for a connection. |
| receive-buffer-size | 8192 | The size of the largest buffer that this endpoint will accept over a connection. |
| receive-window-size | 131072 | The maximum window size of the receive direction for connection channels, in bytes. |
| sasl-protocol |
|
When a |
| send-buffer-size | 8192 | The size of the largest buffer that this endpoint will transmit over a connection. |
| server-name | The server side of the connection passes it’s name to the client in the initial greeting, by default the name is automatically discovered from the local address of the connection or it can be overridden using this. | |
| transmit-window-size | 131072 | The maximum window size of the transmit direction for connection channels, in bytes. |
| worker |
| Worker to use |
When using the management CLI to update the endpoint element, it is available under configuration in the remoting element. For example: /subsystem=remoting/configuration=endpoint/.
Connector Attributes
The connector component has the following structure:
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| authentication-provider |
The | |
| sasl-authentication-factory | Reference to the SASL authentication factory to secure this connector. | |
| sasl-protocol |
| The protocol to pass into the SASL mechanisms used for authentication. |
| security-realm | The associated security realm to use for authentication for this connector. | |
| server-name | The server name to send in the initial message exchange and for SASL based authentication. | |
| socket-binding | The name (or names) of the socket binding(s) to attach to. | |
| ssl-context | Reference to the SSL context to use for this connector. |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| value | The property value. |
Security Attributes
The security component allows you to configure the security for the connector, but contains no direct configuration attributes. It can be configured using its nested components, such as sasl.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| include-mechanisms |
The optional nested | |
| qop |
The optional nested Quality-of-protection values for this list are:
| |
| reuse-session | false |
The optional nested |
| server-auth | false |
The optional nested |
| strength |
The optional nested Cipher strength values for this list are:
|
sasl-policy Attributes
The sasl-policy component allows you to specify an optional policy to use to narrow down the available set of mechanisms, but contains no direct configuration attributes. It can be configured using its nested components, such as policy.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| forward-secrecy | true |
The optional nested |
| no-active | true |
The optional nested |
| no-anonymous | true |
The optional nested |
| no-dictionary | true |
The optional nested |
| no-plain-text | true |
The optional nested |
| pass-credentials | true |
The optional nested |
HTTP Connector Attributes
The http-connector component has the following structure:
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| authentication-provider |
The | |
| connector-ref |
The name (or names) of a connector in the | |
| sasl-authentication-factory | Reference to the SASL authentication factory to secure this connector. | |
| sasl-protocol |
| The protocol to pass into the SASL mechanisms used for authentication. |
| security-realm | The associated security realm to use for authentication for this connector. | |
| server-name | The server name to send in the initial message exchange and for SASL based authentication. |
Outbound Connection Attributes
The outbound-connection component has the following structure:
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| uri | The connection URI for the outbound connection. |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| value | The property value. |
The above property attributes are related to the XNIO Options that will be used during the connection creation.
Remote Outbound Connection
The remote-outbound-connection component has the following structure:
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| authentication-context | Reference to the authentication context instance containing the configuration for outbound connections. | |
| outbound-socket-binding-ref |
Name of the | |
| protocol |
|
The protocol to use for the remote connection. Defaults to |
| security-realm |
Reference to the security realm to use to obtain the password and SSL configuration. Deprecated: Outbound security settings should be migrated to an | |
| username |
The user name to use when authenticating against the remote server. Deprecated: Outbound security settings should be migrated to an |
Local Outbound Connection Attributes
The local-outbound-connection component has the following structure:
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| outbound-socket-binding-ref |
Name of the |
A.30. IO Subsystem Attributes
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-io_3_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| io-threads | The number of I/O threads to create for the worker. If not specified, the number of threads is set to the number of CPUs × 2. | |
| stack-size | 0 | The stack size, in bytes, to attempt to use for worker threads. |
| task-keepalive | 60000 | The number of milliseconds to keep non-core task threads alive. |
| task-core-threads | 2 | The number of threads for the core task thread pool. |
| task-max-threads |
The maximum number of threads for the worker task thread pool. If not specified, the maximum number of threads is set to the number of CPUs × 16, taking the |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| buffer-size | The size, in bytes, of each buffer slice. If not specified, the size is set based on the available RAM of your system:
For performance tuning advice on this attribute, see Configuring Buffer Pools in the JBoss EAP Performance tuning for JBoss EAP. | |
| buffers-per-slice | How many slices, or sections, to divide the larger buffer into. This can be more memory efficient than allocating many separate buffers. If not specified, the number of slices is set based on the available RAM of your system:
| |
| direct-buffers | Whether the buffer pool uses direct buffers, which are faster in many cases with NIO. Note that some platforms do not support direct buffers. | |
A.31. Jakarta Server Faces Module Templates
The following are example templates used for the various Jakarta Server Faces modules required when installing a different Jakarta Server Faces version for JBoss EAP. See Installing a Jakarta Server Faces Implementation for full instructions.
Example: Mojarra Jakarta Server Faces Implementation JAR module.xml
Be sure to use the appropriate values for the following replaceable variables in the template:
-
IMPL_NAME -
VERSION
Example: MyFaces Jakarta Server Faces Implementation JAR module.xml
Be sure to use the appropriate values for the following replaceable variables in the template:
-
IMPL_NAME -
VERSION
Example: Mojarra Jakarta Server Faces API JAR module.xml
Be sure to use the appropriate values for the following replaceable variables in the template:
-
IMPL_NAME -
VERSION
Example: MyFaces Jakarta Server Faces API JAR module.xml
Be sure to use the appropriate values for the following replaceable variables in the template:
-
IMPL_NAME -
VERSION
Example: Mojarra Jakarta Server Faces Injection JAR module.xml
Be sure to use the appropriate values for the following replaceable variables in the template:
-
IMPL_NAME -
VERSION -
INJECTION_VERSION -
WELD_VERSION
Example: MyFaces Jakarta Server Faces Injection JAR module.xml
Be sure to use the appropriate values for the following replaceable variables in the template:
-
IMPL_NAME -
VERSION -
INJECTION_VERSION -
WELD_VERSION
Example: MyFaces commons-digester JAR module.xml
Be sure to use the appropriate value for the VERSION replaceable variable in the template.
A.32. JGroups Subsystem Attributes
See the tables below for the attributes of the various elements of the jgroups subsystem.
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/jboss-as-jgroups_5_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| default-channel | ee | The default JGroups channel. |
| default-stack | The default JGroups protocol stack. |
Channel Attributes
The channel element has the following structure:
fork-
protocol
-
-
protocol
channel Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cluster | The cluster name of the JGroups channel. If undefined, the name of the channel will be used. | |
| module | org.wildfly.clustering.server | The module from which to load channel services. |
| stack | The protocol stack of the JGroups channel. | |
| statistics-enabled | false | Whether statistics are enabled. |
| stats-enabled | false |
Whether statistics are enabled. Deprecated: Use the |
Stack Attributes
The stack element has the following structure:
stack Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| statistics-enabled | false | Indicates whether or not all protocols in the stack will collect statistics. |
protocol Attributes
For a list of commonly used protocols, see the JGroups Protocols section.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| module | org.jgroups | The module with which to resolve the protocol type. |
| properties | Properties of this protocol. | |
| statistics-enabled | false | Indicates whether or not this protocol will collect statistics, overriding the stack configuration. |
relay Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| module | org.jgroups | The module with which to resolve the protocol type. |
| properties | Properties of this protocol. | |
| site | The name of the local site. | |
| statistics-enabled | false | Indicates whether or not this protocol will collect statistics, overriding the stack configuration. |
remote-site Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| channel | The name of the bridge channel used to communicate with this remote site. | |
| cluster |
The cluster name of the bridge channel to this remote site. Deprecated: Use an explicitly defined | |
| stack |
The stack from which to create a bridge to this remote site. Deprecated: Use an explicitly defined |
transport Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| default-executor |
The thread pool executor to handle incoming messages. Deprecated: Configure the predefined | |
| diagnostics-socket-binding | The diagnostics socket binding specification for this protocol layer, used to specify IP interfaces and ports for communication. | |
| machine | Machine, or host, identifier for this node. Used by Infinispan’s topology-aware consistent hash. | |
| module | org.jgroups | Module with which to resolve the protocol type. |
| oob-executor |
The thread pool executor to handle incoming out-of-band messages. Deprecated: Configure the predefined | |
| properties | Properties of this transport. | |
| rack | Rack, such as the server rack, identifier for this node. Used by Infinispan’s topology-aware consistent hash. | |
| shared | false |
If |
| site | Site, such as the data center, identifier for this node. Used by Infinispan’s topology-aware consistent hash. | |
| socket-binding | The socket binding specification for this protocol layer, used to specify IP interfaces and ports for communication. | |
| statistics-enabled | false | Indicates whether or not this protocol will collect statistics, overriding the stack configuration. |
| thread-factory |
The thread factory to use for handling asynchronous transport-specific tasks. Deprecated: Configure the predefined | |
| timer-executor |
The thread pool executor to handle protocol-related timing tasks. Deprecated: Configure the predefined |
thread-pool Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| keepalive-time | 5000L | The amount of milliseconds that pool threads should be kept running when idle. If not specified, then threads will run until the executor is shut down. |
| max-threads | 4 | The maximum thread pool size. |
| min-threads | 2 |
The core thread pool size, which is smaller than |
| queue-length | 500 | The queue length. |
A.33. JGroups Protocols
| Protocol | Protocol Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ASYM_ENCRYPT | Encryption | Uses a secret key, stored in a coordinator on the cluster, for encrypting messages between cluster members. |
| AUTH | Authentication | Provides a layer of authentication to cluster members. |
| azure.AZURE_PING | Discovery | Supports node discovery using Microsoft Azure’s blob storage. |
| FD_ALL | Failure Detection | Provides failure detection based on a simple heartbeat protocol. |
| FD_SOCK | Failure Detection | Provides failure detection based on a ring of TCP sockets created between cluster members. |
| JDBC_PING | Discovery | Discovers cluster members by using a shared database where members write their address. |
| MERGE3 | Merge | Merges the subclusters together in the event of a cluster split. |
| MFC | Flow Control | Provides multicast flow control between a sender and all cluster members. |
| MPING | Discovery | Discovers cluster members with IP multicast. |
| pbcast.GMS | Group Membership |
Handles group membership, including new members joining the cluster, leave requests by existing members, and |
| pbcast.NAKACK2 | Message Transmission | Ensures message reliability and order, guaranteeing that all messages sent by one sender will be received in the order they were sent. |
| pbcast.STABLE | Message Stability | Deletes messages that have been seen by all members. |
| PING | Discovery | Initial discovery of members, with support for dynamic discovery of cluster members. |
| SASL | Authentication | Provides a layer of authentication to cluster members using SASL mechanisms. |
| SYM_ENCRYPT | Encryption | Uses a shared keystore for encrypting messages between cluster members. |
| S3_PING | Discovery | Uses Amazon S3 to discover initial members. |
| TCPGOSSIP | Discovery | Discovers cluster members by using an external gossip router. |
| TCPPING | Discovery | Contains a static list of cluster member’s addresses to form the cluster. |
| UFC | Flow Control | Provides unicast flow control between a sender and all cluster members |
| UNICAST3 | Message Transmission | Ensures message reliability and order for unicast messages, guaranteeing that all messages sent by one sender will be received in the order they were sent. |
| VERIFY_SUSPECT | Failure Detection | Verifies that a suspected member has died by pinging the member one final time before evicting it. |
Generic Protocol Attributes
All of the protocols have access to the following attributes.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| module | org.jgroups | The module with which to resolve the protocol type. |
| properties | Properties of this protocol. | |
| statistics-enabled | false | Whether statistics are enabled. |
Authentication Protocols
The authentication protocols are used to perform authentication, and are primarily responsible for ensuring that only authenticated members can join the cluster. These protocols sit below the GMS protocol, so that they may listen for requests to join the cluster.
AUTH Attributes
While the AUTH protocol contains no additional attributes, it must have a token defined as a child element.
When defining this protocol, the auth-protocol element is used instead of the protocol element.
Token Types
When using Elytron for security, it is recommended to use one of the following authentication tokens. These authentication tokens were intentionally designed for use with Elytron, and may not be used with legacy security configurations.
| Token | Description |
|---|---|
| cipher-token | An authentication token where the shared secret is transformed. RSA is the default algorithm used for the transformation. |
| digest-token | An authentication token where the shared secret is transformed. SHA-256 is the default algorithm used for the transformation. |
| plain-token | An authentication token with no additional transformations to the shared secret. |
The following authentication tokens are inherited from JGroups, and are eligible for use in any configuration where authentication is desired.
| Token | Description |
|---|---|
| MD5Token | An authentication token where the shared secret is encrypted using either an MD5 or SHA hash. MD5 is the default algorithm used for the encryption. |
| SimpleToken | An authentication token with no additional transformations to the shared secret. This token is case-insensitive, and case is not considered when determining if strings match. |
| X509Token | An authentication token where the shared secret is encrypted using an X509 certificate. |
SASL Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| client_callback_handler |
The class name of the | |
| client_name | The name to use when a node acts as a client. This name will also be used to obtain the subject if using a JAAS login module. | |
| client_password | The password to use when a node acts as a client. This password will also be used to obtain the subject if using a JAAS login module. | |
| login_module_name |
The name of the JAAS login module to use as a subject for creating the SASL client and server. This attribute is only required by certain | |
| mech |
The name of the SASL authentication mechanism. This name can be any mechanism supported by the local SASL provider, and the JDK supplies | |
| sasl_props |
Properties of the defined | |
| server_callback_handler |
The class name of the | |
| server_name | The fully qualified server name. | |
| timeout | 5000 | The number of milliseconds to wait for a response to a challenge. |
Discovery Protocols
The following protocols are used to find an initial membership for the cluster, which can then be used to determine the current coordinator. A list of the discovery protocols are below.
- AZURE_PING
- JDBC_PING
- MPING
- PING
- S3_PING
- TCPGOSSIP
- TCPPING
AZURE_PING Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| container | The name of the blob container to use for PING data. This must be a valid DNS name. | |
| storage_access_key | The secret access key for the storage account. | |
| storage_account_name | The name of the Microsoft Azure storage account that contains your blob container. |
JDBC_PING Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data-source | Datasource reference, to be used instead of the connection and JNDI lookup properties. |
When defining a JDBC_PING protocol, the jdbc-protocol element is used instead of the protocol element.
S3_PING Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| access_key | The Amazon S3 access key used to access an S3 bucket. | |
| host | s3.amazonaws.com | Destination of the S3 web service. |
| location | Name of the Amazon S3 bucket to use. The bucket must exist and use a unique name. | |
| pre_signed_delete_url | The pre-signed URL to be used for the DELETE operation. | |
| port |
| The port on which the web service is listening. |
| pre_signed_put_url | The pre-signed URL to be used for the PUT operation. | |
| prefix |
If set, and | |
| secret_access_key | The Amazon S3 secret access key used to access an S3 bucket. | |
| use_ssl | true | Determines if SSL is used when contacting the host and port combination. |
TCPGOSSIP Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| socket-binding |
The socket binding specification for this protocol layer. Deprecated: Use | |
| socket-bindings | The outbound socket bindings for this protocol. |
When defining a TCPGOSSIP protocol, the socket-discovery-protocol element is used instead of the protocol element.
TCPPING Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| socket-binding |
The socket binding specification for this protocol layer. Deprecated: Use | |
| socket-bindings | The outbound socket bindings for this protocol. |
When defining a TCPPING protocol, the socket-discovery-protocol element is used instead of the protocol element.
Encrypt Protocols
The following protocols are used to secure the communication stack. Encryption is based on a shared secret key that all members of the cluster have. This key is either acquired from a shared keystore, when using SYM_ENCRYPT or from a public/private key exchange, when using ASYM_ENCRYPT. When defining any of the following protocols an encrypt-protocol element is created in the resulting XML.
If using ASYM_ENCRYPT, then the same stack must have an AUTH protocol defined. The AUTH protocol is optional when using SYM_ENCRYPT.
ASYM_ENCRYPT Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key-alias | The alias of the encryption key from the specified keystore. | |
| key-credential-reference | The credentials required to obtain the encryption key from the keystore. | |
| key-store | A reference to a keystore containing the encryption key. |
SYM_ENCRYPT Attributes
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key-alias | The alias of the encryption key from the specified keystore. | |
| key-credential-reference | The credentials required to obtain the encryption key from the keystore. | |
| key-store | A reference to a keystore containing the encryption key. |
Failure Detection Protocols
The following protocols are used to probe members of the cluster to determine if they are still alive. These protocols do not have any additional attributes beyond the generic attributes.
- FD_ALL
- FD_SOCK
- VERIFY_SUSPECT
Flow Control Protocols
The following protocols are responsible for flow control, or the process of adjusting the rate of a message sender to the slowest receiver. If a sender continuously sends messages at a rate faster than the receiver, then the receivers will either queue up or discard messages, resulting in retransmissions. These protocols do not have any additional attributes beyond the generic attributes.
- MFC - Multicast Flow Control
- UFC - Unicast Flow Control
Group Membership Protocols
The pbcast.GMS protocol is responsible for new members joining the cluster, existing members leaving the cluster, and members that are suspected of having crashed. This protocol does not have any additional attributes beyond the generic attributes.
Merge Protocols
If the cluster becomes split, then the MERGE3 protocol is responsible for merging the subclusters back together. While this protocol is responsible for merging the cluster members back together, this will not merge the state of the cluster. The application is responsible for handling the callback to merge states. This protocol does not have any additional attributes beyond the generic attributes.
Message Stability
The pbcast.STABLE protocol is responsible for garbage collecting messages that have been seen by all members of the cluster. This protocol initiates a stable message containing message numbers for a given member, called a digest. Once all members of the cluster have received the others' digests, then the message may be removed from the retransmission table. This protocol does not have any additional attributes beyond the generic attributes.
Reliable Message Transmission
The following protocols provide reliable message delivery and FIFO properties for messages sent to all nodes in a cluster. Reliable delivery means that no messages sent by a sender will ever be lost, as all messages are numbered, and retransmission requests are sent if a sequence number is not received. These protocols do not have any additional attributes beyond the generic attributes.
- pbcast.NAKACK2
- pbcast.UNICAST3
Deprecated Protocols
The following protocols have been deprecated, and have been replaced by a protocol that contains only the class name. For instance, instead of specifying org.jgroups.protocols.ASYM_ENCRYPT, the protocol name would be ASYM_ENCRYPT.
- org.jgroups.protocols.ASYM_ENCRYPT
- org.jgroups.protocols.AUTH
- org.jgroups.protocols.JDBC_PING
- org.jgroups.protocols.SYM_ENCRYPT
- org.jgroups.protocols.TCPGOSSIP
- org.jgroups.protocols.TCPPING
A.34. Apache HTTP Server mod_cluster Directives
The mod_cluster connector is an Apache HTTP Server-based load balancer. It uses a communication channel to forward requests from the Apache HTTP Server to one of a set of application server nodes. The following directives can be set to configure mod_cluster.
There is no need to use ProxyPass directives because mod_cluster automatically configures the URLs that must be forwarded to Apache HTTP Server.
| Directive | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
| CreateBalancers |
Defines how the balancers are created in the Apache HTTP Server VirtualHosts. This allows directives like: |
|
| UseAlias | Check that the alias corresponds to the server name. |
|
| LBstatusRecalTime | Time interval in seconds for load-balancing logic to recalculate the status of a node. | Default: 5 seconds |
| WaitBeforeRemove | Time in seconds before a removed node is forgotten by httpd. | Default: 10 seconds |
| ProxyPassMatch/ProxyPass |
ProxyPassMatch and ProxyPass are mod_proxy directives which, when using ! instead of the back-end URL, prevent reverse-proxy in the path. This is used to allow Apache HTTP Server to serve static content. For example: |
Due to performance optimizations for sessions in JBoss EAP 8.0, configuring hot-standby nodes is not supported.
mod_manager
The context of a mod_manager directive is VirtualHost in all cases, except when mentioned otherwise. server config context implies that the directive must be outside a VirtualHost configuration. If not, an error message is displayed and the Apache HTTP Server does not start.
| Directive | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
| EnableMCPMReceive | Allow the VirtualHost to receive the MCPM from the nodes. Include EnableMCPMReceive in the Apache HTTP Server configuration to allow mod_cluster to work. Save it in the VirtualHost where you configure advertising. | |
| MemManagerFile | The base name for the names that mod_manager uses to store configuration, generate keys for shared memory or locked files. This must be an absolute path name; the directories are created if needed. It is recommended that these files are placed on a local drive and not an NFS share. Context: server config |
|
| Maxcontext | The maximum number of contexts supported by mod_cluster. Context: server config |
Default: |
| Maxnode | The maximum number of nodes supported by mod_cluster. Context: server config |
Default: |
| Maxhost | The maximum number of hosts, or aliases, supported by mod_cluster. It also includes the maximum number of balancers. Context: server config |
Default: |
| Maxsessionid | The number of active sessionid stored to provide the number of active sessions in the mod_cluster-manager handler. A session is inactive when mod_cluster does not receive any information from the session within 5 minutes. Context: server config. This field is for demonstration and debugging purposes only. |
|
| MaxMCMPMaxMessSize | The maximum size of MCMP messages from other Max directives |
Calculated from other Max directives. Min: |
| ManagerBalancerName | The name of balancer to use when the JBoss EAP instance does not provide a balancer name. | mycluster |
| PersistSlots | Tells mod_slotmem to persist nodes, aliases and contexts in files. Context: server config | Off |
| CheckNonce | Switch check of nonce when using mod_cluster-manager handler. | on/off Default: on - Nonce checked |
| AllowDisplay | Switch additional display on mod_cluster-manager main page. | on/off Default: off - only version is displayed |
| AllowCmd | Allow commands using mod_cluster-manager URL. | on/off Default: on - Commands allowed |
| ReduceDisplay | Reduce the information displayed on the main mod_cluster-manager page, so that more nodes can be displayed on the page. | on/off Default: off - full information is displayed |
| SetHandler mod_cluster-manager | Displays information about the node that mod_cluster sees from the cluster. The information includes generic information and additionally counts the number of active sessions. <Location /mod_cluster-manager> SetHandler mod_cluster-manager Require ip 127.0.0.1 </Location> | on/off Default: off |
When accessing the location defined in httpd.conf:
- Transferred: Corresponds to the POST data sent to the back-end server.
- Connected: Corresponds to the number of requests that have been processed when the mod_cluster status page was requested.
- Num_sessions: Corresponds to the number of sessions mod_cluster report as active (on which there was a request within the past 5 minutes). This field is not present when Maxsessionid is zero and is for demonstration and debugging purposes only.
A.35. ModCluster Subsystem Attributes
The modcluster subsystem has the following structure:
- load-provider=simple
- ssl
The load-provider=dynamic resource allows you to configure factors, such as CPU, sessions, heap, memory, and weight to determine the load balancing behavior.
The load-provider=simple resource allows setting only a static constant as the factor attribute. This helps when the user does not need dynamic or complex rules to load balance the incoming HTTP requests.
Attribute names in these tables are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/jboss-as-mod-cluster_3_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| advertise | true | Whether to enable multicast-based advertise mechanism. |
| advertise-security-key | It is a shared secret between an httpd instance and the JBoss EAP servers listening for advertisements from the httpd instance. | |
| advertise-socket | The name of the balancer on the reverse proxy to register with. | |
| auto-enable-contexts | true |
If set to |
| balancer |
The name of the balancer on the reverse proxy to register with. If not set, the value is configured on the Apache HTTP Server side with the | |
| connector | The name of Undertow listener that mod_cluster reverse proxy will connect to. | |
| excluded-contexts |
A list of contexts to exclude from registration with the reverse proxies. If no host is indicated, the host is assumed to be | |
| flush-packets | false | Whether or not to enable packet flushing to the web server. |
| flush-wait | -1 |
Time to wait before flushing packets in httpd. Max value is |
| listener | The name of the Undertow listener that will be registered with the reverse proxy. | |
| load-balancing-group | If set, requests are sent to the specified load balancing group on the load balancer. | |
| max-attempts | 1 | The number of times the reverse proxy will attempt to send a given request to a worker before giving up. |
| node-timeout | -1 |
Timeout, in seconds, for proxy connections to a worker. This is the time that mod_cluster will wait for the back-end response before returning an error. If the |
| ping | 10 | Time, in seconds, in which to wait for a pong answer to a ping. |
| proxies |
List of proxies for mod_cluster to register with defined by | |
| proxy-list |
List of proxies. The format is | |
| proxy-url | / | Base URL for MCMP requests. |
| session-draining-strategy | DEFAULT |
Session draining strategy used during undeployment of a web application. Valid values are
|
| load-provider=simple |
A load provider to use if no dynamic load provider is present. It assigns each cluster member a load factor of | |
| smax | -1 | Soft maximum idle connection count in httpd. |
| socket-timeout | 20 | Number of seconds to wait for a response from an httpd proxy to MCMP commands before timing out, and flagging the proxy as in error. |
| ssl-context |
Reference to the | |
| status-interval | 10 |
Number of seconds a STATUS message is sent from the application server to the reverse proxy. Allowed values are between |
| sticky-session | true | Whether subsequent requests for a given session should be routed to the same node, if possible. |
| sticky-session-force | false | Whether the reverse proxy should return an error in the event that the balancer is unable to route a request to the node to which it is stuck. This setting is ignored if sticky sessions are disabled. |
| sticky-session-remove | false | Remove session information on failover. |
| stop-context-timeout | 10 | The maximum time, in seconds, to wait for a context to process pending requests, for a distributable context, or to destroy active sessions, for a non-distributable context. |
| ttl | -1 |
Time to live, in seconds, for idle connections above smax. Allowed values are between |
| worker-timeout | -1 |
Timeout to wait in httpd for an available worker to process the requests. Allowed values are between |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| decay | 2 | The decay. |
| history | 9 | The history. |
| initial-load | 0 |
The initial load reported by a node. The valid range is This attribute helps to gradually increase the load value of a newly joined node to avoid overloading it while joining a cluster.
You can disable this behavior by setting the value as |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| capacity | 1.0 | The capacity of the metric. |
| class | The class name of the custom metric. | |
| property | The properties for the metric. | |
| weight | 1 | The weight of the metric. |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| capacity | 1.0 | The capacity of the metric. |
| property | The properties for the metric. | |
| type |
The type of the metric. Valid values are | |
| weight | 1 | The weight of the metric. |
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ca-certificate-file | Certificate authority. | |
| ca-revocation-url | Certificate authority revocation list. | |
| certificate-key-file | ${user.home}/.keystore | Key file for the certificate. |
| cipher-suite | The allowed cipher suite. | |
| key-alias | The key alias. | |
| password | changeit | Password. |
| protocol | TLS | The SSL protocols that are enabled. |
A.36. mod_jk Worker Properties
The workers.properties file defines the behavior of the workers to which mod_jk passes client requests. The workers.properties file defines where the different application servers are located and the way the workload should be balanced across them.
The general structure of a property is worker.WORKER_NAME.DIRECTIVE. The WORKER_NAME is a unique name that must match the instance-id configured in the JBoss EAP undertow subsystem. The DIRECTIVE is the setting to be applied to the worker.
Configuration Reference for Apache mod_jk Load Balancers
Templates specify default per-load-balancer settings. You can override the template within the load-balancer settings itself.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| worker.list | A comma separated list of worker names that will be used by mod_jk. |
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| type |
The type of worker. The default type is |
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| balance_workers | Specifies the worker nodes that the load balancer must manage. You can use the directive multiple times for the same load balancer. It consists of a comma-separated list of worker node names. |
| sticky_session |
Specifies whether requests from the same session are always routed to the same worker. The default is |
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| host |
The host name or IP address of the back-end server. The back-end server must support the |
| port |
The port number of the back-end server instance listening for defined protocol requests. The default value is |
| ping_mode | The conditions under which connections are probed for network status. The probe uses an empty AJP13 packet for CPing, and expects a CPong in response. Specify the conditions by using a combination of directive flags. The flags are not separated by a comma or any white-space. The ping_mode can be any combination of C, P, I, and A.
|
| ping_timeout, connect_timeout, prepost_timeout, connection_ping_interval |
The timeout values for the connection probe settings above. The value is specified in milliseconds, and the default value for |
| lbfactor |
Specifies the load-balancing factor for an individual back-end server instance. This is useful to give a more powerful server more of the workload. To give a worker 3 times the default load, set this to |
The example below demonstrates load balancing with sticky sessions between two worker nodes, node1 and node2, listening on port 8009.
Example: workers.properties File
Further configuration details for Apache mod_jk are out of the scope of this document and can be found in the Apache documentation.
A.37. Security Manager Subsystem Attributes
The security-manager subsystem itself does not have configurable attributes, but it has one child resource with configurable attributes: deployment-permissions=default.
Attribute names in this table are listed as they appear in the management model, for example, when using the management CLI. See the schema definition file located at EAP_HOME/docs/schema/wildfly-security-manager_1_0.xsd to view the elements as they appear in the XML, as there may be differences from the management model.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| maximum-permissions | The maximum set of permissions that can be granted to a deployment or JARs. |
| minimum-permissions | The minimum set of permissions to be granted to a deployment or JARs. |
A.38. Install OpenSSL from JBoss Core Services
The JBoss Core Services OpenSSL files can be installed either from the ZIP or from the RPM distributions. Follow the below steps depending on your installation method of choice.
On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8, standard system OpenSSL is supported thus installation of OpenSSL from JBoss Core Services is not necessary anymore.
Using JBoss Core Services OpenSSL ZIP File Distribution
The path to libs/ directory in the ZIP archive is jbcs-openssl-VERSION/openssl/lib(64) for Linux and jbcs-openssl-VERSION/openssl/bin for Windows.
- Download the OpenSSL package from the Software Downloads page that pertains to your operating system and architecture.
- Extract the downloaded ZIP file to your installation directory.
Notify JBoss EAP where to find the OpenSSL libaries.
You can do this using either of the following methods. In each of the following commands, be sure to replace
JBCS_OPENSSL_PATHwith the path to the JBoss Core Services OpenSSL libraries, for example,/opt/rh/jbcs-httpd24/root/usr/lib64.You can add the OpenSSL path to the
JAVA_OPTSvariable in thestandalone.confordomain.confconfiguration file using the following argument.JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dorg.wildfly.openssl.path=JBCS_OPENSSL_PATH
JAVA_OPTS="$JAVA_OPTS -Dorg.wildfly.openssl.path=JBCS_OPENSSL_PATHCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can define a system property that specifies the OpenSSL path using the following management CLI command.
/system-property=org.wildfly.openssl.path:add(value=JBCS_OPENSSL_PATH)
/system-property=org.wildfly.openssl.path:add(value=JBCS_OPENSSL_PATH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantRegardless of the method you use, you must perform a server restart for either the
JAVA_OPTSvalue or the system property to take effect. A server reload is not sufficient.
Using JBoss Core Services OpenSSL RPM Distribution
Ensure that the system is registered to the JBoss Core Services channel:
Determine the JBoss Core Services CDN repository name for your operating system version and architecture:
- RHEL 6: jb-coreservices-1-for-rhel-6-server-rpms
- RHEL 7: jb-coreservices-1-for-rhel-7-server-rpms
Enable the repository on the system:
subscription-manager repos --enable REPO_NAME
# subscription-manager repos --enable REPO_NAMECopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow Ensure the following message is seen:
Repository REPO_NAME is enabled for this system.
Repository REPO_NAME is enabled for this system.Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow
Install OpenSSL from this channel:
yum install jbcs-httpd24-openssl
# yum install jbcs-httpd24-opensslCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow -
Once the installation completes, the JBCS OpenSSL libraries will be available in
/opt/rh/jbcs-httpd24/root/usr/lib64, or just/opt/rh/jbcs-httpd24/root/usr/libon x86 architecture. Notify JBoss EAP where to find the OpenSSL libaries.
You can do this using either of the following methods. In each of the following commands, be sure to replace
JBCS_OPENSSL_PATHwith the path to the JBoss Core Services OpenSSL libraries, for example,/opt/rh/jbcs-httpd24/root/usr/lib64.You can update the
WILDFLY_OPTSvariable for theeap7-standaloneoreap7-domainsettings in the service configuration file.WILDFLY_OPTS="$WILDFLY_OPTS -Dorg.wildfly.openssl.path=JBCS_OPENSSL_PATH"
WILDFLY_OPTS="$WILDFLY_OPTS -Dorg.wildfly.openssl.path=JBCS_OPENSSL_PATH"Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow You can define a system property that specifies the OpenSSL path using the following management CLI command.
/system-property=org.wildfly.openssl.path:add(value=JBCS_OPENSSL_PATH)
/system-property=org.wildfly.openssl.path:add(value=JBCS_OPENSSL_PATH)Copy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow ImportantRegardless of the method you use, you must perform a server restart for either the
WILDFLY_OPTSvalue or the system property to take effect. A server reload is not sufficient.
A.39. Configure JBoss EAP to use OpenSSL
There are multiple ways in which you can configure JBoss EAP to use OpenSSL:
You can reconfigure the
elytronsubsystem to give OpenSSL priority so that it is used in all cases by default.NoteAlthough OpenSSL is installed in the
elytronsubsystem, it is not the default TLS provider./subsystem=elytron:write-attribute(name=initial-providers, value=combined-providers) /subsystem=elytron:undefine-attribute(name=final-providers) reload
/subsystem=elytron:write-attribute(name=initial-providers, value=combined-providers) /subsystem=elytron:undefine-attribute(name=final-providers) reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow In the
elytronsubsystem, the OpenSSL provider can also be specified on thessl-contextresource. That way, the OpenSSL protocol can be selected on a case-by-case basis instead of using the default priority.To create the
ssl-contextresource and use the OpenSSL libraries in your Elytron-based SSL/TLS configuration, use the following command./subsystem=elytron/server-ssl-context=httpsSSC:add(key-manager=localhost-manager, trust-manager=ca-manager, provider-name=openssl) reload
/subsystem=elytron/server-ssl-context=httpsSSC:add(key-manager=localhost-manager, trust-manager=ca-manager, provider-name=openssl) reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow To use the OpenSSL libraries in your legacy
securitysubsystem SSL/TLS configuration:/core-service=management/security-realm=ApplicationRealm/server-identity=ssl:write-attribute(name=protocol,value=openssl.TLSv1.2) reload
/core-service=management/security-realm=ApplicationRealm/server-identity=ssl:write-attribute(name=protocol,value=openssl.TLSv1.2) reloadCopy to Clipboard Copied! Toggle word wrap Toggle overflow The different OpenSSL protocols that can be used are:
- openssl.TLS
- openssl.TLSv1
- openssl.TLSv1.1
- openssl.TLSv1.2
JBoss EAP will automatically try to search for the OpenSSL libraries on the system and use them. You can also specify a custom OpenSSL libraries location by using the org.wildfly.openssl.path property during JBoss EAP startup. Only the OpenSSL library version 1.0.2 or greater provided by JBoss Core Services is supported.
If OpenSSL is loaded properly, you will see a message in the server.log during JBoss EAP startup, similar to:
15:37:59,814 INFO [org.wildfly.openssl.SSL] (MSC service thread 1-7) WFOPENSSL0002 OpenSSL Version OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 23 Mar 2017
15:37:59,814 INFO [org.wildfly.openssl.SSL] (MSC service thread 1-7) WFOPENSSL0002 OpenSSL Version OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 23 Mar 2017A.40. Comparison of validation timing methods
You can compare different aspects of the validate-on-match and background-validation methods to determine which method is suitable for configuring database connection validation.
The following table includes a comparison matrix for validation timing methods:
| Comparison aspect | Validate-on-match method | Background-validation method |
| Reliability |
The |
The When the background validation method runs frequently, the validation is performed only for those connections in the pool, which are not reserved by the application for use. This also means no validation is performed to test connections that are checked out of the pool for use. |
| Performance, which depends on the use of the system, network performance, and the timing and scope of any connectivity issues |
Users of systems that remain idle for long periods are more likely to see brief or longer delays when requesting connections using
Users of systems with a more efficient validation mechanism, such as the JDBC 4 validation mechanism may notice fewer delays when using
Following a wide-spread outage that impacts most or all of the connections in the pool, users of datasources configured with |
Users of systems that remain idle for long periods are less likely to see brief or longer delays when requesting connections using
Users of systems with a more efficient validation mechanism, such as the JDBC 4 validation mechanism may notice fewer delays when using
Following a wide-spread outage that impacts most or all of the connections in the pool, users of datasources configured with |
| Coding for fault tolerance |
In case of any fault, the application logic remains the same when using
The broken connections are less likely to present when using |
In case of any fault, the application logic remains the same when using
The broken connections are more likely to present when using |
A.41. Managed domain reference
You can use the following resources to configure JBoss EAP running as a managed domain.
Server attributes and child resources
A server requires the following attributes and child resources:
-
name: The name of the server. -
group: The name of a server group from the domain model.
A server includes the following optional attributes:
-
auto-start: Whether or not this server should be started when the host controller starts. -
socket-binding-default-interface: The socket binding group default interface for this server. -
socket-binding-group: The socket binding group to which this server belongs. -
socket-binding-port-offset: An offset to be added to the port values given by the socket binding group for this server. -
update-auto-start-with-server-status: Update theauto-startattribute with the status of the server.
A server group includes the following child resources:
-
interface: A list of fully-specified named network interfaces available for use on the server. -
jvm: The JVM settings for this server. If not declared, the settings are inherited from the parent server group or host. -
path: A list of named file system paths. -
ssl: SSL/TLS configuration for when the server instance is connecting back to its host controller. -
system-property: A list of system properties to set on this server.
Server group attributes and child resources
A server group requires the following child resources:
-
name: The server group name. -
profile: The server group profile name. -
socket-binding-group: The default socket binding group used for servers in the group. This can be overridden on a per-server basis.
A server group includes the following optional attributes:
-
graceful-startup: Start the servers gracefully, queuing or cleanly rejecting incoming requests until the server is fully started. By defaulttrue. -
management-subsystem-endpoint: Set totrueto have servers belonging to the server group connect back to the host controller using the endpoint from theirremotingsubsystem. Theremotingsubsystem must be present for this to work. -
socket-binding-default-interface: The socket binding group default interface for this server. -
socket-binding-port-offset: The default offset to be added to the port values given by the socket binding group.
A server group includes the following child resources:
-
deployment-overlay: Links between a defined deployment overlay and deployments in this server group. -
deployment: The deployment content to be deployed on the servers in the group. -
jvm: The default JVM settings for all servers in the group. The host controller merges these settings with any other configuration provided inhost.xmlto derive the settings used to launch the server’s JVM. -
system-property: The system properties to be set on servers in the group.
Revised on 2025-05-27 10:58:09 UTC